Maps
Mapped: Recognition of Palestine by Country
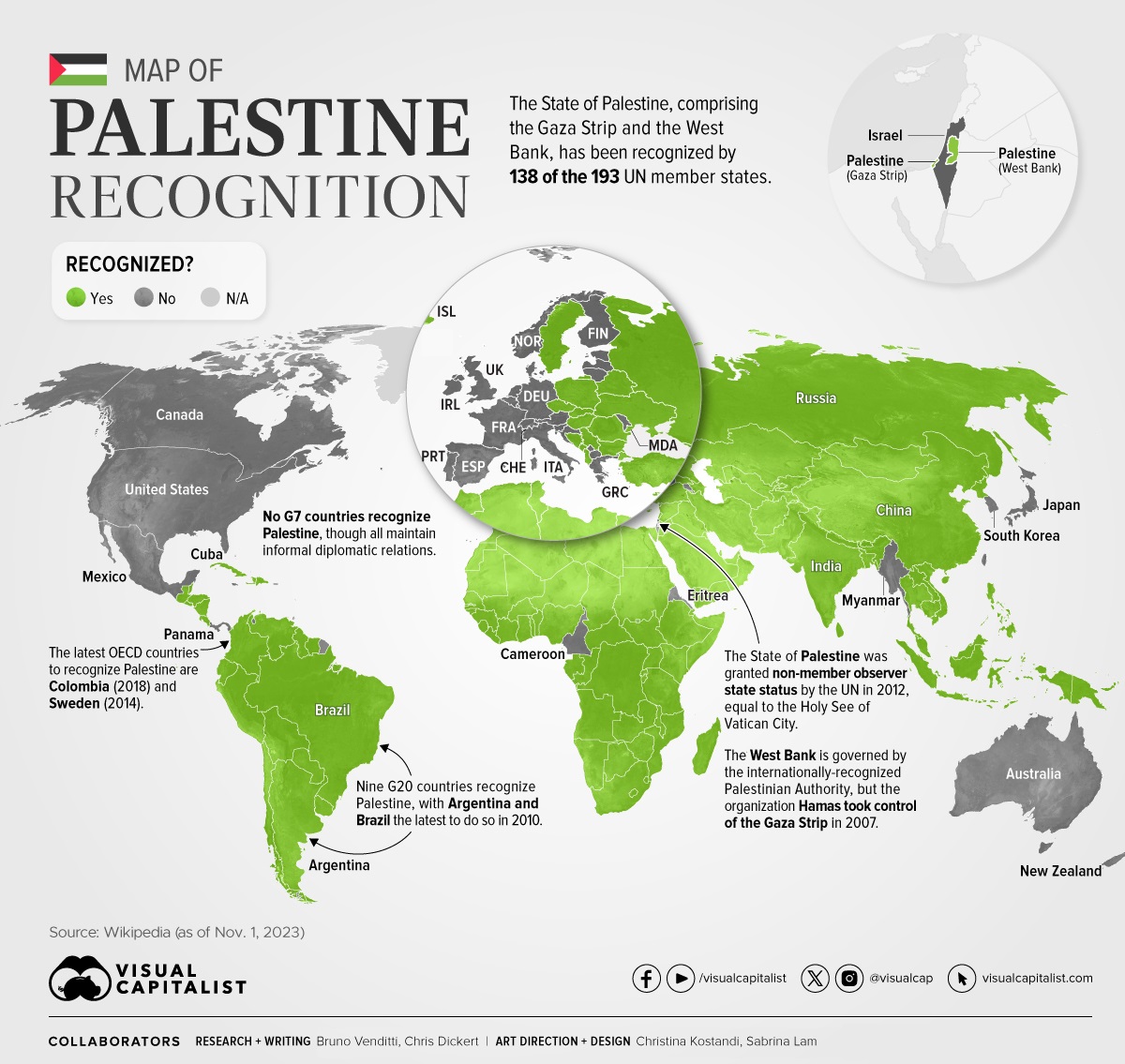
Mapped: Recognition of Palestine by Country
The recent conflict between Hamas and Israel has brought the Gaza Strip, and the partially recognized State of Palestine, prominently into the focus of the global news cycle.
In the graphic above, we use Wikipedia data to map the countries that currently recognize Palestine as a state and those that don’t.
This post is a companion piece to our map showing the recognition of Israel by country.
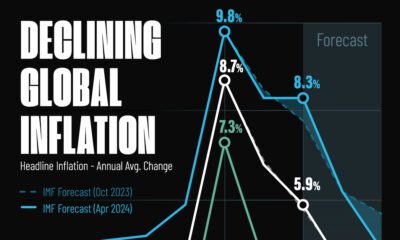
55 Countries Do Not Recognize Palestine
On November 15, 1988, the State of Palestine was officially proclaimed by the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) coalition. The state claimed sovereignty of the Gaza Strip, the West Bank, and East Jerusalem.
As of November 2023, 138 of the 193 UN members (72%) recognize the State of Palestine.
Here are the 55 countries that don’t recognize Palestine:
| State | Recognizes Palestine? |
|---|---|
| 🇦🇩 Andorra | No |
| 🇦🇲 Armenia | No |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | No, informal relations |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | No, informal relations |
| 🇧🇸 Bahamas | No |
| 🇧🇧 Barbados | No |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | No, informal relations |
| 🇨🇲 Cameroon | No, informal relations |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | No, informal relations |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | No, informal relations |
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | No, informal relations |
| 🇪🇷 Eritrea | No, informal relations |
| 🇪🇪 Estonia | No, informal relations |
| 🇫🇲 Federated States of Micronesia | No |
| 🇫🇯 Fiji | No |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | No, informal relations |
| 🇫🇷 France | No, informal relations |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | No, informal relations |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | No, informal relations |
| 🇮🇪 Ireland | No, informal relations |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | No, informal relations |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | No, informal relations |
| 🇯🇲 Jamaica | No |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | No, informal relations |
| 🇰🇮 Kiribati | No |
| 🇱🇻 Latvia | No, informal relations |
| 🇱🇮 Liechtenstein | No |
| 🇱🇹 Lithuania | No, informal relations |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | No, informal relations |
| 🇲🇭 Marshall Islands | No |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | No, informal relations |
| 🇲🇩 Moldova | No, informal relations |
| 🇲🇨 Monaco | No |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | No |
| 🇳🇷 Nauru | No |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | No, informal relations |
| 🇳🇿 New Zealand | No, informal relations |
| 🇲🇰 North Macedonia | No |
| 🇳🇴 Norway | No, informal relations |
| 🇵🇼 Palau | No |
| 🇵🇦 Panama | No |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | No, informal relations |
| 🇼🇸 Samoa | No |
| 🇸🇲 San Marino | No |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | No |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | No, informal relations |
| 🇸🇧 Solomon Islands | No |
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | No, informal relations |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | No, informal relations |
| 🇨🇭 Switzerland | No, informal relations |
| 🇹🇴 Tonga | No |
| 🇹🇹 Trinidad and Tobago | No |
| 🇹🇻 Tuvalu | No |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | No, informal relations |
| 🇺🇸 United States | No, informal relations |
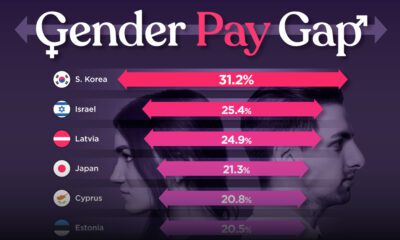
Many of the world’s Western countries, including the entire G7, do not recognize Palestine. Instead, many maintain informal diplomatic relations.
In contrast, emerging major economies like those within BRICS and other G20 nations, including Argentina, Indonesia, Türkiye, and Saudi Arabia, officially recognize the state.
In 2012, the State of Palestine was also upgraded by the UN to become a non-member observer state, a status shared only by the Holy See of Vatican City.
Hamas and the Gaza Strip
Officially, the United Nations recognizes the PLO as the governing entity in the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip, both of which fell under Israeli control following the 1967 Six-Day War.
After the Oslo Accords were signed by Israel and the PLO in the mid 1990s, the PLO gained control over the Gaza Strip and 40% of the West Bank through the newly-created Palestinian Authority administration.
However, following a 2007 military conflict between rival Palestinian factions Fatah (the majority party of the PLO) and Hamas (a militant political party separate from the PLO), the Gaza Strip has been governed by Hamas.
As of November 2023, just under 72% of UN members recognized Palestine as a country, compared to 84% for the State of Israel.
Maps
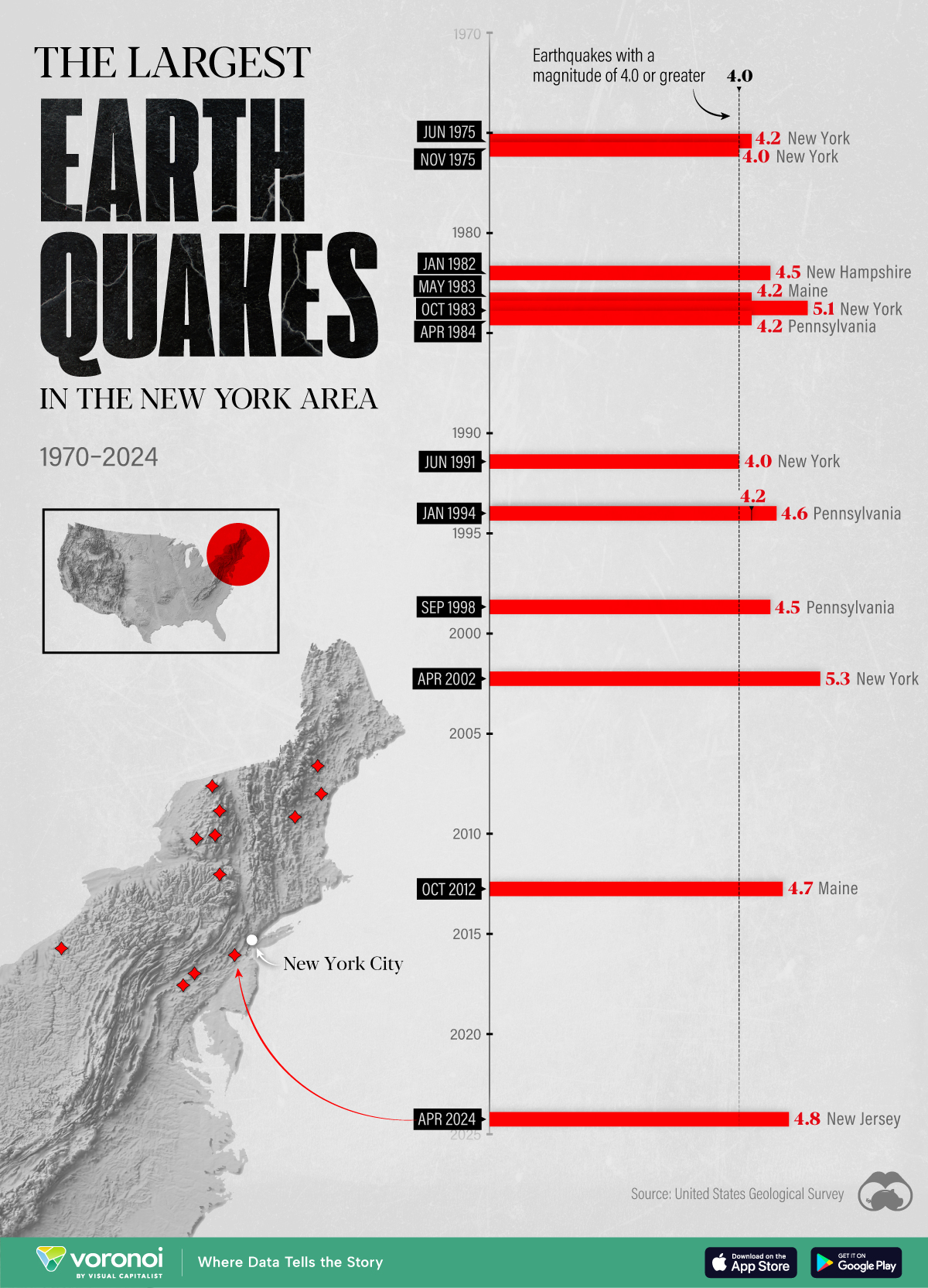
The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
The earthquake that shook buildings across New York in April 2024 was the third-largest quake in the Northeast U.S. over the past 50 years.

The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The 4.8 magnitude earthquake that shook buildings across New York on Friday, April 5th, 2024 was the third-largest quake in the U.S. Northeast area over the past 50 years.
In this map, we illustrate earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.0 or greater recorded in the Northeastern U.S. since 1970, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Shallow Quakes and Older Buildings
The earthquake that struck the U.S. Northeast in April 2024 was felt by millions of people from Washington, D.C., to north of Boston. It even caused a full ground stop at Newark Airport.
The quake, occurring just 5 km beneath the Earth’s surface, was considered shallow, which is what contributed to more intense shaking at the surface.
According to the USGS, rocks in the eastern U.S. are significantly older, denser, and harder than those on the western side, compressed by time. This makes them more efficient conduits for seismic energy. Additionally, buildings in the Northeast tend to be older and may not adhere to the latest earthquake codes.
Despite disrupting work and school life, the earthquake was considered minor, according to the Michigan Technological University magnitude scale:
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 or less | Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph. | Millions |
| 2.5 to 5.4 | Often felt, but only causes minor damage. | 500,000 |
| 5.5 to 6.0 | Slight damage to buildings and other structures. | 350 |
| 6.1 to 6.9 | May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas. | 100 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
The largest earthquake felt in the area over the past 50 years was a 5.3 magnitude quake that occurred in Au Sable Forks, New York, in 2002. It damaged houses and cracked roads in a remote corner of the Adirondack Mountains, but caused no injuries.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 20, 2002 | 5.3 | Au Sable Forks | New York |
| October 7, 1983 | 5.1 | Newcomb | New York |
| April 5, 2024 | 4.8 | Whitehouse Station | New Jersey |
| October 16, 2012 | 4.7 | Hollis Center | Maine |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.6 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| January 19, 1982 | 4.5 | Sanbornton | New Hampshire |
| September 25, 1998 | 4.5 | Adamsville | Pennsylvania |
| June 9, 1975 | 4.2 | Altona | New York |
| May 29, 1983 | 4.2 | Peru | Maine |
| April 23, 1984 | 4.2 | Conestoga | Pennsylvania |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.2 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| November 3, 1975 | 4 | Long Lake | New York |
| June 17, 1991 | 4 | Worcester | New York |
The largest earthquake in U.S. history, however, was the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska, measuring 9.2 magnitude and killing 131 people.
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands2 weeks ago
Brands2 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?