Healthcare
Visualizing Global Attitudes Towards the COVID-19 Vaccines
Visualizing Global Attitudes Towards COVID-19 Vaccines
View the high-resolution of the infographic by clicking here.
To vaccinate, or not to vaccinate? That is the question.
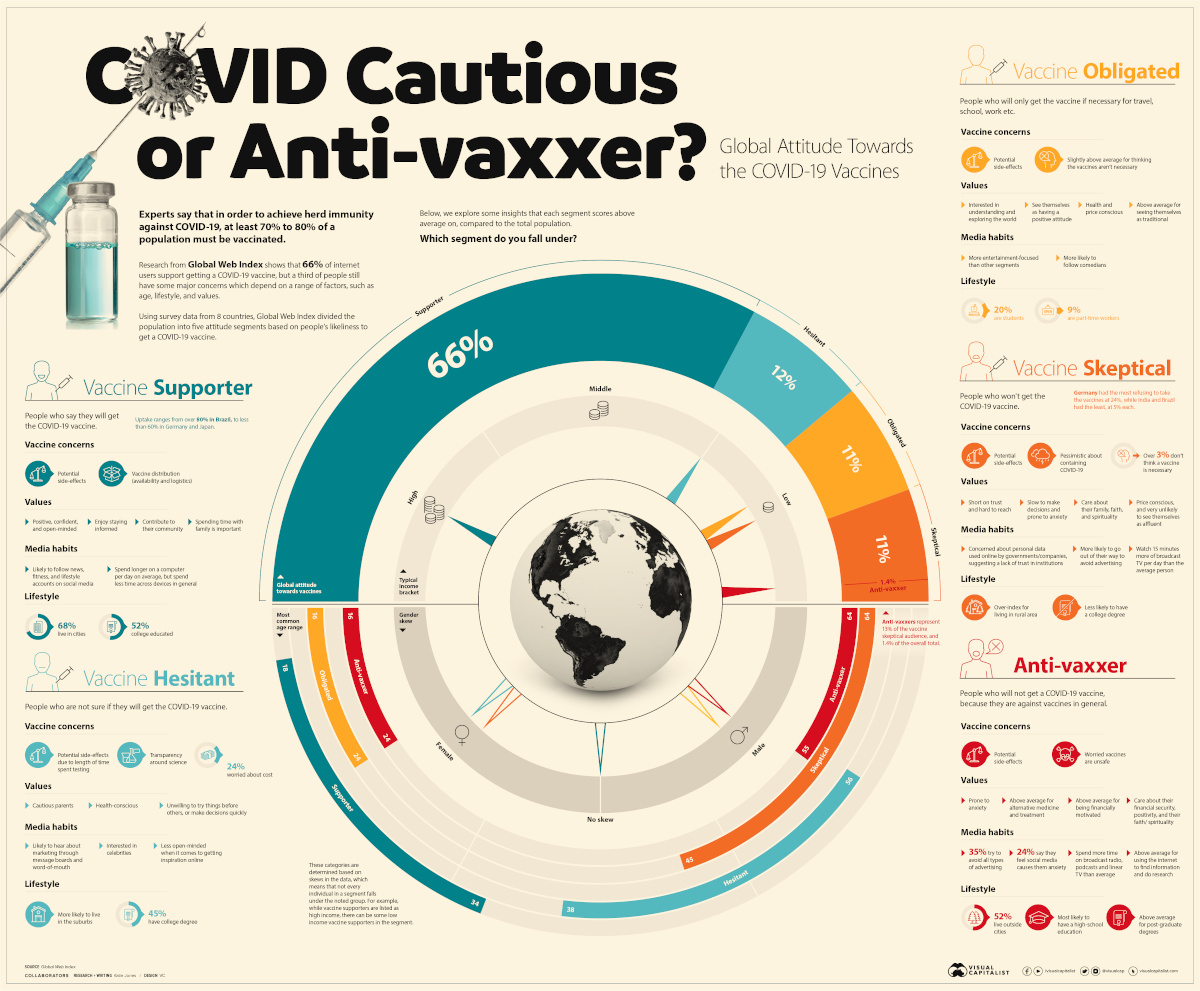
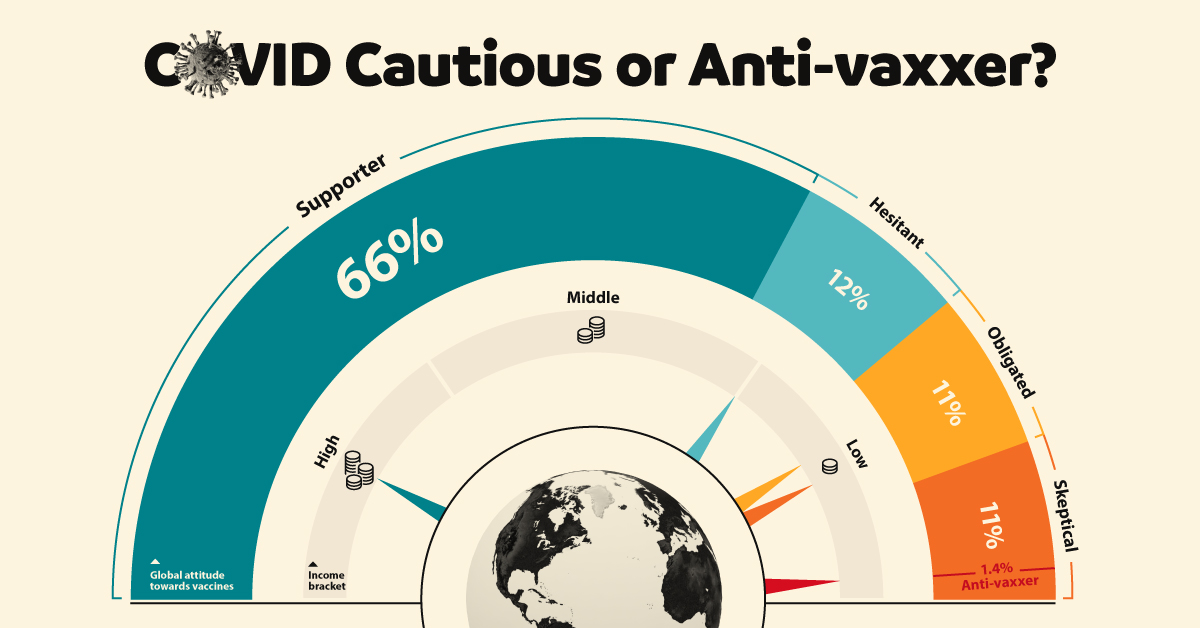
In order to achieve herd immunity against COVID-19, some experts believe that between 70% to 80% of a population must be vaccinated.
But attitudes towards these vaccines are undoubtedly mixed. In fact, it’s estimated that one-third of people globally have some major concerns.
Using survey data from eight different countries, Global Web Index created five archetypes to help illustrate how typical attitudes towards vaccines differ depending on a range of factors, such as age, income, lifestyle, and values.
| Segment | Breakdown | Age Skew | Gender Skew | Income | Vaccine Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Supporter | 66% | 18-34 | None | High income | Potential side-effects, availability, and logistics of vaccine distribution. |
| Vaccines Hesitant | 12% | 38-56 | Female | Low/Middle income | Potential side-effects specifically due to no long-term testing, cost of vaccine, and more transparency around science required. |
| Vaccine Obligated | 11% | 16-24 | Male | Low income | Potential side-effects, not sure COVID-19 vaccine is necessary to combat the virus. |
| Vaccine Skeptical | 11% | 45-64 | Female | Low income | Potential side-effects, don’t believe vaccines can curtail the pandemic. |
| Anti-vaxxer | 1.4% (13% of the Vaccine Skeptical segment) | 16-24, 55-64 | Male | Low income | Potential side-effects, don’t believe vaccines in general are safe. |
Countries surveyed: United States, Germany, United Kingdom, Brazil, China, India, Japan, and Italy.
Which segment are you most likely to fall under, according to these segments?
Vaccine Supporters
[People who say they will get the COVID-19 vaccine.]
Out of all participants surveyed, 66% of them support the idea of getting a COVID-19 vaccine. Within this group, there is a skew towards younger people (aged 18-34) who are likely working professionals earning a high income and living in a city.
Despite their optimism towards COVID-19 vaccines, however, one-third of vaccine supporters say they will wait to get one, due to lingering concerns regarding issues with vaccine distribution and any potential side-effects.
Interestingly, this procrastination mindset has been seen before during the H1N1 (swine flu) pandemic when both members of the general public and healthcare workers showed low levels of vaccine acceptance due to safety concerns.
Vaccine Hesitant
[People who are not sure if they will get the COVID-19 vaccine.]
The vaccine hesitant group, which is more common among cautious suburban parents, makes up 12% of the total study. They are more likely to be female, and feel anxious about the length of time spent testing vaccines and therefore require more transparency around the science.
With that being said, this group could be easily swayed, as they are more receptive to word-of-mouth and messaging boards to get advice from their peers over any other medium.
Vaccine Obligated
[People who will only get the vaccine if it’s necessary for travel, school, work etc.]
The vaccine obligated group makes up 11% of the total, and has a skew towards males aged between 16 and 24 years old.
While this group is also concerned with potential side-effects, their responses suggesting that a vaccine may not be necessary to combat COVID-19 was above average compared to other segments in the study. They also index above average when it comes to viewing themselves as traditionalists.
Vaccine Skeptical
[People who won’t get the COVID-19 vaccine.]
The vaccine skeptical group makes up another 11% of the total. However, this group is mostly female, who are aged between 45-64 and earn a lower-than-average income. They are less likely to have a college degree, and are more likely to live in a rural area.
Along with the worry of potential side-effects, this group is generally more pessimistic about containing COVID-19 at all. Therefore a small percentage do not believe a vaccine will help tackle the global health crisis.
With notably low trust levels, this group is one of the hardest to reach and potentially persuade. What makes them unique however, is their lack of faith in the scientific process.
Anti-Vaxxers
[People who will not get the vaccine, because they are against vaccines in general.]
It is important to note that those who choose not to get a COVID-19 vaccine should not be confused with anti-vaxxers.
Anti-vaxxers are a sub-segment of the vaccine skeptical group that makes up 1.4% of the total population. The difference is, anti-vaxxers do not believe in getting any vaccine due to safety concerns, not just not a vaccine for COVID-19.
According to the study, anti-vaxxers tend to fall into one of two age brackets, between 16-24 years or 55-64 years old, and are typically males with lower incomes.
Another Tool in the Arsenal Against COVID-19
The study demonstrates that broad segments of society—regardless of their demographic or views—are at least somewhat concerned about COVID-19 vaccines becoming widely available.
While scientists are not quite sure if the current vaccines on the market can stop infection or transmission of the virus, they are an important part of our global defenses against COVID-19, along with other safety restrictions like wearing masks and keeping a distance.
Healthcare
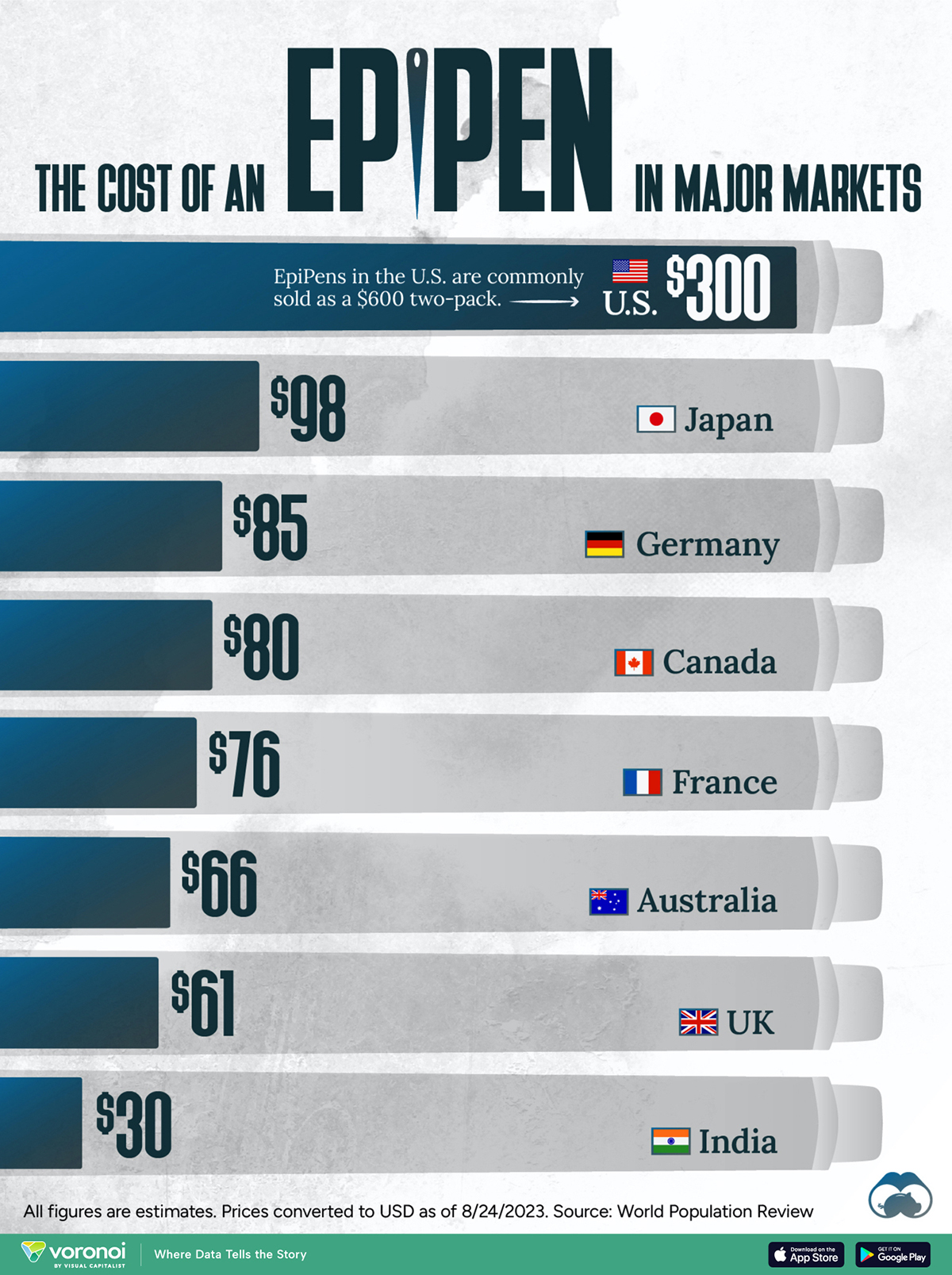
The Cost of an EpiPen in Major Markets
This visualization compares EpiPen prices around the world, with the U.S. having the highest prices by far.

The Cost of an EpiPen in Major Markets
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
EpiPens are auto-injectors containing epinephrine, a drug that can treat or reverse severe allergic reactions, potentially preventing death.
The global epinephrine market was valued at $1.75 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $4.08 billion by 2030. North America represents over 60% of the market.
EpiPens, however, can be prohibitively expensive in some regions.
In this graphic, we present estimated EpiPen prices in major global markets, compiled by World Population Review and converted to U.S. dollars as of August 2023.
Why are U.S. Prices so High?
The U.S. stands out as the most expensive market for EpiPens, despite over 1 million Americans having epinephrine prescriptions. After Mylan (now part of Pfizer) acquired the rights to produce EpiPens in the U.S. in 2007, the cost of a two-pack skyrocketed to $600, up from about $60.
| Country | Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 300* |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 98 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 85 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 76 |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | 66 |
| 🇬🇧 UK | 61 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 30 |
*Per unit cost. Commonly sold as a two-pack, meaning total cost is equal to $600
Former Mylan CEO Heather Bresch defended the price hikes to Congress, citing minimal profit margins. Mylan eventually settled with the U.S. government for a nine-figure sum.
Notably, EpiPens are available at a fraction of the cost in other developed countries like Japan, Germany, and Canada.
Making EpiPens More Affordable
Efforts to improve EpiPen affordability are underway in several U.S. states. For instance, the Colorado House approved a $60 price cap on epinephrine, now under review by the state Senate.
Similar measures in Rhode Island, Delaware, Missouri, and Vermont aim to ensure insurance coverage for epinephrine, which is not currently mandatory, although most health plans cover it.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees