Investor Education
The 6 Biggest Mistakes Ordinary Investors Make
.container {
max-width: 1070px;
}
.button {
display: inline-block;
height: 45px;
color: #ffffff;
text-align: center;
font-family: helvetica;
letter-spacing: .01rem;
text-decoration: none;
white-space: nowrap;
border-radius: 0px;
line-height: 45px;
border: 1px;
font-size: em(13);
cursor: pointer;
box-sizing: border-box;
background: #0A4845;
transition-duration: 0.4s;
margin-bottom: 1px;
width: 16.6666%;
}
.button-group {
position: left;
width: 100%;
display: inline-block;
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
/* IE hacks */
zoom: 1;
*display: inline;
}
.button-group li {
float: left;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.button-group .button {
display: inline-block;
box-sizing: border-box;
color: white;
}
.button-group > .button:not(:first-child):not(:last-child), .button-group li:not(:first-child):not(:last-child) .button {
border-radius: 0;
}
.button-group > .button:first-child, .button-group li:first-child .button {
margin-left: 0;
border-top-right-radius: 0;
border-bottom-right-radius: 0;
}
.button-group > .button:last-child, .button-group li:last-child > .button {
border-top-left-radius: 0;
border-bottom-left-radius: 0;
border-bottom-right-radius: 0;
}
.button:hover {
background-color: #8E8059;
}
.button.active {
background-color: #8E8059;
}
.button-group :not(:last-child) {
border-right: 1px solid white;
padding-right: 2px;
}
.button-group {
border-right: none;
margin-right: none;
}
@media (max-width: 600px) {
.button {
font-size: 13px;}
}

The 6 Biggest Mistakes Ordinary Investors Make
In many areas of life, we are often our own worst enemies. The realm of personal finance is no different.
What’s the biggest threat to achieving financial independence?
Unfortunately, it’s your own brain.
You can invest in all the right things, minimize fees and taxes, and even diversify your holdings. But if you fail to master your own psychology, it’s still possible to fall victim to financial self-sabotage.
The Brain’s Design
Today’s infographic is from Tony Robbins, and it uses data and talking points from his #1 Best Selling book Unshakeable: Your Financial Freedom Playbook, which is now available on paperback.
The graphic is based on a chapter in the book that reveals the key psychological limitations of the human brain. It turns out that these fallible survival instincts have been hardwired into our brains over millions of years, and they become very troublesome when we try to make rational financial decisions.
To overcome these instincts, investors need to adopt simple systems, rules, and procedures that can ensure the decisions around money we make are in our best long-term interest.
What I’ve found again and again is that 80% of success is psychology and 20% is mechanics.
– Tony Robbins
Six Psychological Pitfalls to Avoid
Remember these six pitfalls – and how to counteract them – and you’ll be able to avoid the biggest mistakes often made by investors.
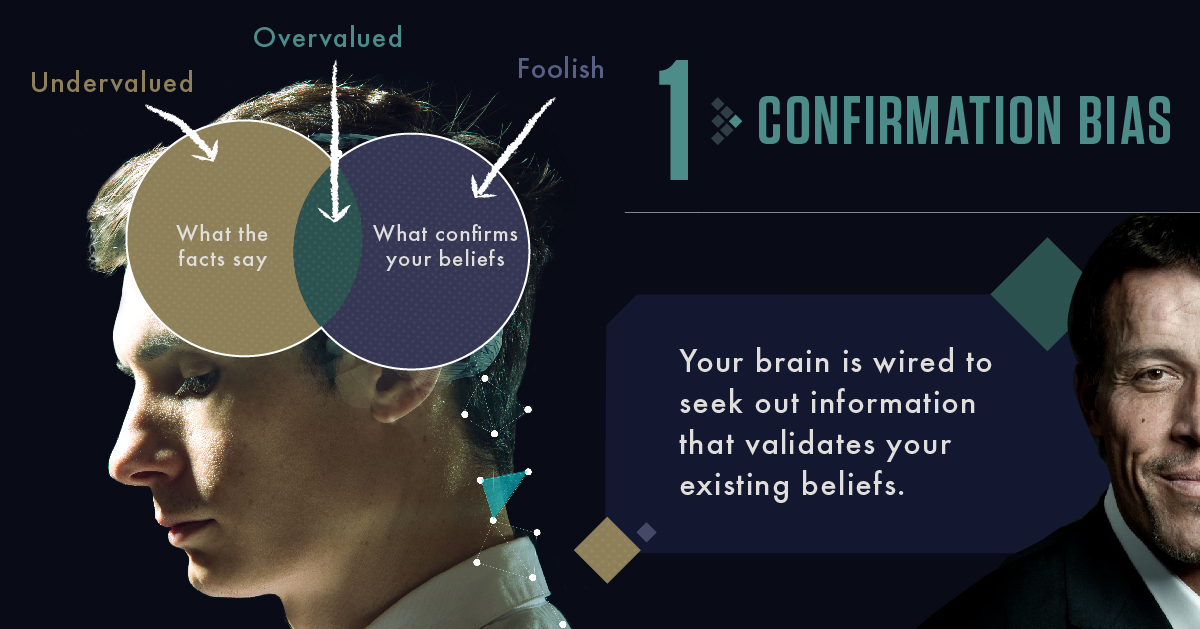
Mistake #1:
Seeking confirmation of your own beliefs
Your brain is wired to seek and believe information that validates your existing beliefs. Our minds love “proof” of how smart and right we are.
Even worse, this is magnified by the online echo chambers of the modern world.
- News media (MSNBC, Fox News, etc.) tend to favor one point of view
- Google and Facebook filter our search results
- Unsubstantiated rumors can run unchecked, as long as they reinforce existing points of view
This can be exceptionally detrimental in investing.
Convincing yourself that a particular stock or strategy is correct, without taking into account contradicting evidence, can be the nail in the coffin of financial freedom.
The Solution: Welcome opinions that contradict your own
The best investors know they are vulnerable to confirmation bias, and actively ask questions and seek qualified opinions that disagree with their own.
Ray Dalio, for example, seeks the smartest detractor of his idea, and then tries to find out their full reasoning behind their contrary opinion.
The power of thoughtful disagreement is a great thing.
– Ray Dalio
Mistake #2:
Conflating recent events with ongoing trends
One of the most common – and dangerous – investing mistakes is to believe that the current trend of the day will continue.
In psychology speak, this is known as recency bias, or putting more weight on recent events when evaluating the odds of something happening in the future
For example, an investor might think that because a stock has performed well recently, that it will also do well in the future. Therefore, she buys more – effectively buying at a high point in the stock.
The Solution: Re-balance
Our memories are short, so what can we do?
The best way to avoid this impulsive and faulty decision making is to commit to portfolio allocations (i.e. 60% stocks, 40% bonds) in advance, and then re-balancing on a regular basis.
This effectively ensures you are buying low, and selling high. When stocks to well, you sell some of them to buy other assets in the underweighted part of your portfolio, and vice versa.
Mistake #3:
Overconfidence
Very successful and driven people often assume they will be just as good at investing as they are at other aspects of their life. However, this overconfidence is a common cognitive bias: we constantly overestimate our abilities, our knowledge, and our future prospects.
The Solution: Get Real, and Get Honest
By admitting you have no special advantage, you give yourself an enormous advantage – and you’ll beat the overconfident investors that delude themselves in believing they can outperform.
If you can’t predict the future, the most important thing is to admit it. If it’s true that you can’t make forecasts and yet you try anyway, then that’s really suicide.
– Howard Marks
Mistake #4:
Swinging for the Fences
It’s tempting to go for the big wins in your quest to build financial wealth. But swinging for the fences also means more strikeouts – many which can be difficult to recover from.
The Solution: Think Long Term
The best way to win the game of investing is to achieve sustainable long-term returns that compound over time. Don’t get distracted by the short-term noise on Wall Street, and re-orient your approach to build wealth over the long term.
The stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient.
– Warren Buffett
Mistake #5:
Staying Home
This psychological bias is known as “home bias”, and it is the tendency for people to invest disproportionately in markets that are familiar to them. For example, investing in:
- Your employer’s stock
- Your own industry
- Your own country’s stock market
- Only one asset class
Home bias can leave you overweighted in “what you know”, which can wreak havoc on your portfolio in some circumstances.
The Solution: Diversify
Diversify broadly, in different asset classes and in different countries. From 2000 to 2009, the S&P 500 only returned 1.4% per year, but foreign markets picked up the slack:
- International stocks: 3.9% per year
- Emerging markets: 16.2% per year
A well-diversified portfolio would have done well, no matter what.
Mistake #6:
Negativity Bias
Our brains are wired to bombard us with memories of negative experiences.
In fact, one part of our brain – the amygdala – is a biological alarm system that floods the body with fear signals when we are losing money.
The problem with this? When markets plunge, fear takes over and it’s easy to act irrationally. Some people panic, selling their entire portfolios to go into cash.
The Solution: Prepare
The best way to avoid negativity bias is to:
- Keep record of why you invested in certain securities in the first place
- Maintain the right asset allocation that will help you through volatility
- Partner with the right financial advisor to offer advice
- Focus on the long term, and avoid short-term market distractions
By failing to prepare, you are preparing to fail.
– Benjamin Franklin
Conclusion
These simple rules and procedures will make it easier for you to invest for the long term.
They’ll help you:
- Trade less
- Lower investment fees and transaction costs
- Be more open to views that differ from your own
- Reduce risk by diversifying globally
- Control the fears that could otherwise derail you
Will you be perfect? No.
But will you do better? You bet!
And the difference this makes over a lifetime can be substantial.
Investor Education
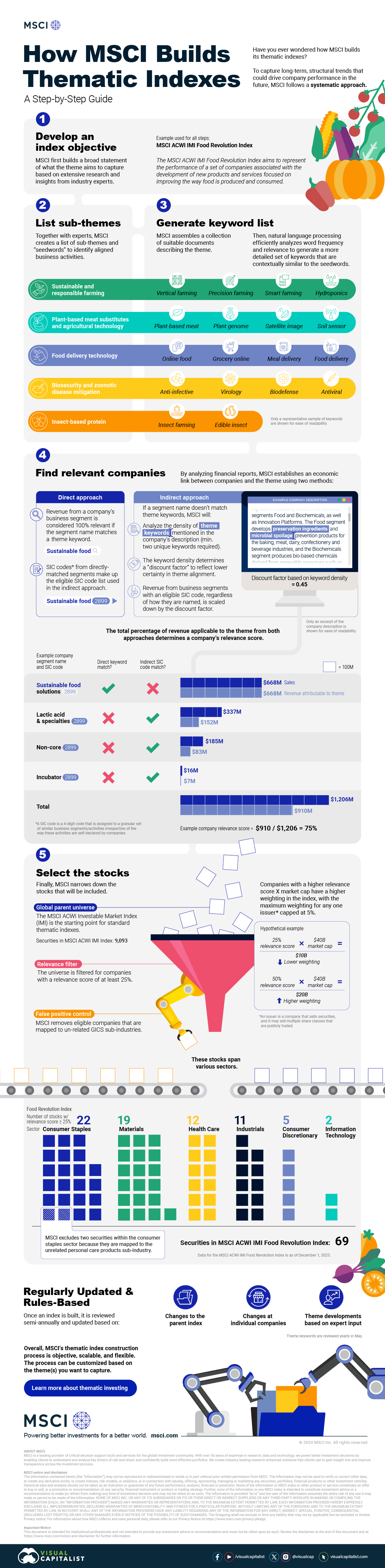
How MSCI Builds Thematic Indexes: A Step-by-Step Guide
From developing an index objective to choosing relevant stocks, this graphic breaks down how MSCI builds thematic indexes using examples.
How MSCI Builds Thematic Indexes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Have you ever wondered how MSCI builds its thematic indexes?
To capture long-term, structural trends that could drive business performance in the future, the company follows a systematic approach. This graphic from MSCI breaks down each step in the process used to create its thematic indexes.
Step 1: Develop an Index Objective
MSCI first builds a broad statement of what the theme aims to capture based on extensive research and insights from industry experts.
Steps 2 and 3: List Sub-Themes, Generate Keyword List
Together with experts, MSCI creates a list of sub-themes or “seedwords” to identify aligned business activities.
The team then assembles a collection of suitable documents describing the theme. Natural language processing efficiently analyzes word frequency and relevance to generate a more detailed set of keywords contextually similar to the seedwords.
Step 4: Find Relevant Companies
By analyzing financial reports, MSCI picks companies relevant to the theme using two methods:
- Direct approach: Revenue from a company’s business segment is considered 100% relevant if the segment name matches a theme keyword. Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes from these directly-matched segments make up the eligible SIC code list used in the indirect approach.
- Indirect approach: If a segment name doesn’t match theme keywords, MSCI will:
- Analyze the density of theme keywords mentioned in the company’s description. A minimum of two unique keywords is required.
- The keyword density determines a “discount factor” to reflect lower certainty in theme alignment.
- Revenue from business segments with an eligible SIC code, regardless of how they are named, is scaled down by the discount factor.
The total percentage of revenue applicable to the theme from both approaches determines a company’s relevance score.
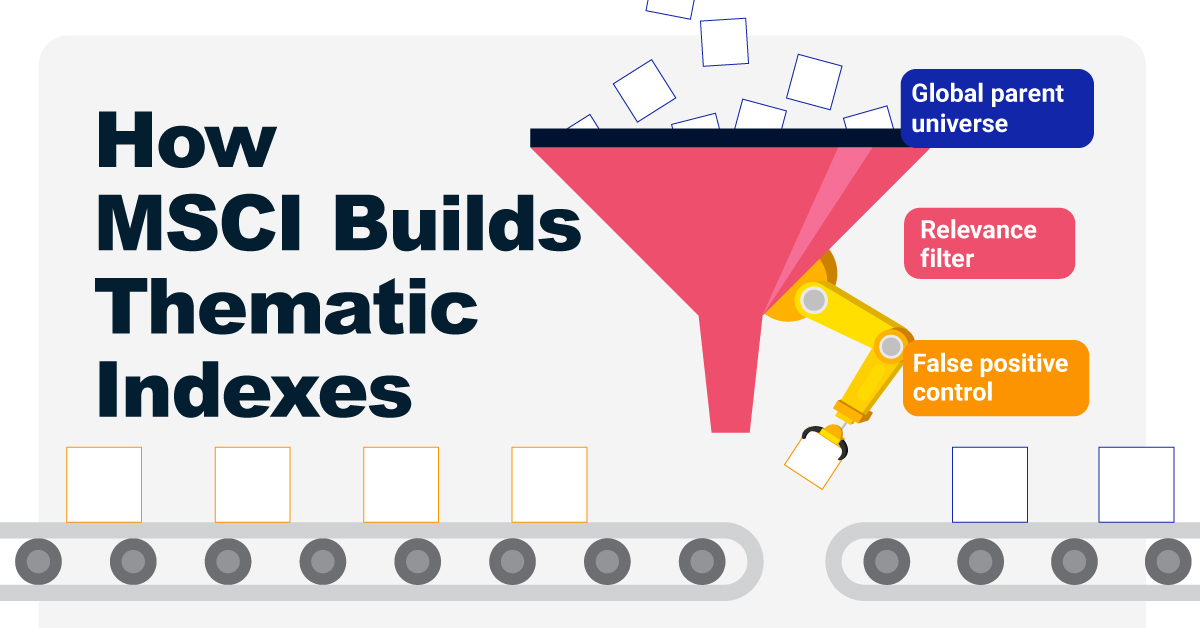
Step 5: Select the Stocks
Finally, MSCI narrows down the stocks that will be included:
- Global parent universe: The ACWI Investable Market Index (IMI) is the starting point for standard thematic indexes.
- Relevance filter: The universe is filtered for companies with a relevance score of at least 25%.
- False positive control: Eligible companies that are mapped to un-related GICS sub-industries are removed.
Companies with higher relevance scores and market caps have a higher weighting in the index, with the maximum weighting for any one issuer capped at 5%. The final selected stocks span various sectors.
MSCI Thematic Indexes: Regularly Updated and Rules-Based
Once an index is built, it is reviewed semi-annually and updated based on:
- Changes to the parent index
- Changes at individual companies
- Theme developments based on expert input
Theme keywords are reviewed yearly in May. Overall, MSCI’s thematic index construction process is objective, scalable, and flexible. The process can be customized based on the theme(s) you want to capture.

Learn more about MSCI’s thematic indexes.

-

 Investor Education6 months ago
Investor Education6 months agoThe 20 Most Common Investing Mistakes, in One Chart
Here are the most common investing mistakes to avoid, from emotionally-driven investing to paying too much in fees.
-
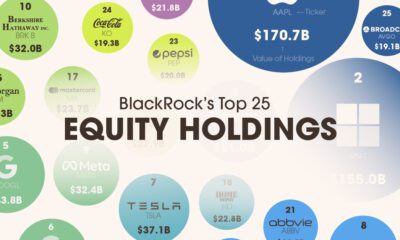
 Stocks10 months ago
Stocks10 months agoVisualizing BlackRock’s Top Equity Holdings
BlackRock is the world’s largest asset manager, with over $9 trillion in holdings. Here are the company’s top equity holdings.
-
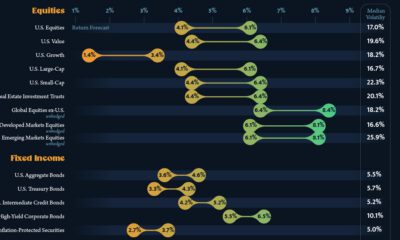
 Investor Education11 months ago
Investor Education11 months ago10-Year Annualized Forecasts for Major Asset Classes
This infographic visualizes 10-year annualized forecasts for both equities and fixed income using data from Vanguard.
-

 Investor Education1 year ago
Investor Education1 year agoVisualizing 90 Years of Stock and Bond Portfolio Performance
How have investment returns for different portfolio allocations of stocks and bonds compared over the last 90 years?
-
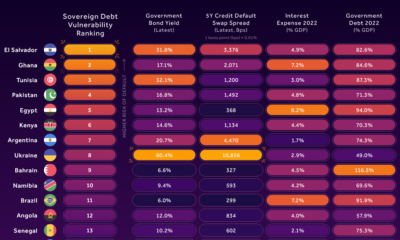
 Debt2 years ago
Debt2 years agoCountries with the Highest Default Risk in 2022
In this infographic, we examine new data that ranks the top 25 countries by their default risk.
-
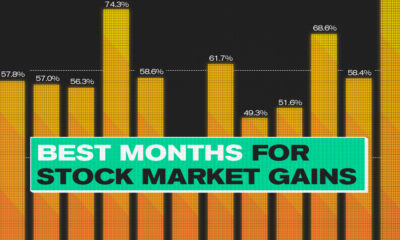
 Markets2 years ago
Markets2 years agoThe Best Months for Stock Market Gains
This infographic analyzes over 30 years of stock market performance to identify the best and worst months for gains.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries