Culture
Mapped: The Most Common Illicit Drugs in the World
How to Use: The below maps will transition automatically. To pause, move your cursor on the image. Arrows on left/right navigate.
Mapped: The Most Common Illicit Drugs in the World
Despite strict prohibitory laws around much of the world, many common illicit drugs still see widespread use.
Humans have a storied and complicated relationship with drugs. Defined as chemical substances that cause a change in our physiology or psychology, many drugs are taken medicinally or accepted culturally, like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol.
But many drugs—including medicines and non-medicinal substances taken as drugs—are taken recreationally and can be abused. Each country and people have their own relationship to drugs, with some embracing the use of specific substances while others shun them outright.
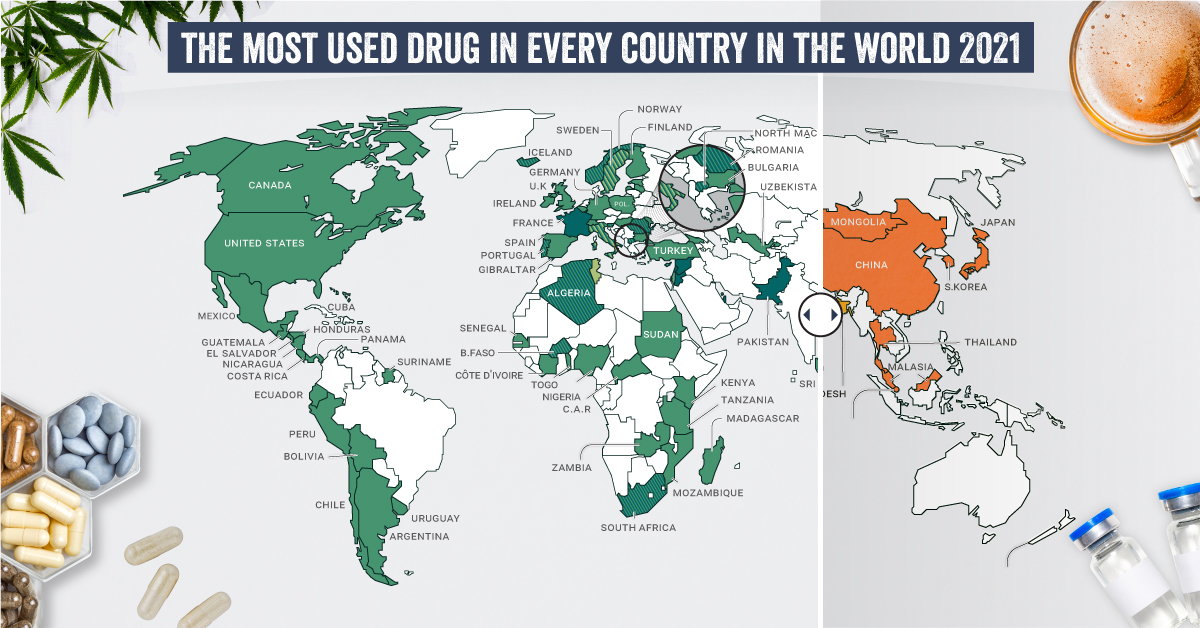
What are the most common drugs that are considered generally illicit in different parts of the world? Today’s graphics use data from the UN’s World Drug Report 2021 to highlight the most prevalent drug used in each country.
What Types of Common Drugs Are Tracked?
The World Drug Report looks explicitly at the supply and demand of the international illegal drug market, not including commonly legal substances like caffeine and alcohol.
Drugs are grouped by class and type, with six main types of drugs found as the most prevalent drugs worldwide.
- Cannabis*: Drugs derived from cannabis, including hemp. This category includes marijuana (dried flowers), hashish (resin), and other for various other parts of the plant or derived oils.
- Cocaine: Drugs derived from the leaves of coca plants. Labeled as either cocaine salts for powder form or crack for cocaine processed with baking soda and water into rock form.
- Opioids: Includes opiates which are derived directly from the opium poppy plant, including morphine, codeine, and heroin, as well as synthetic alkaloids.
- Amphetamine-type Stimulants (ATS): Amphetamine and drugs derived from amphetamine, including meth (also known as speed), MDMA, and ecstasy.
- Sedatives and Tranquilizers: Includes other drugs whose main purpose is to reduce energy, excitement, or anxiety, as well as drugs used primarily to initiate or help with sleep (also called hypnotics).
- Solvents and Inhalants: Gases or chemicals that can cause intoxication but are not intended to be drugs, including fuels, glues, and other industrial substances.
The report also tracked the prevalence of hallucinogens—psychoactive drugs which strongly affect the mind and cause a “trip”—but no hallucinogens ranked as the most prevalent drug in any one country.
*Editor’s note: Recreational cannabis is legal in five countries, and some non-federal jurisdictions (i.e. states). However, in the context of this report, it was included because it is still widely illicit in most countries globally.
The Most Prevalent Drug in Each Country
According to the report, 275 million people used drugs worldwide in 2020. Between the ages of 15–64, around 5.5% of the global population used drugs at least once.
Many countries grouped different types of the same drug class together, and a few like Saudi Arabia and North Macedonia had multiple different drug types listed as the most prevalent.
But across the board, cannabis was the most commonly prevalent drug used in 107 listed countries and territories:
| Country or territory | Most Prevalent Drug(s) |
|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Heroin, opium |
| Albania | Sedatives and tranquillizers (general) |
| Algeria | Cannabis (general) |
| Argentina | Cannabis (herb) |
| Australia | Cannabis (general) |
| Azerbaijan | Heroin |
| Bahamas | Cannabis (herb) |
| Bahrain | Cannabis (general) |
| Bangladesh | Amphetamine |
| Belarus | Opium |
| Belgium | Cannabis (herb) |
| Bolivia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Brunei | Cannabis (herb) |
| Bulgaria | Cannabis (herb) |
| Burkina Faso | Cannabis (general) |
| Canada | Cannabis (herb) |
| Central African Republic | Cannabis (herb) |
| Chile | Cannabis (herb) |
| China | Methamphetamine |
| Costa Rica | Cannabis (herb) |
| Côte d'Ivoire | Cannabis (herb) |
| Croatia | Heroin |
| Cyprus | Cannabis (general) |
| Czech Republic | Benzodiazepines |
| Dominican Republic | Cocaine (powder) |
| Ecuador | Cannabis (herb) |
| El Salvador | Cannabis (herb) |
| Estonia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Finland | Cannabis (herb) |
| France | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Georgia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Germany | Cannabis (herb) |
| Gibraltar | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Greece | Solvents and inhalants (general) |
| Guatemala | Cannabis (herb) |
| Honduras | Cannabis (herb) |
| Hong Kong | Heroin, opium, opioids |
| Hungary | Cannabis (herb) |
| Iceland | Cannabis (general) |
| India | Heroin |
| Indonesia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Iran | Opium |
| Ireland | Cannabis (herb) |
| Israel | Cannabis (herb) |
| Italy | Cannabis (general) |
| Japan | Methamphetamine |
| Jordan | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Kenya | Cannabis (herb) |
| Latvia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Lebanon | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Liechtenstein | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Lithuania | Sedatives and tranquillizers (general) |
| Luxembourg | Cannabis (general) |
| Macao | Methamphetamine |
| Madagascar | Cannabis (herb) |
| Malaysia | Methamphetamine |
| Malta | Heroin |
| Mexico | Cannabis (herb) |
| Moldova | Cannabis (herb) |
| Mongolia | Methamphetamine |
| Mozambique | Cannabis (herb) |
| Myanmar | Heroin |
| Netherlands | Benzodiazepines |
| New Zealand | Methamphetamine, solvent and inhalants |
| Nicaragua | Cannabis (herb) |
| Nigeria | Cannabis (herb) |
| North Macedonia | Multiple types |
| Norway | Cannabis (general) |
| Oman | Opium |
| Pakistan | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Panama | Cannabis (herb) |
| Peru | Cannabis (herb) |
| Philippines | Cannabis (herb) |
| Poland | Cannabis (herb) |
| Portugal | Cannabis (general) |
| Qatar | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Romania | Cannabis (general) |
| Saudi Arabia | Multiple types |
| Senegal | Cannabis (herb) |
| Serbia | Benzodiazepines |
| Singapore | Methamphetamine |
| Slovenia | Cannabis (general) |
| South Africa | Cannabis (general) |
| South Korea | Methamphetamine |
| Spain | Cannabis (herb) |
| Sri Lanka | Cannabis (herb) |
| Sudan | Cannabis (herb) |
| Suriname | Cannabis (herb) |
| Sweden | Cannabis (general) |
| Switzerland | Cannabis (herb) |
| Syrian Arab Republic | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Tajikistan | Heroin, opium |
| Tanzania | Cannabis (herb) |
| Thailand | Methamphetamine |
| Togo | Cannabis (herb) |
| Trinidad and Tobago | Cocaine (crack) |
| Tunisia | Cannabis (general) |
| Turkey | Cannabis (herb) |
| Turkmenistan | Opium |
| U.S. | Cannabis (herb) |
| UK | Cannabis (herb) |
| Ukraine | Opioids |
| Uruguay | Cannabis (herb) |
| Uzbekistan | Cannabis (herb) |
| Venezuela | Benzodiazepines |
| Vietnam | Heroin |
| Zambia | Cannabis (herb) |
How prevalent is cannabis worldwide? 72 locations or more than two-thirds of those reporting listed cannabis as the most prevalent drug.
Unsurprisingly these include countries that have legalized recreational cannabis: Canada, Georgia, Mexico, South Africa, and Uruguay.
How Common Are Opioids and Other Drugs?
Though the global prevalence of cannabis is unsurprising, especially as it becomes legalized and accepted in more countries, other drugs also have strong footholds.
Opioids (14 locations) were the most prevalent drugs in the Middle-East, South and Central Asia, including in India and Iran. Notably, Afghanistan is the world’s largest producer of opium, supplying more than 90% of illicit heroin globally.
Amphetamine-type drugs (9 locations) were the third-most common drugs overall, mainly in East Asia. Methamphetamine was the reported most prevalent drug in China, South Korea, and Japan, while amphetamine was only the most common drug in Bangladesh.
However, it’s important to note that illicit drug usage is tough to track. Asian countries where cannabis is less frequently found (or reported) might understate its usage. At the same time, the opioid epidemic in the U.S. and Canada reflects high opioid usage in the West.
As some drugs become more widespread and others face a renewed “war,” the landscape is certain to shift over the next few years.
Brands
How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.

How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
One would be hard-pressed to find a company that has never changed its logo. Granted, some brands—like Rolex, IBM, and Coca-Cola—tend to just have more minimalistic updates. But other companies undergo an entire identity change, thus necessitating a full overhaul.
In this graphic, we visualized the evolution of prominent tech companies’ logos over time. All of these brands ranked highly in a Q1 2024 YouGov study of America’s most famous tech brands. The logo changes are sourced from 1000logos.net.
How Many Times Has Google Changed Its Logo?
Google and Facebook share a 98% fame rating according to YouGov. But while Facebook’s rise was captured in The Social Network (2010), Google’s history tends to be a little less lionized in popular culture.
For example, Google was initially called “Backrub” because it analyzed “back links” to understand how important a website was. Since its founding, Google has undergone eight logo changes, finally settling on its current one in 2015.
| Company | Number of Logo Changes |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| HP | 8 |
| Amazon | 6 |
| Microsoft | 6 |
| Samsung | 6 |
| Apple | 5* |
Note: *Includes color changes. Source: 1000Logos.net
Another fun origin story is Microsoft, which started off as Traf-O-Data, a traffic counter reading company that generated reports for traffic engineers. By 1975, the company was renamed. But it wasn’t until 2012 that Microsoft put the iconic Windows logo—still the most popular desktop operating system—alongside its name.
And then there’s Samsung, which started as a grocery trading store in 1938. Its pivot to electronics started in the 1970s with black and white television sets. For 55 years, the company kept some form of stars from its first logo, until 1993, when the iconic encircled blue Samsung logo debuted.
Finally, Apple’s first logo in 1976 featured Isaac Newton reading under a tree—moments before an apple fell on his head. Two years later, the iconic bitten apple logo would be designed at Steve Jobs’ behest, and it would take another two decades for it to go monochrome.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001