Politics
24 Iconic World Flags, and What They Mean
From the skull and bones at the top of a pirate ship to a white flag on a battlefield, a single piece of fabric can be interpreted in a multitude of ways. Depending on where they fly, flags can represent freedom or control, danger or safety.
In the context of modern times, flags are best known as national symbols — and they’re used to air a country’s past, present, and future vision all rolled into one.
The Meaning of Flags
Today’s infographic from Just the Flight looks at some the world’s most iconic flags, and the intricate stories and ideals that can be found in their designs.

The Americas
Since 1777, the star-spangled banner of the United States has gone through several facelifts. The current version has been in use since Hawaii gained statehood in 1960. Puerto Rico has been voting to become the 51st state in recent years — and if the U.S. government proved to accept such a resolution, the flag would be amended once more.
The largest country in South America, Brazil adopted its flag design in 1889. The primarily green background represents its lush Amazonian forest while the yellow diamond signifies its wealth in gold. Meanwhile, the Portuguese slogan on the flag, Ordem e Progresso, is a nod to democracy.
Europe
Denmark holds the Guinness world record for the oldest continuous use of their national flag, since 1625. The Danish flag is known as the Dannebrog, or Danish Cloth — as legend has it, the Dannebrog ‘miraculously’ fell from the sky in a battle during the Northern Crusades.
The Union Jack of the United Kingdom combines aspects of three older national flags and was adopted in 1801. Displaying the flag upside down is considered lèse-majesté — “to do wrong to majesty”, or an insult to the Crown — and is offensive to some.
Asia and Oceania
India’s tricolor flag was first flown in 1923. However, the colors do not represent religions or hours in the day — saffron symbolizes indifference to material gains, the white band represents light while the navy blue Dharma Chakra (wheel of truth) depicts dynamic change, and green demonstrates the country’s relationship to nature.
New Zealand’s flag features elements from the British Commonwealth. Since 2015, there have been ongoing debates among Kiwis about whether to amend the flag’s design. Frequent confusion with Australia is a significant pro for change, but national identity and financial costs are strong arguments against it.
Nepal is the only country without a rectangular (or square) national flag. The two triangles pay tribute to its geographic location in the Himalayas as well as the Shah and Rana dynasties. The sun and moon symbols on the flag used to have human faces on them, but were removed in 1962.
Africa
South Africa boasts one of the world’s most colorful flags. When it was first adopted after Nelson Mandela’s release from prison, it was the first world flag to have six colors but no seal or brocade. Interestingly, while there is no inherent meaning in its colors, the Y shape symbolizes the convergence of diverse elements and societal unity.
Mozambique is the only national flag in the world to feature a modern weapon – specifically, an AK-47 with an attached bayonet. Adopted in 1983, the rifle represents vigilance and defense, while the hoe crossing it represents the country’s agriculture.
Economy
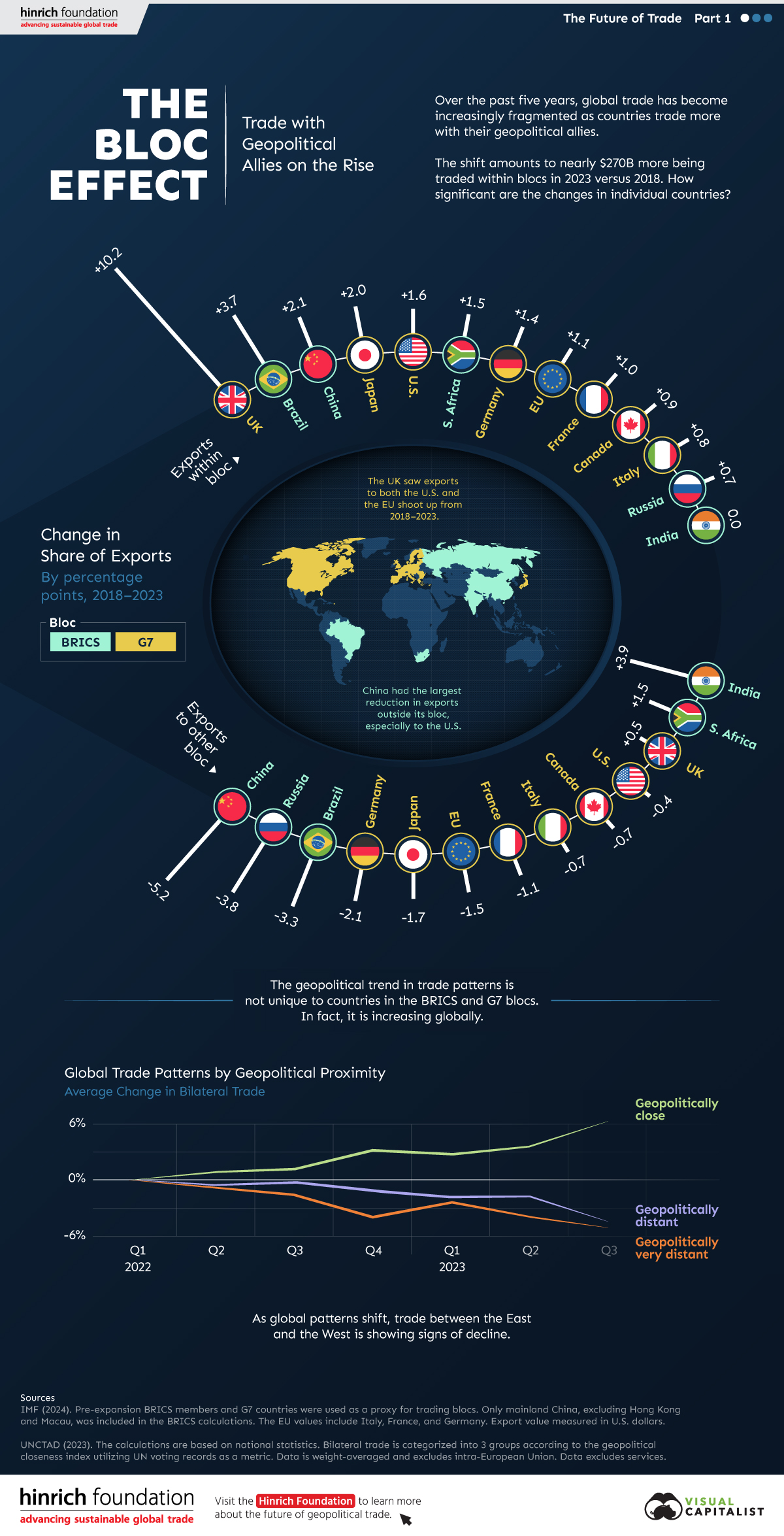
The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Geopolitical Allies on the Rise
Rising geopolitical tensions are shaping the future of international trade, but what is the effect on trading among G7 and BRICS countries?

The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Allies on the Rise
International trade has become increasingly fragmented over the last five years as countries have shifted to trading more with their geopolitical allies.
This graphic from The Hinrich Foundation, the first in a three-part series covering the future of trade, provides visual context to the growing divide in trade in G7 and pre-expansion BRICS countries, which are used as proxies for geopolitical blocs.
Trade Shifts in G7 and BRICS Countries
This analysis uses IMF data to examine differences in shares of exports within and between trading blocs from 2018 to 2023. For example, we looked at the percentage of China’s exports with other BRICS members as well as with G7 members to see how these proportions shifted in percentage points (pp) over time.
Countries traded nearly $270 billion more with allies in 2023 compared to 2018. This shift came at the expense of trade with rival blocs, which saw a decline of $314 billion.
Country Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
🇮🇳 India 0.0 3.9
🇷🇺 Russia 0.7 -3.8
🇮🇹 Italy 0.8 -0.7
🇨🇦 Canada 0.9 -0.7
🇫🇷 France 1.0 -1.1
🇪🇺 EU 1.1 -1.5
🇩🇪 Germany 1.4 -2.1
🇿🇦 South Africa 1.5 1.5
🇺🇸 U.S. 1.6 -0.4
🇯🇵 Japan 2.0 -1.7
🇨🇳 China 2.1 -5.2
🇧🇷 Brazil 3.7 -3.3
🇬🇧 UK 10.2 0.5
All shifts reported are in percentage points. For example, the EU saw its share of exports to G7 countries rise from 74.3% in 2018 to 75.4% in 2023, which equates to a 1.1 percentage point increase.
The UK saw the largest uptick in trading with other countries within the G7 (+10.2 percentage points), namely the EU, as the post-Brexit trade slump to the region recovered.
Meanwhile, the U.S.-China trade dispute caused China’s share of exports to the G7 to fall by 5.2 percentage points from 2018 to 2023, the largest decline in our sample set. In fact, partly as a result of the conflict, the U.S. has by far the highest number of harmful tariffs in place.
The Russia-Ukraine War and ensuing sanctions by the West contributed to Russia’s share of exports to the G7 falling by 3.8 percentage points over the same timeframe.
India, South Africa, and the UK bucked the trend and continued to witness advances in exports with the opposing bloc.
Average Trade Shifts of G7 and BRICS Blocs
Though results varied significantly on a country-by-country basis, the broader trend towards favoring geopolitical allies in international trade is clear.
Bloc Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
Average 2.1 -1.1
BRICS 1.6 -1.4
G7 incl. EU 2.4 -1.0
Overall, BRICS countries saw a larger shift away from exports with the other bloc, while for G7 countries the shift within their own bloc was more pronounced. This implies that though BRICS countries are trading less with the G7, they are relying more on trade partners outside their bloc to make up for the lost G7 share.
A Global Shift in International Trade and Geopolitical Proximity
The movement towards strengthening trade relations based on geopolitical proximity is a global trend.
The United Nations categorizes countries along a scale of geopolitical proximity based on UN voting records.
According to the organization’s analysis, international trade between geopolitically close countries rose from the first quarter of 2022 (when Russia first invaded Ukraine) to the third quarter of 2023 by over 6%. Conversely, trade with geopolitically distant countries declined.
The second piece in this series will explore China’s gradual move away from using the U.S. dollar in trade settlements.

Visit the Hinrich Foundation to learn more about the future of geopolitical trade

-

 Economy3 days ago
Economy3 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
We visualized product categories that saw the highest % increase in price due to U.S. inflation as of March 2024.
-

 Economy1 month ago
Economy1 month agoG20 Inflation Rates: Feb 2024 vs COVID Peak
We visualize inflation rates across G20 countries as of Feb 2024, in the context of their COVID-19 pandemic peak.
-

 Jobs1 month ago
Jobs1 month agoMapped: Unemployment Claims by State
This visual heatmap of unemployment claims by state highlights New York, California, and Alaska leading the country by a wide margin.
-
 Markets2 months ago
Markets2 months agoConfidence in the Global Economy, by Country
Will the global economy be stronger in 2024 than in 2023?
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)