Maps
Mapped: The Expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
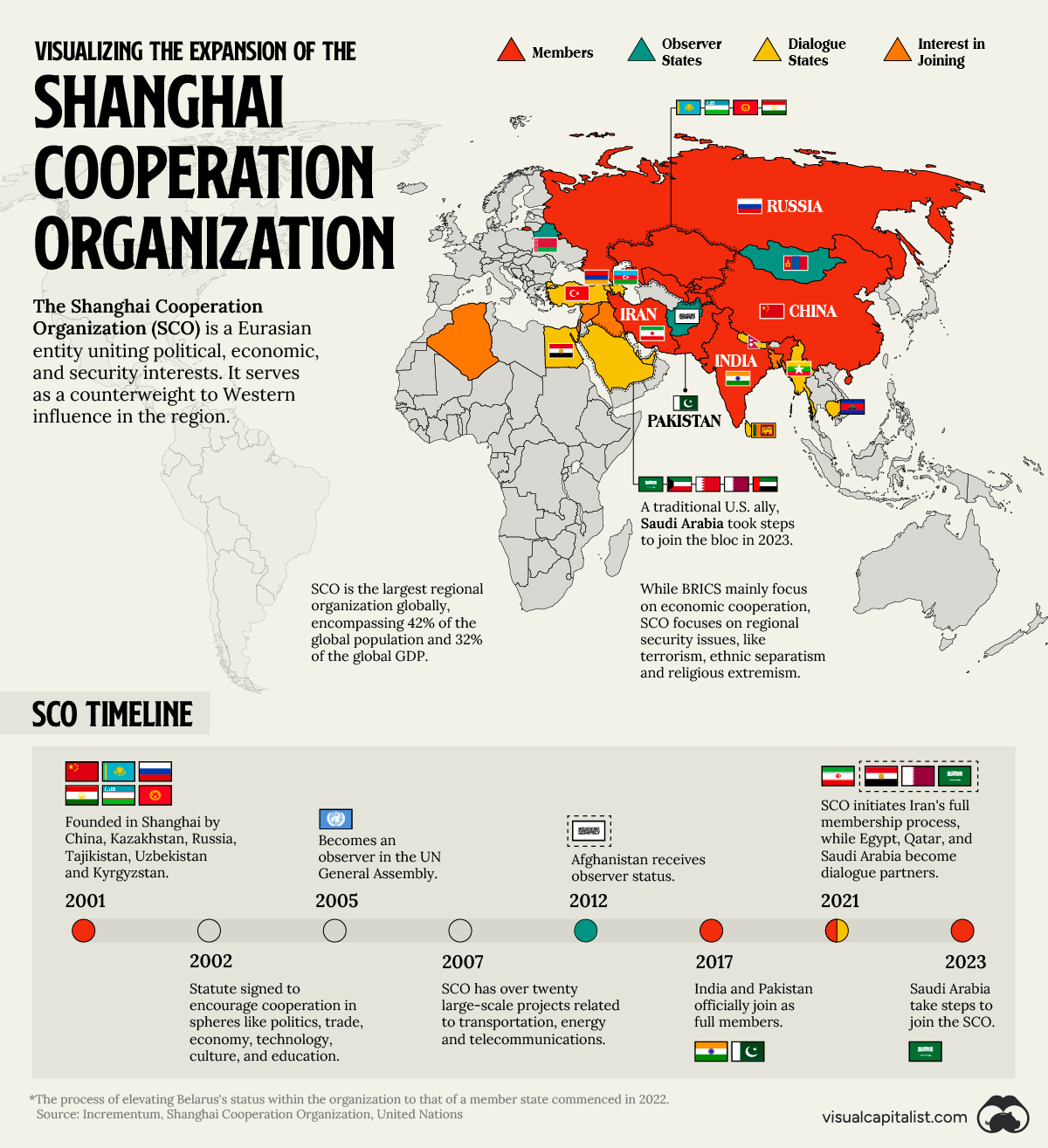
Expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
China has actively pursued the expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), a Eurasian political, economic, and international security entity.
Established in 2001 by Russia, China, and former Soviet states, the organization serves as a counterbalance to Western influence in the region.
The map above uses data from Incrementum, the UN, and the SCO to illustrate the development of the largest regional organization globally.
SCO Timeline
The SCO, formed with objectives such as combating terrorism, promoting border security, strengthening political ties, and expanding economic cooperation, initially included China, Kazakhstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan.
| Country | Status | Joining date |
|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 China | Member | 2001 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | Member | 2001 |
| 🇮🇳 India | Member | 2005 |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | Member | 2005 |
| 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | Member | 2005 |
| 🇹🇯 Tajikistan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | Observer | 2012 |
| 🇧🇾 Belarus | Observer | 2015 |
| 🇲🇳 Mongolia | Observer | 2004 |
| 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | Dialogue Partner | 2016 |
| 🇦🇲 Armenia | Dialogue Partner | 2016 |
| 🇧🇭 Bahrain | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇪🇬 Egypt | Dialogue Partner | 2022 |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | Dialogue Partner | 2015 |
| 🇶🇦 Qatar | Dialogue Partner | 2022 |
| 🇰🇼 Kuwait | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇲🇻 Maldives | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇳🇵 Nepal | Dialogue Partner | 2016 |
| 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | Dialogue Partner | 2022 |
| 🇹🇷 Turkey | Dialogue Partner | 2013 |
| 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | Dialogue Partner | 2010 |
In 2002, member states ratified the organization statute to encourage political, trade, economic, technological, cultural, and educational collaboration.
Since then, the organization has undertaken over 20 large-scale projects related to transportation, energy, and telecommunications. A notable initiative is China’s expansive Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to rebuild the Silk Road and connect China to Asia, Europe, and beyond through significant infrastructure investments.
The organization has also expanded its geopolitical influence. It attained observer status in the UN General Assembly in 2005 and gave Afghanistan observer status in 2012. Currently, it is working with the interim Taliban administration to include Afghan representatives in its future meetings.
India and Pakistan officially became members of the SCO in 2017, and Iran is in the process of obtaining full-time membership. Egypt and Qatar are dialogue partners, and Saudi Arabia, a traditional U.S. ally, has taken steps to join. Belarus is set to become a member in 2024 after signing a memorandum of obligations.
Furthermore, the organization also plays a crucial role in Chinese military ambitions.
In 2007, the SCO signed an agreement outlining the legal rights and responsibilities for military exercises in another member country.
The agreement allows Chinese armed forces to engage in air-ground combat operations abroad, covering activities like long-distance mobilization, counterterrorism missions, stability maintenance operations, and conventional warfare.
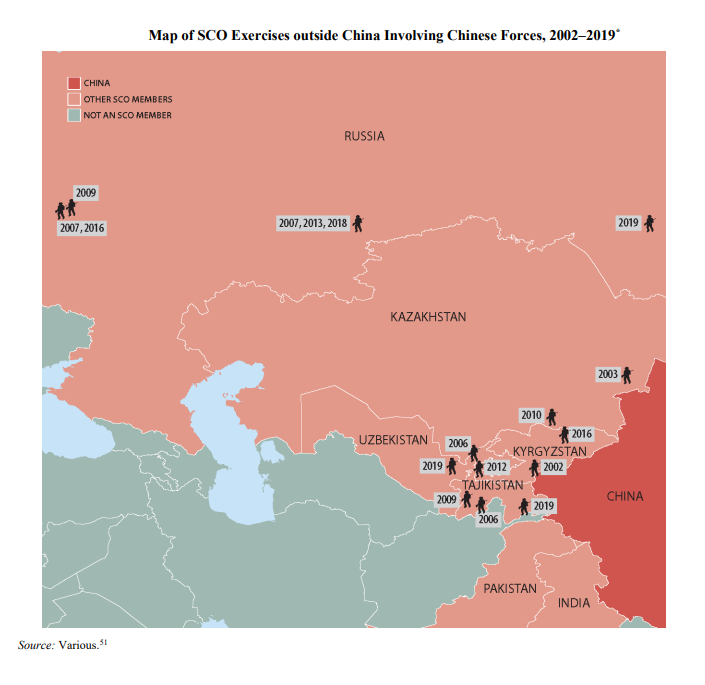
Military presence is particularly important for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), which fears that separatist movements in the Uyghur-dominated autonomous region of Xinjiang could gain support from other Central Asian states.
Implications for the United States
Today, the SCO encompasses 42% of the global population and 32% of the global GDP.
Due to its growing influence, U.S. policymakers have been monitoring the development of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization.
In a 2020 report to the U.S. Congress, the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission highlighted that through the SCO, China is establishing diplomatic relationships and expeditionary capabilities that could support power projection beyond its borders.
According to the document, “there is a significant risk that Beijing may leverage its relationships with SCO countries to limit the ability of U.S. armed forces to operate in Central Asia.”
Nonetheless, the same report mentions that the SCO could serve as a beneficial tool for Central Asian states, offering a platform for cooperation and presenting an alternative to potential domination by Russia, particularly in areas such as energy.
Maps
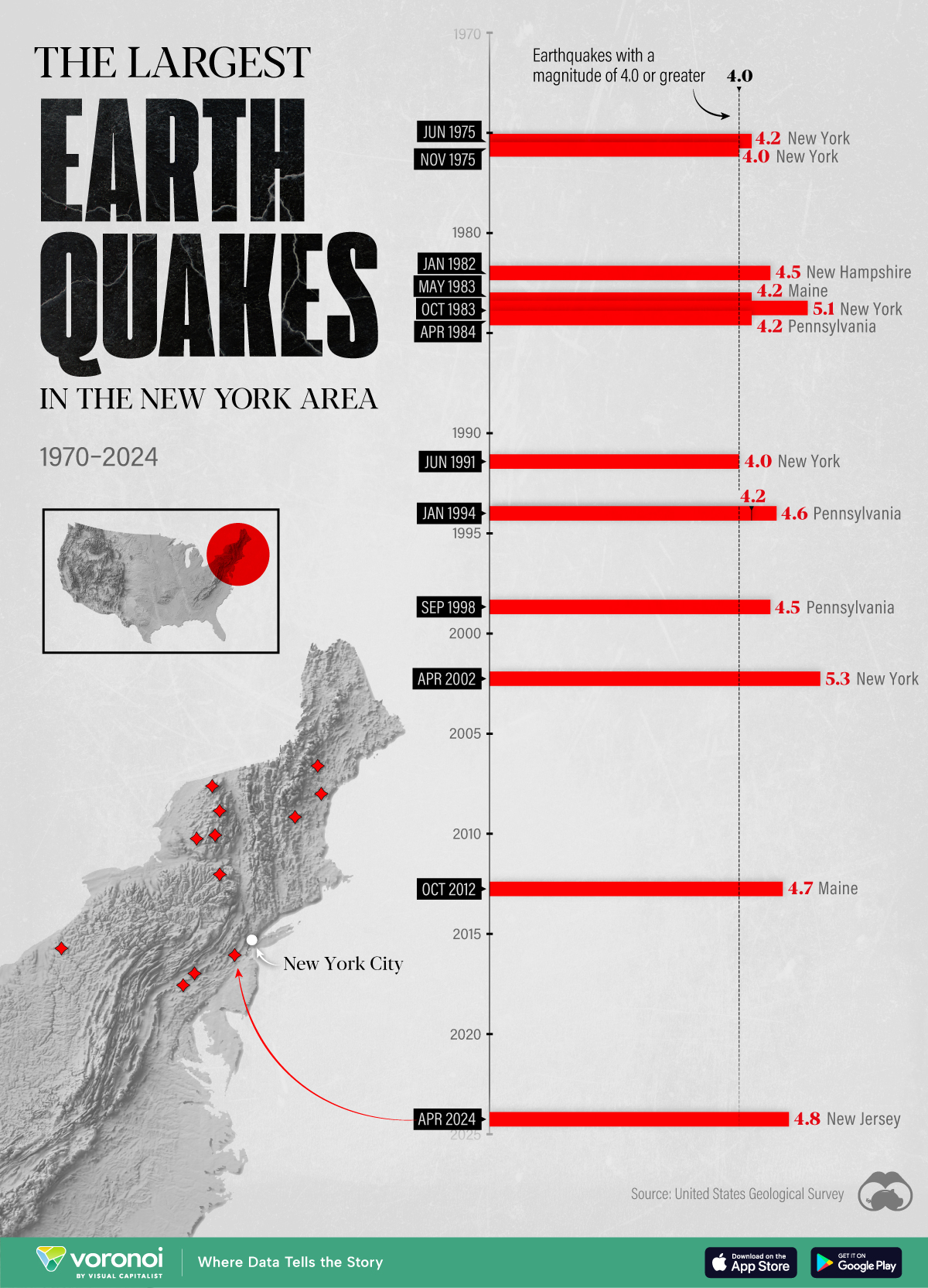
The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
The earthquake that shook buildings across New York in April 2024 was the third-largest quake in the Northeast U.S. over the past 50 years.

The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The 4.8 magnitude earthquake that shook buildings across New York on Friday, April 5th, 2024 was the third-largest quake in the U.S. Northeast area over the past 50 years.
In this map, we illustrate earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.0 or greater recorded in the Northeastern U.S. since 1970, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Shallow Quakes and Older Buildings
The earthquake that struck the U.S. Northeast in April 2024 was felt by millions of people from Washington, D.C., to north of Boston. It even caused a full ground stop at Newark Airport.
The quake, occurring just 5 km beneath the Earth’s surface, was considered shallow, which is what contributed to more intense shaking at the surface.
According to the USGS, rocks in the eastern U.S. are significantly older, denser, and harder than those on the western side, compressed by time. This makes them more efficient conduits for seismic energy. Additionally, buildings in the Northeast tend to be older and may not adhere to the latest earthquake codes.
Despite disrupting work and school life, the earthquake was considered minor, according to the Michigan Technological University magnitude scale:
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 or less | Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph. | Millions |
| 2.5 to 5.4 | Often felt, but only causes minor damage. | 500,000 |
| 5.5 to 6.0 | Slight damage to buildings and other structures. | 350 |
| 6.1 to 6.9 | May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas. | 100 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
The largest earthquake felt in the area over the past 50 years was a 5.3 magnitude quake that occurred in Au Sable Forks, New York, in 2002. It damaged houses and cracked roads in a remote corner of the Adirondack Mountains, but caused no injuries.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 20, 2002 | 5.3 | Au Sable Forks | New York |
| October 7, 1983 | 5.1 | Newcomb | New York |
| April 5, 2024 | 4.8 | Whitehouse Station | New Jersey |
| October 16, 2012 | 4.7 | Hollis Center | Maine |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.6 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| January 19, 1982 | 4.5 | Sanbornton | New Hampshire |
| September 25, 1998 | 4.5 | Adamsville | Pennsylvania |
| June 9, 1975 | 4.2 | Altona | New York |
| May 29, 1983 | 4.2 | Peru | Maine |
| April 23, 1984 | 4.2 | Conestoga | Pennsylvania |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.2 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| November 3, 1975 | 4 | Long Lake | New York |
| June 17, 1991 | 4 | Worcester | New York |
The largest earthquake in U.S. history, however, was the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska, measuring 9.2 magnitude and killing 131 people.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001