Money
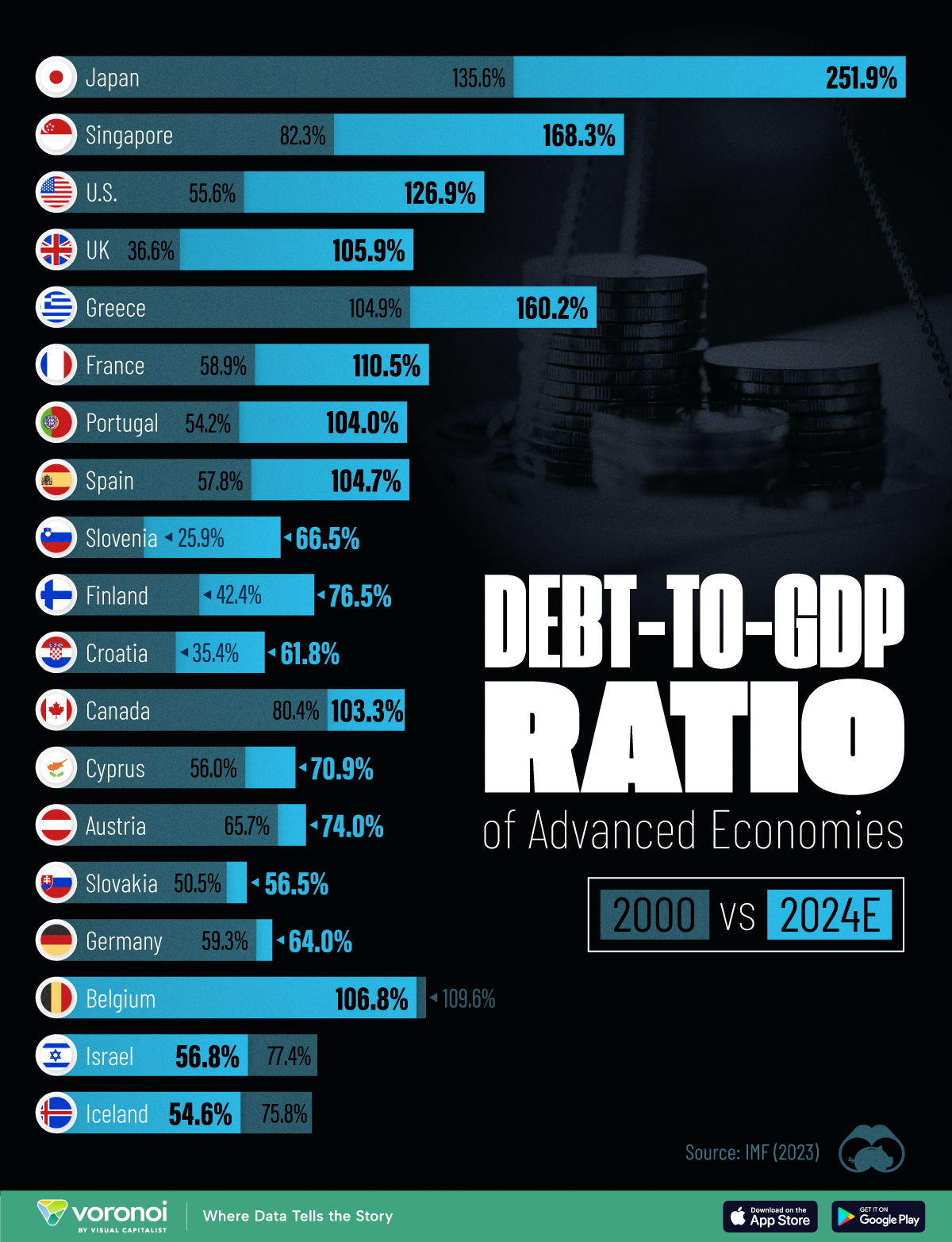
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
![]() See this visualization first on the Voronoi app.
See this visualization first on the Voronoi app.
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Government debt levels have grown in most parts of the world since the 2008 financial crisis, and even more so after the COVID-19 pandemic.
To gain perspective on this long-term trend, we’ve visualized the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies, as of 2000 and 2024 (estimated). All figures were sourced from the IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Data and Highlights
The data we used to create this graphic is listed in the table below. “Government gross debt” consists of all liabilities that require payment(s) of interest and/or principal in the future.
| Country | 2000 (%) | 2024 (%) | Change (pp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 135.6 | 251.9 | +116.3 |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 82.3 | 168.3 | +86.0 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 55.6 | 126.9 | +71.3 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 36.6 | 105.9 | +69.3 |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 104.9 | 160.2 | +55.3 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 58.9 | 110.5 | +51.6 |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 54.2 | 104.0 | +49.8 |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 57.8 | 104.7 | +46.9 |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 25.9 | 66.5 | +40.6 |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 42.4 | 76.5 | +34.1 |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 35.4 | 61.8 | +26.4 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80.4 | 103.3 | +22.9 |
| 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 56.0 | 70.9 | +14.9 |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 65.7 | 74.0 | +8.3 |
| 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 50.5 | 56.5 | +6.0 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 59.3 | 64.0 | +4.7 |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 109.6 | 106.8 | -2.8 |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | 77.4 | 56.8 | -20.6 |
| 🇮🇸 Iceland | 75.8 | 54.6 | -21.2 |
The debt-to-GDP ratio indicates how much a country owes compared to the size of its economy, reflecting its ability to manage and repay debts. Percentage point (pp) changes shown above indicate the increase or decrease of these ratios.
Countries with the Biggest Increases
Japan (+116 pp), Singapore (+86 pp), and the U.S. (+71 pp) have grown their debt as a percentage of GDP the most since the year 2000.
All three of these countries have stable, well-developed economies, so it’s unlikely that any of them will default on their growing debts. With that said, higher government debt leads to increased interest payments, which in turn can diminish available funds for future government budgets.
This is a rising issue in the U.S., where annual interest payments on the national debt have surpassed $1 trillion for the first time ever.
Only 3 Countries Saw Declines
Among this list of advanced economies, Belgium (-2.8 pp), Iceland (-21.2 pp), and Israel (-20.6 pp) were the only countries that decreased their debt-to-GDP ratio since the year 2000.
According to Fitch Ratings, Iceland’s debt ratio has decreased due to strong GDP growth and the use of its cash deposits to pay down upcoming maturities.
See More Debt Graphics from Visual Capitalist
Curious to see which countries have the most government debt in dollars? Check out this graphic that breaks down $97 trillion in debt as of 2023.
Money
Ranked: The Top 20 Countries in Debt to China
The 20 nations featured in this graphic each owe billions in debt to China, posing concerns for their economic future.

Ranked: The Top 20 Countries in Debt to China
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
In this graphic, we ranked the top 20 countries by their amount of debt to China. These figures are as of 2022, and come from the World Bank (accessed via Yahoo Finance).
The data used to make this graphic can be found in the table below.
| Country | Total external debt to China ($B) |
|---|---|
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | $26.6 |
| 🇦🇴 Angola | $21.0 |
| 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | $8.9 |
| 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | $6.8 |
| 🇰🇪 Kenya | $6.7 |
| 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | $6.1 |
| 🇿🇲 Zambia | $6.1 |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | $5.3 |
| 🇪🇬 Egypt | $5.2 |
| 🇳🇬 Nigeria | $4.3 |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | $4.1 |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | $4.0 |
| 🇨🇮 Côte d'Ivoire | $3.9 |
| 🇧🇾 Belarus | $3.9 |
| 🇨🇲 Cameroon | $3.8 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | $3.4 |
| 🇨🇬 Republic of the Congo | $3.4 |
| 🇿🇦 South Africa | $3.4 |
| 🇲🇳 Mongolia | $3.0 |
| 🇦🇷 Argentina | $2.9 |
This dataset highlights Pakistan and Angola as having the largest debts to China by a wide margin. Both countries have taken billions in loans from China for various infrastructure and energy projects.
Critically, both countries have also struggled to manage their debt burdens. In February 2024, China extended the maturity of a $2 billion loan to Pakistan.
Soon after in March 2024, Angola negotiated a lower monthly debt payment with its biggest Chinese creditor, China Development Bank (CDB).
Could China be in Trouble?
China has provided developing countries with over $1 trillion in committed funding through its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a massive economic development project aimed at enhancing trade between China and countries across Asia, Africa, and Europe.
Many believe that this lending spree could be an issue in the near future.
According to a 2023 report by AidData, 80% of these loans involve countries in financial distress, raising concerns about whether participating nations will ever be able to repay their debts.
While China claims the BRI is a driver of global development, critics in the West have long warned that the BRI employs debt-trap diplomacy, a tactic where one country uses loans to gain influence over another.
Editor’s note: The debt shown in this visualization focuses only on direct external debt, and does not include publicly-traded, liquid, debt securities like bonds. Furthermore, it’s worth noting the World Bank data excludes some countries with data accuracy or reporting issues, such as Venezuela.
Learn More About Debt from Visual Capitalist
If you enjoyed this post, check out our breakdown of $97 trillion in global government debt.
-

 Markets7 days ago
Markets7 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Uranium2 weeks ago
Uranium2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals