Misc
The Psychology Behind Logo and Color Choice
Some professionals scoff at the importance of branding in business.
For many investors and analysts, this area of marketing seems fluffy and intangible, which makes it very hard to measure any potential benefits. While it’s true that quantifying intangibles is not always easy or accurate, it doesn’t mean that branding has no value to begin with.
In this way, branding may be comparable to the concept of “leadership” in sports. Athletes like Mark Messier, Michael Jordan, Ray Lewis, Mia Hamm, and Steve Yzerman weren’t just good players from a technical perspective, but they also had intangible qualities that elevated the performances of their respective teams. While it is hard to measure work ethic, passion, leadership, drive, and loyalty, or how these qualities rub off on teammates, it’s still clear to many coaches and managers that intangibles help win championships.
Like leadership, we know good branding when we see it, even though it can be tough to quantify. Coca-Cola is recognizable and nostalgic, while the Starbucks name may be the difference in choosing their cafe over an average-looking coffee shop in an unfamiliar neighborhood.
The Psychology Behind Logo and Color Choice
Logo and color choice are two of the most important parts of creating a quality brand. Today we have two infographics from The Logo Company. One shows the five major forms of logos, while the other dives into the meaning behind color choices.
We’ll add some commentary on the implications of logo and color choice in of the areas below.

Companies cannot control the actual emotional responses to their brand on a personal level, but they can do their best to control shape, style, and color to at least guide these interpretations.
In fact, our brains are hardwired to learn and memorize new shapes, so the way a logo is presented can have a big impact on its effectiveness. The five major types of logo forms – brand marks, word marks, letter marks, combo marks, or emblems – are a way to control shape and identity.
Word marks, for example, have the name of the company in the logo itself without any imagery. This helps achieve brand recognition, while the lack of accompanying graphics may convey a sense of sophistication to consumers.
Using just initials in a letter mark can show even more sophistication. Leading luxury consumer brands such as Louis Vuitton or Chanel have used this with much success.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, some companies use just a brand mark to convey a sense of universality. Even though “Shell”, “Apple”, and “Nike” are not spelled out in name, their famous icons are known throughout the world. The Nike swoosh conveys movement, while the World Wildlife Fund can tell a powerful story just by using the famous panda in its brand mark.
Target is another instantly recognizable brand mark. The simplicity and circular shape are key elements to the design, but the bright red color also plays a role. Here’s a guide to how color can evoke different emotions in consumers:

One step further, here is another version with a little more nuance, from Web Designer Depot.

Of course, colors can and do get interpreted in different ways. However, they can also have the power to represent broad ideas for cultural or evolutionary reasons.
In a previous post on the psychology of color, we dive into this in more depth. For example, it explains why the color red stimulates appetite, or why blue brings a sense of productivity and efficiency.
Politics
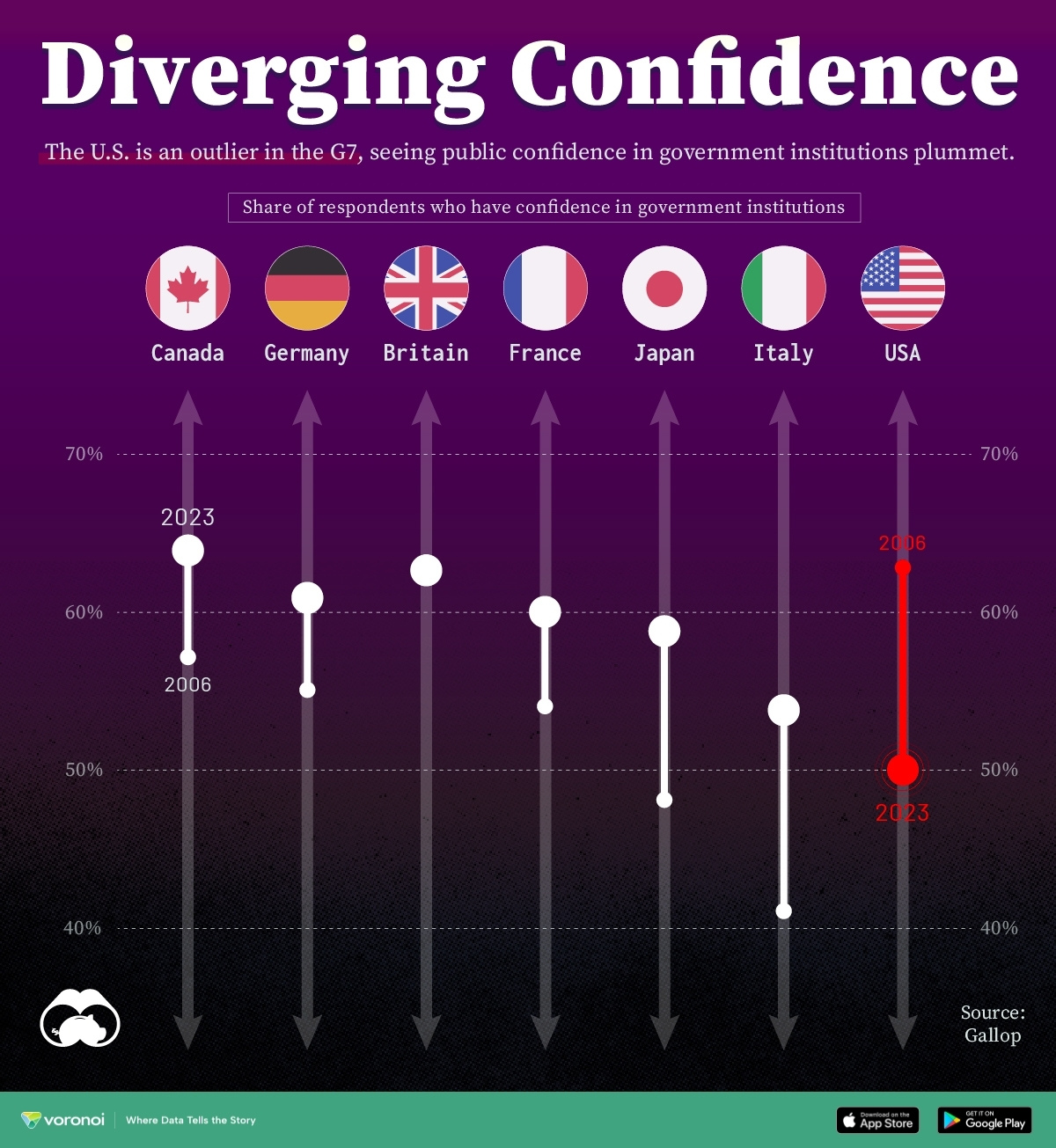
Charted: Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
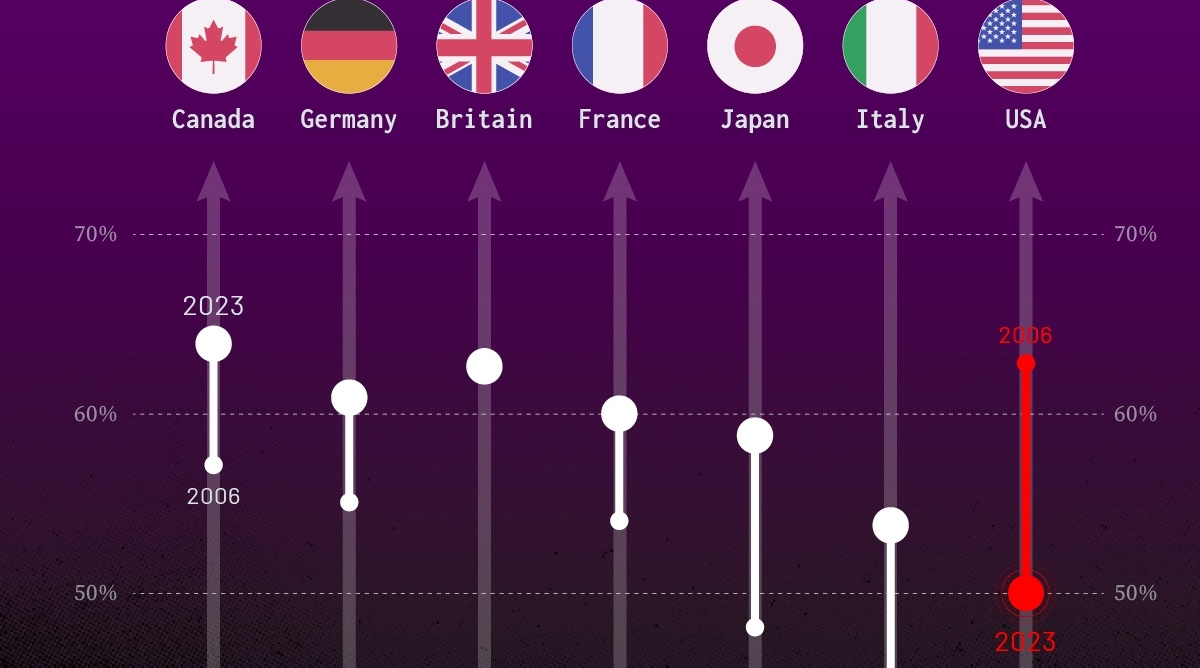
How much do you trust the government and its various institutions? We look at data for G7 countries for the time period of 2006-2023.
Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
How much do you trust the government, and its various institutions?
It’s likely that your level of confidence probably depends on a wide range of factors, such as perceived competency, historical context, economic performance, accountability, social cohesion, and transparency.
And for these same reasons, trust levels in government institutions also change all the time, even in the world’s most developed countries: the G7.
Confidence in Government by G7 Countries (2006-2023)
This chart looks at the changes in trust in government institutions between the years 2006 and 2023, based on data from a multi-country Gallup poll.
Specifically, this dataset aggregates confidence in multiple national institutions, including the military, the judicial system, the national government, and the integrity of the electoral system.
| Country | Confidence (2006) | Confidence (2023) | Change (p.p.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | 57% | 64% | +7 |
| Britain | 63% | 63% | +0 |
| Germany | 55% | 61% | +6 |
| France | 54% | 60% | +6 |
| Japan | 48% | 59% | +11 |
| Italy | 41% | 54% | +13 |
| United States | 63% | 50% | -13 |
What’s interesting here is that in the G7, a group of the world’s most developed economies, there is only one country bucking the general trend: the United States.
Across most G7 countries, confidence in institutions has either improved or stayed the same between 2006 and 2023. The largest percentage point (p.p.) increases occur in Italy and Japan, which saw +13 p.p. and +11 p.p. increases in trust over the time period.
In the U.S., however, confidence in government institutions has fallen by 13 p.p. over the years. What happened?
Key Figures on U.S. Trust in Institutions
In 2006, the U.S. was tied with the UK as having the highest confidence in government institutions, at 63%.
But here’s where the scores stand in 2023, across various institutions:
| 🇺🇸 Institutions | Confidence (2023) |
|---|---|
| Military | 81% |
| Judiciary | 42% |
| National Government | 30% |
| Elections | 44% |
| Overall | 49% |
Based on this data, it’s clear that the U.S. lags behind in three key indicators: confidence in the national government, confidence in the justice system, and confidence in fair elections. It ranked in last place for each indicator in the G7.
One other data point that stands out: despite leading the world in military spending, the U.S. is only the third most confident in its military in the G7. It lags behind France (86%) and the United Kingdom (83%).
-

 Wealth6 days ago
Wealth6 days agoCharted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Uranium2 weeks ago
Uranium2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Debt2 weeks ago
Debt2 weeks agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands1 week ago
Brands1 week agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time