Misc
Mapped: The Ancient Seven Wonders of the World
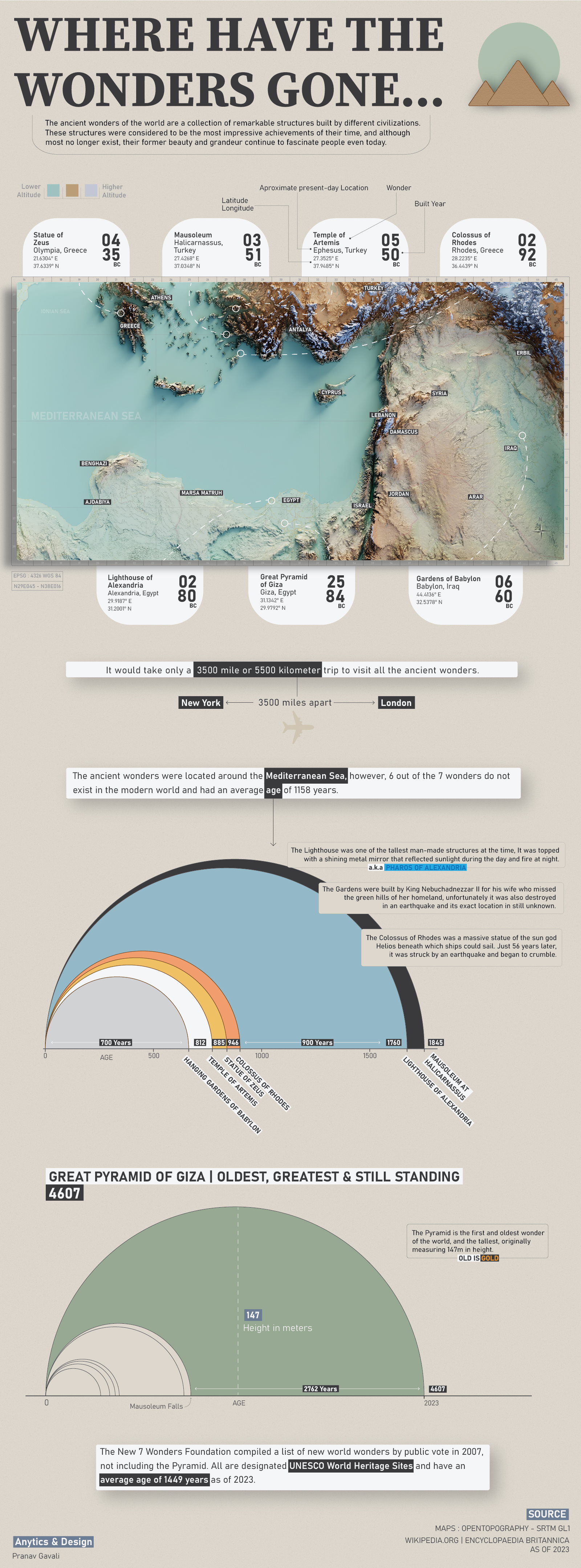
The Ancient Seven Wonders of the World
From skyscrapers that defy gravity to tunnels below the sea, mankind’s civil engineering feats are all around us.
The complexity of older structures like the Great Wall of China, Chichén Itzá, and the Taj Mahal continue to captivate and fascinate visitors today, but it’s worth noting that “wonders” such as these are not a modern concept.
As far back as the 2nd century BCE, ancient guide books and poems were being written by Greeks that had toured the extent of Alexander the Great’s kingdoms, giving us the original “seven wonders of the world” from the Hellenistic world they knew at the time.
This graphic by Pranav Gavali looks at the original ancient seven wonders, including their modern-day locations and features, using data from Encyclopedia Britannica and Wikipedia.
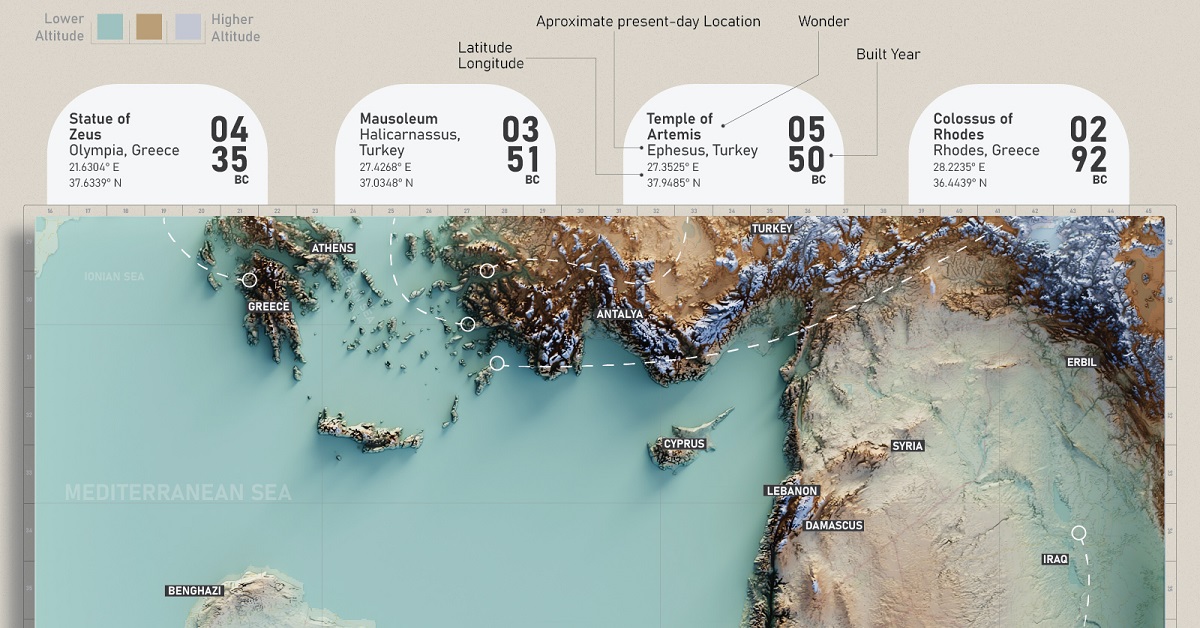
Where Were the Seven Wonder of the World?
The original seven wonders of the world were built around the Mediterranean Sea and in the Middle East over a span of 3,000 years, all before the Common Era.
| Wonders | Modern Location | Year Created |
|---|---|---|
| Great Pyramid of Giza | Egypt | 2,584 BCE |
| Hanging Gardens of Babylon | Iraq | 600 BCE |
| Temple of Artemis at Ephesus | Turkey | 550 BCE |
| Statue of Zeus at Olympia | Greece | 435 BCE |
| Mausoleum at Halicarnassus | Turkey | 351 BCE |
| Colossus of Rhodes | Greece | 292 BCE |
| Lighthouse of Alexandria | Egypt | 280 BCE |
From the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt to the Colossus in Rhodes, each wonder represents a different aspect of human ambition and ingenuity.
And while only one of the wonders still stands today, their legacy lives on. Let’s explore the stories behind the seven wonders of the world:
1. The Great Pyramid of Giza
— 2,584 BCE
The ancient Egyptians believed that death was a pitstop on the way to a new life, and royals were buried in massive royal tombs.
This 4,500-year-old pyramid was one such tomb, built for Pharaoh Khufu. Standing tall at an initial 147 meters (139 meters today), this monument is the oldest and largest of the seven wonders of the world. It is also the only ancient wonder still standing.
2. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon
— 600 BCE
The Gardens of Babylon are believed to have provided a stunning oasis in the middle of the desert in 600 BCE, with tiered gardens of trees, shrubs, and vines.
The common belief is that King Nebuchadnezzar II built these gardens for his wife Amytis, who missed the lush hills of her homeland Media (northwest Iran).
However, their existence has been disputed by historians which have struggled to find concrete archaeological evidence. They are commonly believed to have been destroyed by an earthquake after 700 years, making them the shortest-lived ancient wonder.
3. The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus
— 550 BCE
Built in the 6th century BCE, this temple was dedicated to the Greek goddess Artemis. Even larger than a present-day football field and with more than 127 columns, it was the first all-marble temple ever built in Greece.
It was destroyed and rebuilt several times, with the third phase listed as the grandest world wonder. It was finally closed and destroyed around the start of the 5th century.
4. The Statue of Zeus at Olympia
— 435 BCE
In 435 BC, Greek sculptor Phidias was tasked with creating an enormous statue of Zeus in Olympia, the site of Temple of Zeus and the ancient Olympic Games.
The statue was seated on a throne made from ivory, gold, and wood, holding a massive scepter supporting an eagle in one hand and a small statue of Nike, the goddess of victory, in the other. It was believed to have been destroyed in the times of the Romans around 400 CE, but whether that was in a fire or if it were broken into pieces and sent to different cities, is unknown.
5. The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
— 351 BCE
Much like today’s Alexandria or Babylon, Halicarnassus was a thriving ancient city and capital of Caria. Its most famous ruler was Mausolus, the king of Caria, and when building the capital he also commissioned an elaborate above-ground tomb for himself.
Built in 351 BCE, the Mausoleum was over 45 meters tall and adorned with stunning sculptures and intricate carvings. Though it was destroyed by many local earthquakes between the 12th and 15th centuries, its legacy lives on as the word mausoleum went on to define stately, magnificent tombs.
6. The Colossus of Rhodes
— 292 BCE
Back in 304 BCE, Greece’s harbor city of Rhodes successfully resisted a year-long siege, and its people celebrated by using abandoned weaponry to create an enormous statue of the ancient Greek god of the Sun, Helios.
It stood over the port entry to the city, and was about the same height (33 meters) as the Statue of Liberty from feet to crown. And though the Colossus technically fell after a 226 BCE earthquake, it lay on the ground and was still impressive for another 800 years.
7. The Lighthouse of Alexandria
— 280 BCE
Lighthouses serve as beacons for all those at sea, and the Lighthouse of Alexandria was no different. However, its impressive architectural design of 100 meters of sandstone and limestone was far from simple, being one of the world’s tallest man-made structures for centuries.
Built during the time of pharaoh Ptolemy II Philadelphus on the small island of Pharos, it was said to have been crowned with a mirror that reflected sunlight during the day and fire at night, making it visible from up to 50 km away. Though the lighthouse was damaged in earthquakes and survived until 1480, “pharos” became the root word for lighthouse in Greek and many Romance languages.
The New Seven Wonders of the World
To reflect the continued usage and understanding of the term “seven wonders of the world,” the New 7 Wonders Foundation started a campaign to choose seven new wonders in 2001.
After a large and lengthy campaign, with some countries advocating for statues and others downplaying the new list, the final list of wonders was announced in 2007:
| New Wonders | Location | Year Created |
|---|---|---|
| Great Wall of China | China | 700 BCE |
| Petra | Jordan | 312 BCE |
| Colosseum | Italy | 80 CE |
| Chichén Itzá | Mexico | 600 CE |
| Machu Picchu | Peru | 1450 CE |
| Taj Mahal | India | 1643 CE |
| Christ the Redeemer | Brazil | 1931 CE |
And though it was not included as an option as an attempt to find “new” wonders, the Great Pyramid of Giza was still granted honorary status as a world wonder.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Politics
Charted: Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
How much do you trust the government and its various institutions? We look at data for G7 countries for the time period of 2006-2023.
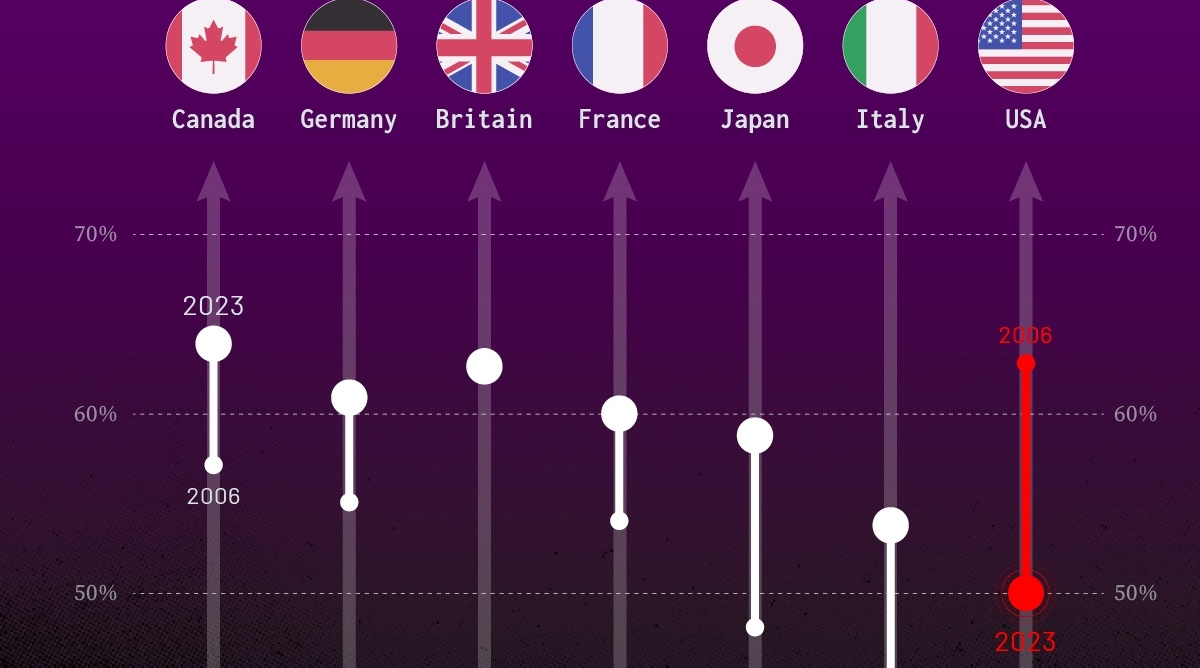
Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
How much do you trust the government, and its various institutions?
It’s likely that your level of confidence probably depends on a wide range of factors, such as perceived competency, historical context, economic performance, accountability, social cohesion, and transparency.
And for these same reasons, trust levels in government institutions also change all the time, even in the world’s most developed countries: the G7.
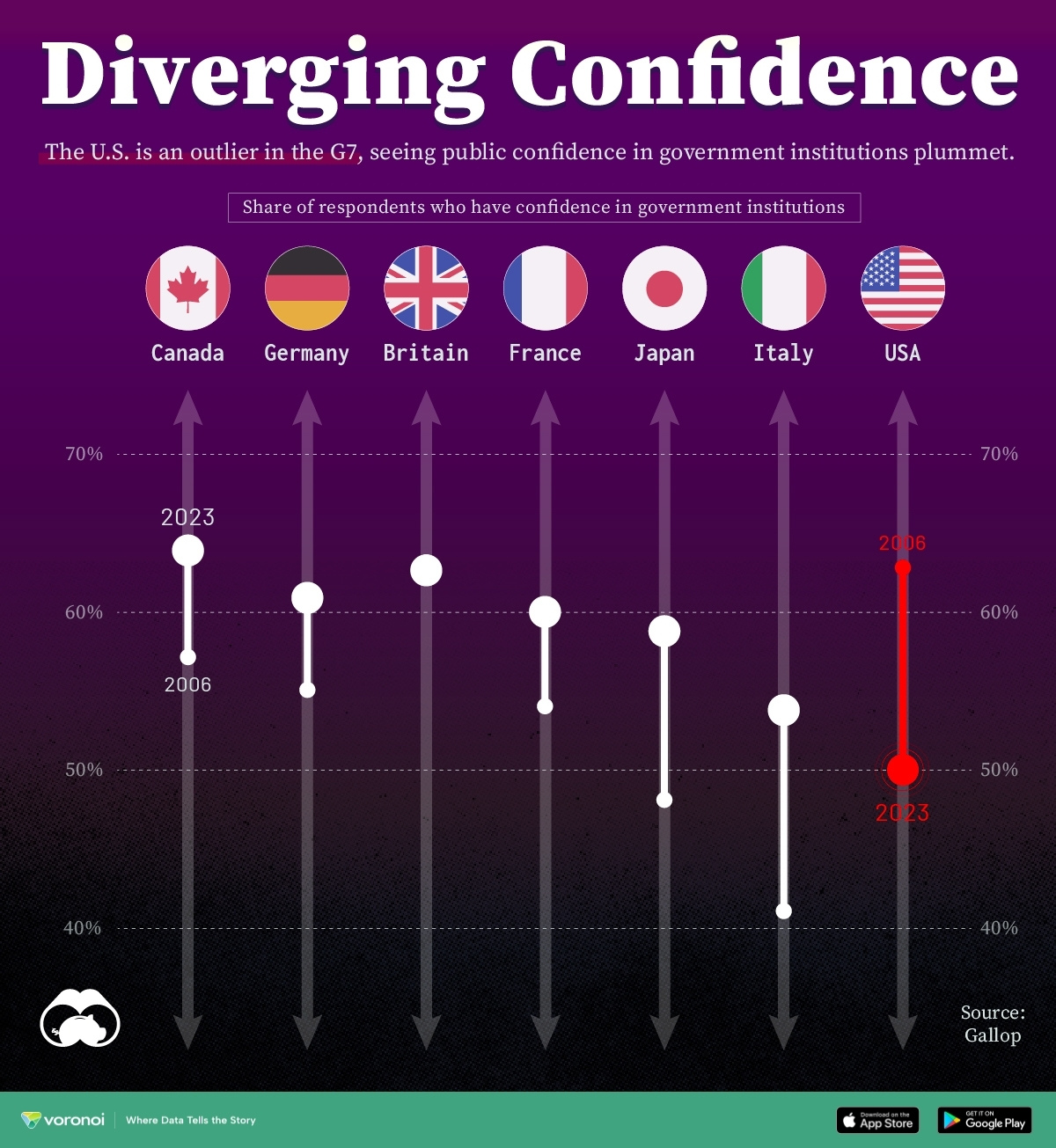
Confidence in Government by G7 Countries (2006-2023)
This chart looks at the changes in trust in government institutions between the years 2006 and 2023, based on data from a multi-country Gallup poll.
Specifically, this dataset aggregates confidence in multiple national institutions, including the military, the judicial system, the national government, and the integrity of the electoral system.
| Country | Confidence (2006) | Confidence (2023) | Change (p.p.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | 57% | 64% | +7 |
| Britain | 63% | 63% | +0 |
| Germany | 55% | 61% | +6 |
| France | 54% | 60% | +6 |
| Japan | 48% | 59% | +11 |
| Italy | 41% | 54% | +13 |
| United States | 63% | 50% | -13 |
What’s interesting here is that in the G7, a group of the world’s most developed economies, there is only one country bucking the general trend: the United States.
Across most G7 countries, confidence in institutions has either improved or stayed the same between 2006 and 2023. The largest percentage point (p.p.) increases occur in Italy and Japan, which saw +13 p.p. and +11 p.p. increases in trust over the time period.
In the U.S., however, confidence in government institutions has fallen by 13 p.p. over the years. What happened?
Key Figures on U.S. Trust in Institutions
In 2006, the U.S. was tied with the UK as having the highest confidence in government institutions, at 63%.
But here’s where the scores stand in 2023, across various institutions:
| 🇺🇸 Institutions | Confidence (2023) |
|---|---|
| Military | 81% |
| Judiciary | 42% |
| National Government | 30% |
| Elections | 44% |
| Overall | 49% |
Based on this data, it’s clear that the U.S. lags behind in three key indicators: confidence in the national government, confidence in the justice system, and confidence in fair elections. It ranked in last place for each indicator in the G7.
One other data point that stands out: despite leading the world in military spending, the U.S. is only the third most confident in its military in the G7. It lags behind France (86%) and the United Kingdom (83%).
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Uranium2 weeks ago
Uranium2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Debt2 weeks ago
Debt2 weeks agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-
 Culture2 weeks ago
Culture2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports