Energy
Visualizing the Range of Electric Cars vs. Gas-Powered Cars
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
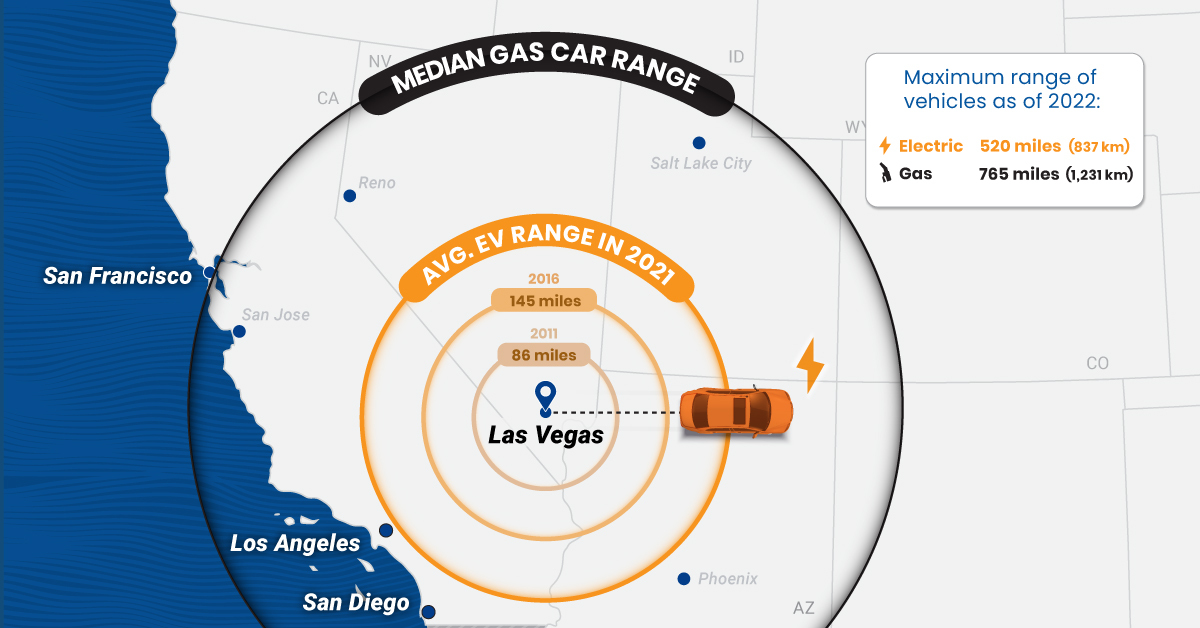
The Range of Electric Cars vs. Gas-Powered Cars
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on natural resource megatrends in your email every week.
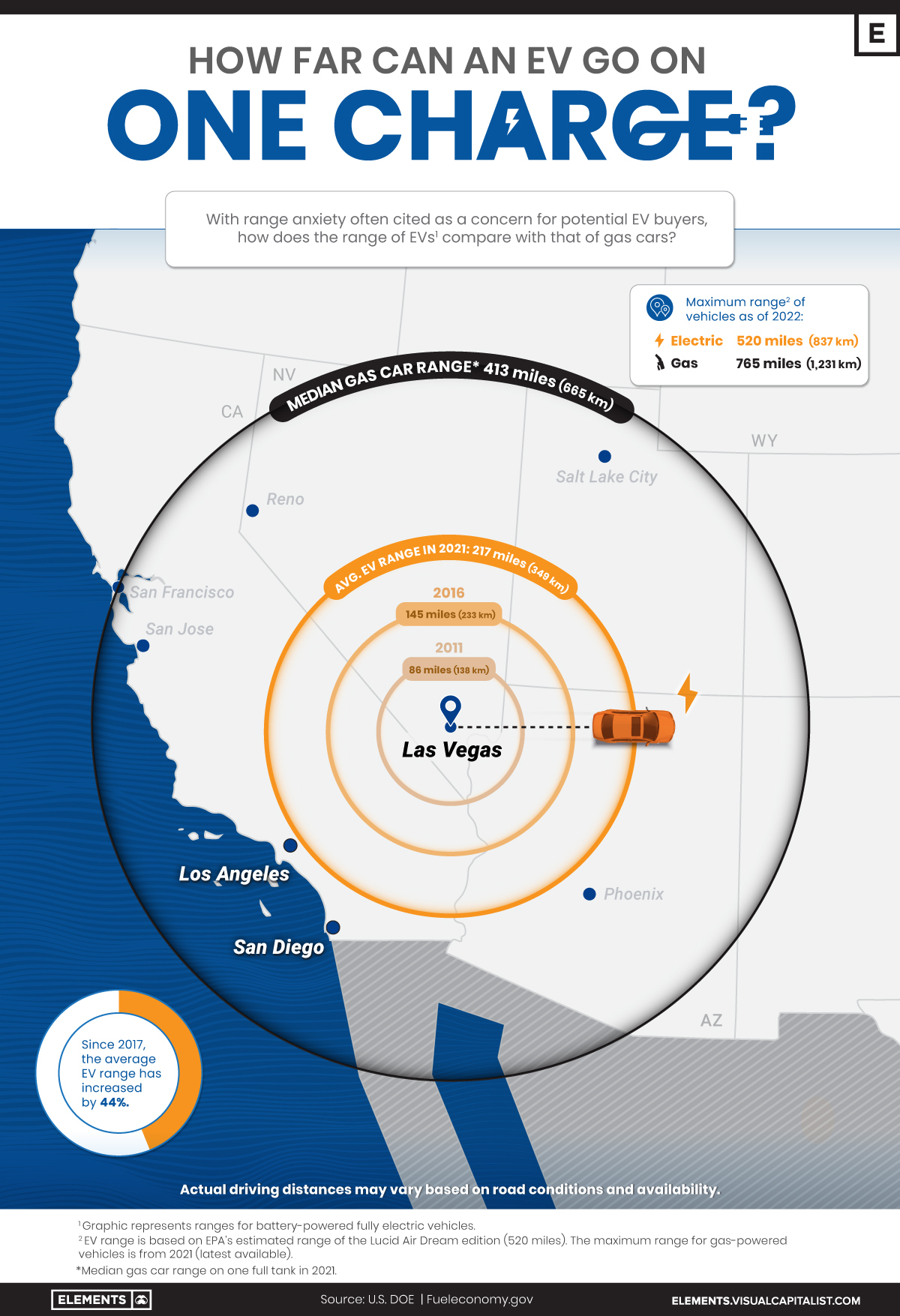
EV adoption has grown rapidly in recent years, but many prospective buyers still have doubts about electric car ranges.
In fact, 33% of new car buyers chose range anxiety—the concern about how far an EV can drive on a full charge—as their top inhibitor to purchasing electric cars in a survey conducted by EY.
So, how far can the average electric car go on one charge, and how does that compare with the typical range of gas-powered cars?
The Rise in EV Ranges
Thanks to improvements in battery technology, the average range of electric cars has more than doubled over the last decade, according to data from the International Energy Agency (IEA).
| Year | Avg. EV Range | Maximum EV Range |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 79 miles (127 km) | N/A |
| 2011 | 86 miles (138 km) | 94 miles (151 km) |
| 2012 | 99 miles (159 km) | 265 miles (426 km) |
| 2013 | 117 miles (188 km) | 265 miles (426 km) |
| 2014 | 130 miles (209 km) | 265 miles (426 km) |
| 2015 | 131 miles (211 km) | 270 miles (435 km) |
| 2016 | 145 miles (233 km) | 315 miles (507 km) |
| 2017 | 151 miles (243 km) | 335 miles (539 km) |
| 2018 | 189 miles (304 km) | 335 miles (539 km) |
| 2019 | 209 miles (336 km) | 370 miles (595 km) |
| 2020 | 210 miles (338 km) | 402 miles (647 km) |
| 2021 | 217 miles (349 km) | 520 miles* (837 km) |
*Max range for EVs offered in the United States.
Source: IEA, U.S. DOE
As of 2021, the average battery-powered EV could travel 217 miles (349 km) on a single charge. It represents a 44% increase from 151 miles (243 km) in 2017 and a 152% increase relative to a decade ago.
Despite the steady growth, EVs still fall short when compared to gas-powered cars. For example, in 2021, the median gas car range (on one full tank) in the U.S. was around 413 miles (664 km)—nearly double what the average EV would cover.
As automakers roll out new models, electric car ranges are likely to continue increasing and could soon match those of their gas-powered counterparts. It’s important to note that EV ranges can change depending on external conditions.
What Affects EV Ranges?
In theory, EV ranges depend on battery capacity and motor efficiency, but real-world results can vary based on several factors:
- Weather: At temperatures below 20℉ (-6.7℃), EVs can lose around 12% of their range, rising to 41% if heating is turned on inside the vehicle.
- Operating Conditions: Thanks to regenerative braking, EVs may extend their maximum range during city driving.
- Speed: When driving at high speeds, EV motors spin faster at a less efficient rate. This may result in range loss.
On the contrary, when driven at optimal temperatures of about 70℉ (21.5℃), EVs can exceed their rated range, according to an analysis by Geotab.
The 10 Longest-Range Electric Cars in America
Here are the 10 longest-range electric cars available in the U.S. as of 2022, based on Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) range estimates:
| Car | Range On One Full Charge | Estimated Base Price |
|---|---|---|
| Lucid Air | 520 miles (837 km) | $170,500 |
| Tesla Model S | 405 miles (652 km) | $106,190 |
| Tesla Model 3 | 358 miles (576 km) | $59,440 |
| Mercedes EQS | 350 miles (563 km) | $103,360 |
| Tesla Model X | 348 miles (560 km) | $122,440 |
| Tesla Model Y | 330 miles (531 km) | $67,440 |
| Hummer EV | 329 miles (529 km) | $110,295 |
| BMW iX | 324 miles (521 km) | $84,195 |
| Ford F-150 Lightning | 320 miles (515 km) | $74,169 |
| Rivian R1S | 316 miles (509 km) | $70,000 |
Source: Car and Driver
The top-spec Lucid Air offers the highest range of any EV with a price tag of $170,500, followed by the Tesla Model S. But the Tesla Model 3 offers the most bang for your buck if range and price are the only two factors in consideration.
Energy
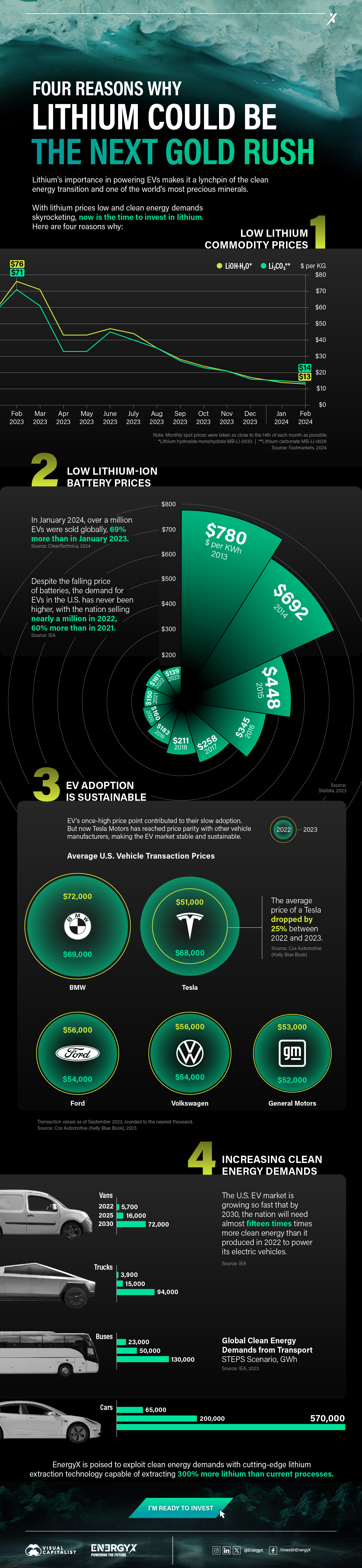
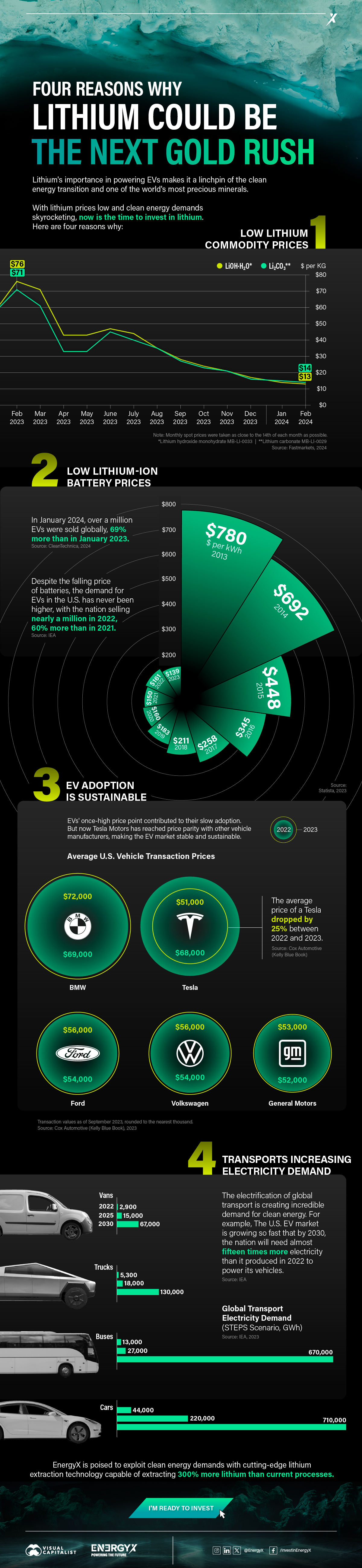
Charted: 4 Reasons Why Lithium Could Be the Next Gold Rush
Visual Capitalist has partnered with EnergyX to show why drops in prices and growing demand may make now the right time to invest in lithium.
4 Reasons Why You Should Invest in Lithium
Lithium’s importance in powering EVs makes it a linchpin of the clean energy transition and one of the world’s most precious minerals.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnered with EnergyX to explore why now may be the time to invest in lithium.
1. Lithium Prices Have Dropped
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating an investment is ensuring that the asset’s value is higher than its price would indicate. Lithium is integral to powering EVs, and, prices have fallen fast over the last year:
| Date | LiOH·H₂O* | Li₂CO₃** |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2023 | $76 | $71 |
| March 2023 | $71 | $61 |
| Apr 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| May 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| June 2023 | $47 | $45 |
| July 2023 | $44 | $40 |
| Aug 2023 | $35 | $35 |
| Sept 2023 | $28 | $27 |
| Oct 2023 | $24 | $23 |
| Nov 2023 | $21 | $21 |
| Dec 2023 | $17 | $16 |
| Jan 2024 | $14 | $15 |
| Feb 2024 | $13 | $14 |
Note: Monthly spot prices were taken as close to the 14th of each month as possible.
*Lithium hydroxide monohydrate MB-LI-0033
**Lithium carbonate MB-LI-0029
2. Lithium-Ion Battery Prices Are Also Falling
The drop in lithium prices is just one reason to invest in the metal. Increasing economies of scale, coupled with low commodity prices, have caused the cost of lithium-ion batteries to drop significantly as well.
In fact, BNEF reports that between 2013 and 2023, the price of a Li-ion battery dropped by 82%.
| Year | Price per KWh |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $139 |
| 2022 | $161 |
| 2021 | $150 |
| 2020 | $160 |
| 2019 | $183 |
| 2018 | $211 |
| 2017 | $258 |
| 2016 | $345 |
| 2015 | $448 |
| 2014 | $692 |
| 2013 | $780 |

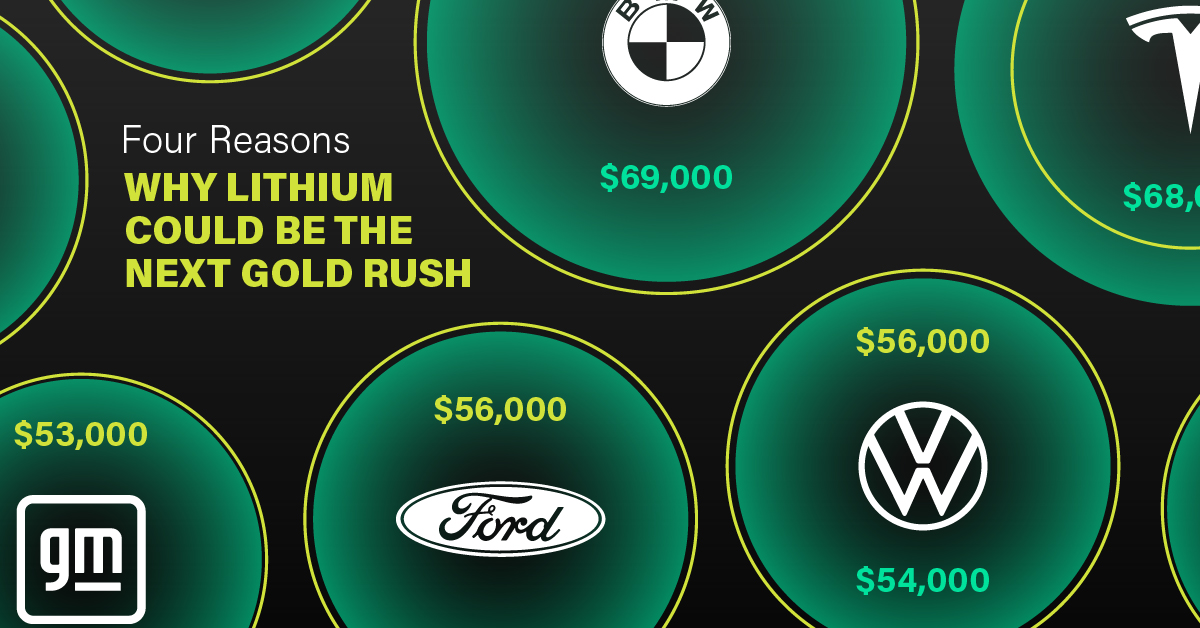
3. EV Adoption is Sustainable
One of the best reasons to invest in lithium is that EVs, one of the main drivers behind the demand for lithium, have reached a price point similar to that of traditional vehicle.
According to the Kelly Blue Book, Tesla’s average transaction price dropped by 25% between 2022 and 2023, bringing it in line with many other major manufacturers and showing that EVs are a realistic transport option from a consumer price perspective.
| Manufacturer | September 2022 | September 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| BMW | $69,000 | $72,000 |
| Ford | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| Volkswagon | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| General Motors | $52,000 | $53,000 |
| Tesla | $68,000 | $51,000 |
4. Electricity Demand in Transport is Growing
As EVs become an accessible transport option, there’s an investment opportunity in lithium. But possibly the best reason to invest in lithium is that the IEA reports global demand for the electricity in transport could grow dramatically by 2030:
| Transport Type | 2022 | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buses 🚌 | 23,000 GWh | 50,000 GWh | 130,000 GWh |
| Cars 🚙 | 65,000 GWh | 200,000 GWh | 570,000 GWh |
| Trucks 🛻 | 4,000 GWh | 15,000 GWh | 94,000 GWh |
| Vans 🚐 | 6,000 GWh | 16,000 GWh | 72,000 GWh |
The Lithium Investment Opportunity
Lithium presents a potentially classic investment opportunity. Lithium and battery prices have dropped significantly, and recently, EVs have reached a price point similar to other vehicles. By 2030, the demand for clean energy, especially in transport, will grow dramatically.
With prices dropping and demand skyrocketing, now is the time to invest in lithium.
EnergyX is poised to exploit lithium demand with cutting-edge lithium extraction technology capable of extracting 300% more lithium than current processes.

-

 Lithium4 days ago
Lithium4 days agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.
-

 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoThe World’s Biggest Oil Producers in 2023
Just three countries accounted for 40% of global oil production last year.
-
 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoHow Much Does the U.S. Depend on Russian Uranium?
Currently, Russia is the largest foreign supplier of nuclear power fuel to the U.S.
-
 Uranium2 months ago
Uranium2 months agoCharted: Global Uranium Reserves, by Country
We visualize the distribution of the world’s uranium reserves by country, with 3 countries accounting for more than half of total reserves.
-
 Energy3 months ago
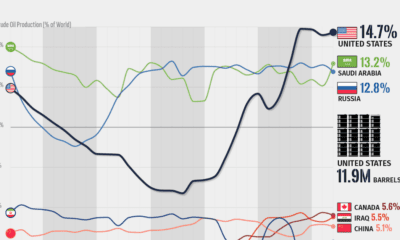
Energy3 months agoVisualizing the Rise of the U.S. as Top Crude Oil Producer
Over the last decade, the United States has established itself as the world’s top producer of crude oil, surpassing Saudi Arabia and Russia.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001