Misc
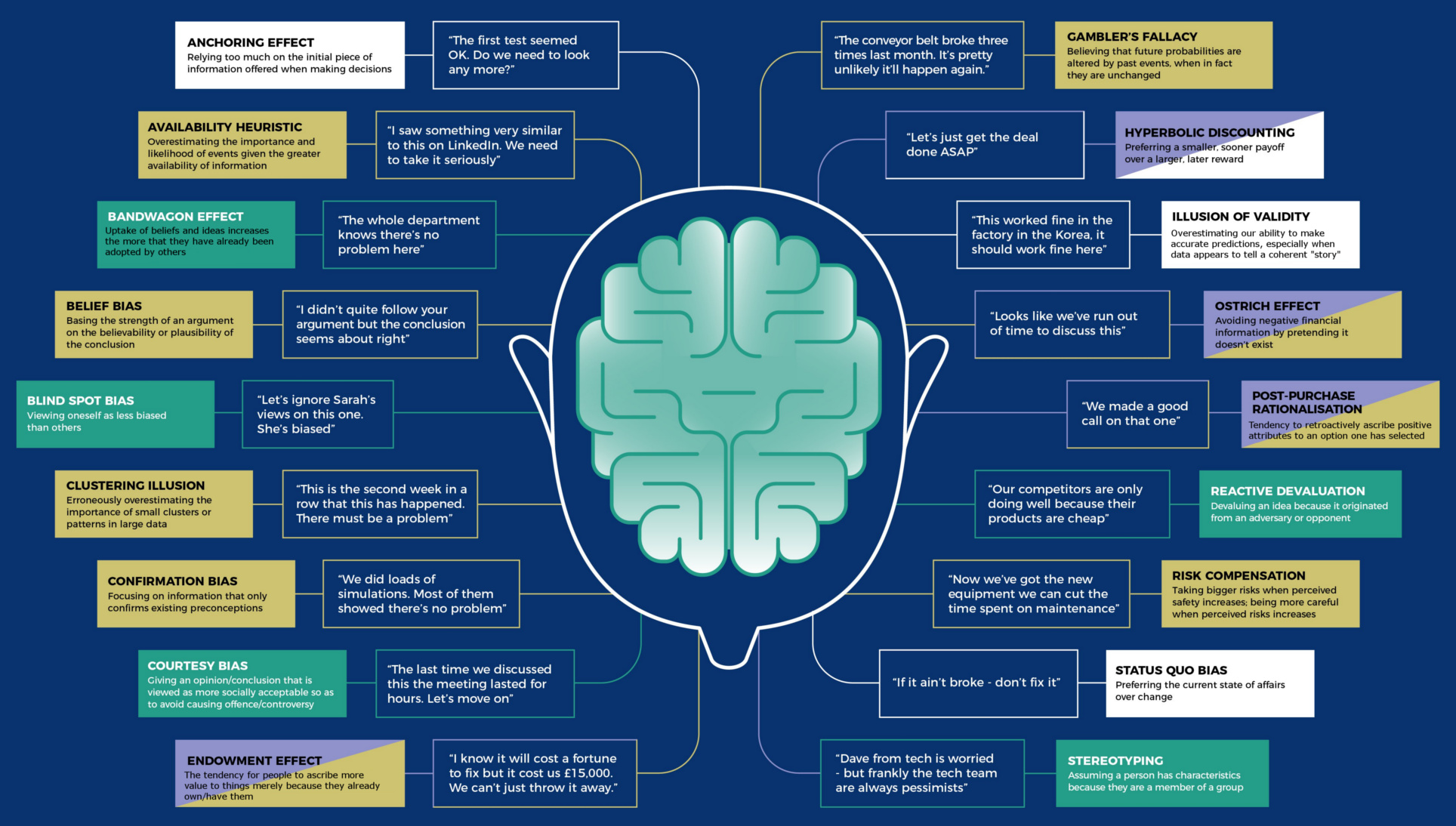
Every Single Cognitive Bias in One Infographic
View a high resolution version of this graphic
Every Single Cognitive Bias in One Infographic
View the high resolution version of today’s graphic by clicking here.
The human brain is capable of incredible things, but it’s also extremely flawed at times.
Science has shown that we tend to make all sorts of mental mistakes, called “cognitive biases”, that can affect both our thinking and actions. These biases can lead to us extrapolating information from the wrong sources, seeking to confirm existing beliefs, or failing to remember events the way they actually happened!
To be sure, this is all part of being human—but such cognitive biases can also have a profound effect on our endeavors, investments, and life in general.
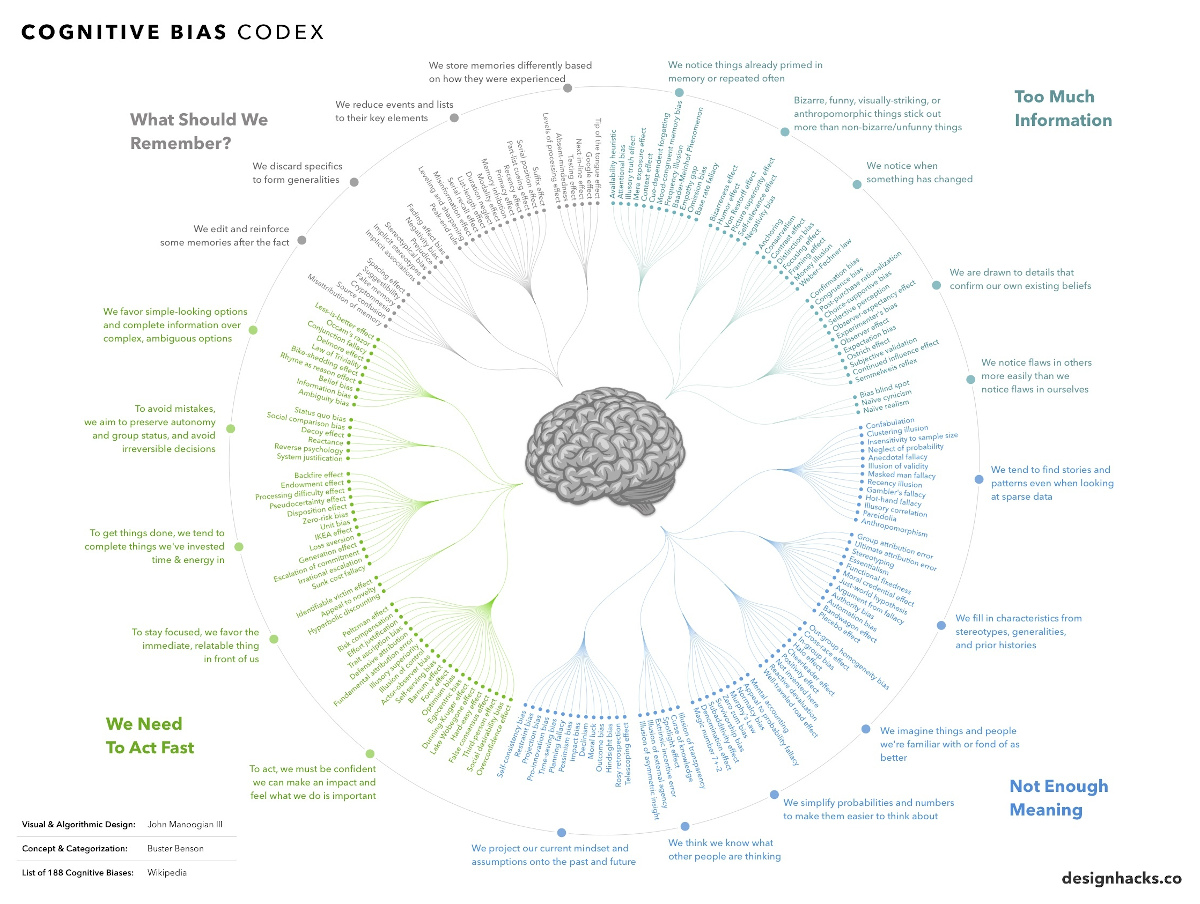
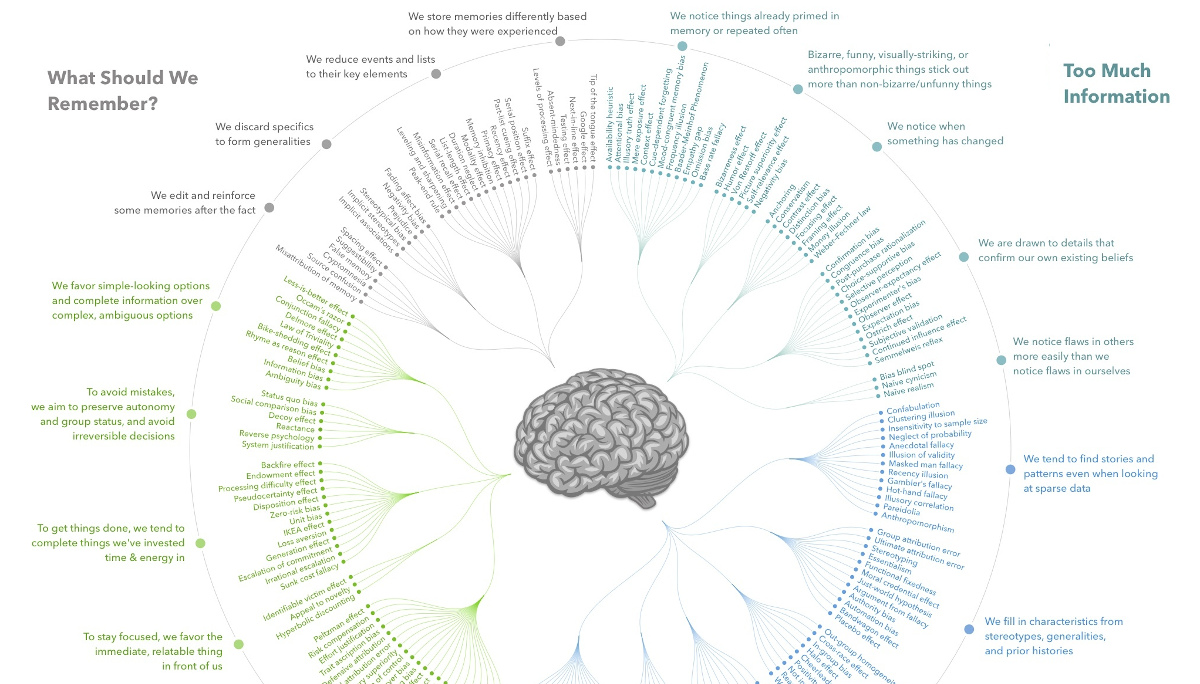
For this reason, today’s infographic from DesignHacks.co is particularly handy. It shows and groups each of the 188 known confirmation biases in existence.
What is a Cognitive Bias?
Humans have a tendency to think in particular ways that can lead to systematic deviations from making rational judgments.
These tendencies usually arise from:
- Information processing shortcuts
- The limited processing ability of the brain
- Emotional and moral motivations
- Distortions in storing and retrieving memories
- Social influence
Cognitive biases have been studied for decades by academics in the fields of cognitive science, social psychology, and behavioral economics, but they are especially relevant in today’s information-packed world. They influence the way we think and act, and such irrational mental shortcuts can lead to all kinds of problems in entrepreneurship, investing, or management.
Cognitive Bias Examples
Here are five examples of how these types of biases can affect people in the business world:
1. Familiarity Bias: An investor puts her money in “what she knows”, rather than seeking the obvious benefits from portfolio diversification. Just because a certain type of industry or security is familiar doesn’t make it the logical selection.
2. Self-Attribution Bias: An entrepreneur overly attributes his company’s success to himself, rather than other factors (team, luck, industry trends). When things go bad, he blames these external factors for derailing his progress.
3. Anchoring Bias: An employee in a salary negotiation is too dependent on the first number mentioned in the negotiations, rather than rationally examining a range of options.
4. Survivorship Bias: Entrepreneurship looks easy, because there are so many successful entrepreneurs out there. However, this is a cognitive bias: the successful entrepreneurs are the ones still around, while the millions who failed went and did other things.
5. Gambler’s Fallacy: A venture capitalist sees a portfolio company rise and rise in value after its IPO, far behind what he initially thought possible. Instead of holding on to a winner and rationally evaluating the possibility that appreciation could still continue, he dumps the stock to lock in the existing gains.
This post was first published in 2017. We have since updated it, adding in new content for 2021.
VC+
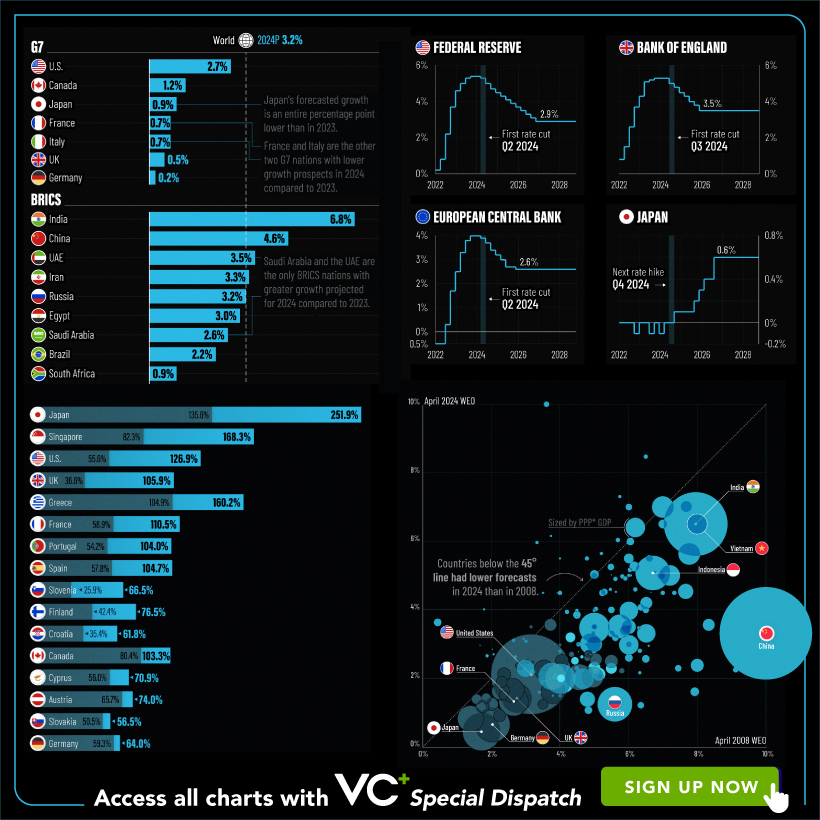
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our VC+ Special Dispatch is available exclusively to VC+ members. All you need to do is log into the VC+ Archive.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to access the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members get to see.
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members can access the full Special Dispatch by logging into the VC+ Archive, where you can also check out previous releases.
Make sure you join VC+ now to see exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001