Misc
29 Psychological Tricks To Make You Buy More
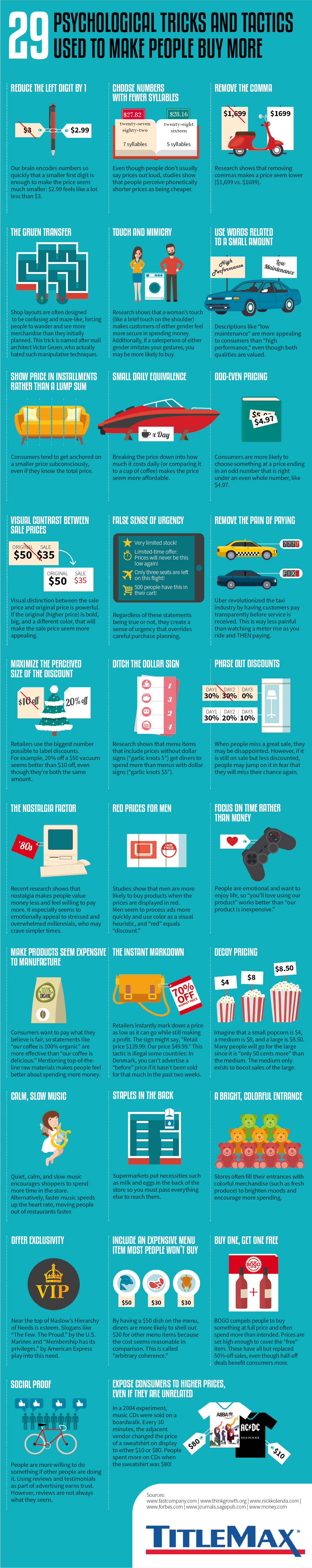
29 Psychological Tricks To Make You Buy More
Ever suffered from buyer’s remorse? You’re not alone.
According to a recent survey, only 5% of people have never felt guilty about buying something. That means the majority of us, at some point in our lives, have regretted a purchase.
But consumers aren’t necessarily only to blame for impulse buys. After all, we’re constantly bombarded with advertisements and marketing tactics specifically tailored to try and get us to spend more money.
Today’s graphic by TitleMax explains 29 different psychological tactics that marketers try to get consumers to buy more.
Tricks are for Marketers
While this list isn’t exhaustive, it provides some key examples of the ways that marketers are attempting to influence your subconscious mind.
We noticed some high-level trends among the 29 tactics, which we compiled into four overarching sections:
- Visual Pricing Tricks
These tricks aim to intentionally minimize the appearance of the price, so it’s more palatable to consumers. For instance, a store will price something at $9.99 instead of $10.00, or label a product as “buy-one-get-one” rather than 50% off. - Intentional Language Tricks
It’s not what you say, but how you say it. Making products seem costly to manufacture, offering exclusivity, and using words associated with small amounts fall under this category. These tricks use semantics to position a product in an appealing way. - Brick-and-Mortar Tricks
A store’s layout is less arbitrary than you may realize. Having a bright and colorful entrance, playing calm and slow music, and putting the essential items at the back of the store are a few tactics that fall into this section. These tricks use displays and product placement to influence consumer behavior. - Urgency Tricks
A false sense of urgency and phase-out discounts are included in this category. If a consumer believes they might miss out on a deal, they’re more likely to buy.
The Theories in Practice
While most retailers are guilty of using at least a few of these tactics, several big companies are notorious for their use of psychological tricks to boost sales.
For instance, Ikea is well known for its confusing, maze-like layout. This is no accident, as an Ikea store’s architecture is designed specifically to maximize product exposure—it’s mastered what’s called the Gruen effect, a term named after architect Victor Gruen, whose elaborate displays were proven to convert browsers into buyers.
Another example is Walmart’s rollback pricing, which uses visual contrast to make the sale price more appealing. It’s clearly served the company well—in 2019, Walmart made $524 billion in revenue, making it the world’s largest retailer.
Costco uses a few tactics on the list, but one it’s notorious for is putting fresh produce in the back of the store. That means customers need to pass through the electronics, clothing, and household goods sections before they can get to the necessities.
While the above tactics are in a gray area, other tricks are flat out dishonest. Makeup brand Sunday Riley was caught writing fake Sephora reviews to boost sales. Employees were encouraged to write outstanding reviews for the company, and the CEO even provided instructions on how to avoid getting caught.
The Influencer Era
As consumers become aware of certain marketing tactics, retailers are forced to switch up their game in order to remain effective.
A relatively recent phenomenon is influencer marketing, which is when brands partner with vloggers or influencers to endorse a product. And these partnerships tend to work—a recent survey revealed that 40% of people have purchased something based on an influencer’s recommendation.
But how long will influencer marketing—or any of these tactics—stay effective? Some of the more subtle pricing tactics might stay relevant for longer, but it’s unlikely that all of these tricks will stand the test of time.
Misc
The Evolution of U.S. Beer Logos
In this graphic, we analyze the evolution of popular U.S. beer logos like Budweiser, Coors Light, Bud Light, and more.

The Evolution of U.S. Beer Logos
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite selling a popular product, beer companies have to be creative to stand out in a competitive market.
In this graphic, we analyze the evolution of some U.S. beer logos based on various sources. We chose brands based on a mixture of criteria, including popularity (based on YouGov surveys), availability of logo assets, and those with interesting developments.
Bud Light Back to the ’80s
Despite recent backlash and calls for a boycott after sending a commemorative can to transgender influencer Dylan Mulvaney, Bud Light remains one of America’s best-selling beers.
The brand of light beer, owned by the Anheuser-Busch company, has switched from its more circular logo with italic letters adopted in the 1990s back to the Bud Light badge of the 1980s. It is composed of heavy uppercase lettering, written in two levels in a shade of blue with the inscription placed on a solid white background and enclosed in a thin rectangular frame.
Miller Lite Goes Old School
After following a similar approach to Bud Light’s branding throughout the 2000s, Miller Lite decided to undergo a major rebranding in 2014.
The company returned to its 1970s roots, once again combining a white can with its original blue, gold, and red logo. The redesign was largely considered a success, given that Miller Lite sales immediately increased following the change.
A Symbol of American Brewing
The oldest brand on our U.S. beer list, the Budweiser logo, has undergone more than 15 changes over the years.
The design of two connected triangles represents a red bow tie, as a symbol of American brewing.
The colors of the Budweiser logo include a vibrant red, which helps the logo stand out and be easily recognizable from a distance. Studies also suggest that the color red stimulates appetite. Meanwhile, the white inscription symbolizes purity and cleanliness.
Curious to learn more about the beer market? Check out this graphic about global beer consumption.
-

 Money7 days ago
Money7 days agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024