Markets
Shapes of Recovery: When Will the Global Economy Bounce Back?
The Shape of Economic Recovery, According to CEOs
Is the glass half full, or half empty?
Whenever the economy is put through the ringer, levels of optimism and pessimism about its potential recovery can vary greatly. The current state mid-pandemic is no exception.
This graphic first details the various shapes that economic recovery can take, and what they mean. We then dive into which of the four scenarios are perceived the most likely to occur, based on predictions made by CEOs from around the world.
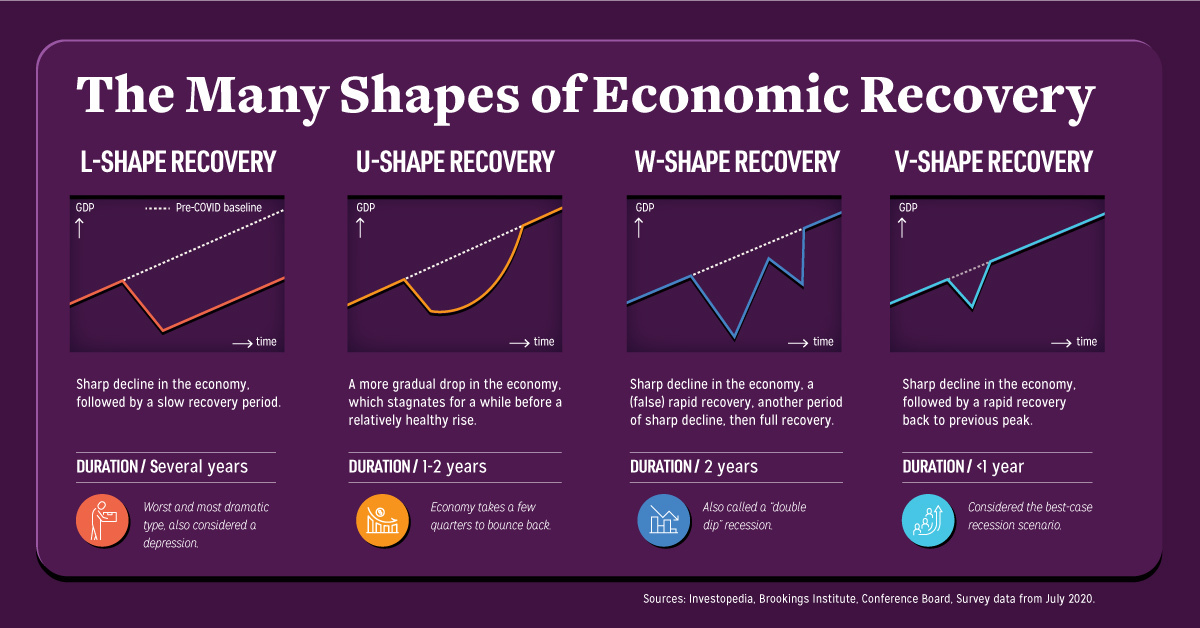
The ABCs of Economic Recovery
Economic recovery comes in four distinct shapes—L, U, W, and V. Here’s what each of these are characterized by, and how long they typically last.
- L-shape
This scenario exhibits a sharp decline in the economy, followed by a slow recovery period. It’s often punctuated by persistent unemployment, taking several years to recoup back to previous levels. - U-shape
Also referred to as the “Nike Swoosh” recovery, in this scenario the economy stagnates for a few quarters and up to two years, before experiencing a relatively healthy rise back to its previous peak. - W-shape
This scenario offers a tempting promise of recovery, dips back into a sharp decline, and then finally enters the full recovery period of up to two years. This is also known as a “double-dip recession“, similar to what was seen in the early 1980s. - V-shape
In this best-case scenario, the sharp decline in the economy is quickly and immediately followed by a rapid recovery back to its previous peak in less than a year, bolstered especially by economic measures and strong consumer spending.
Another scenario not covered here is the Z-shape, defined by a boom after pent-up demand. However, it doesn’t quite make the cut for the present pandemic situation, as it’s considered even more optimistic than a V-shaped recovery.
Depending on who you ask, the sentiments about a post-pandemic recovery differ greatly. So which of these potential scenarios are we really dealing with?
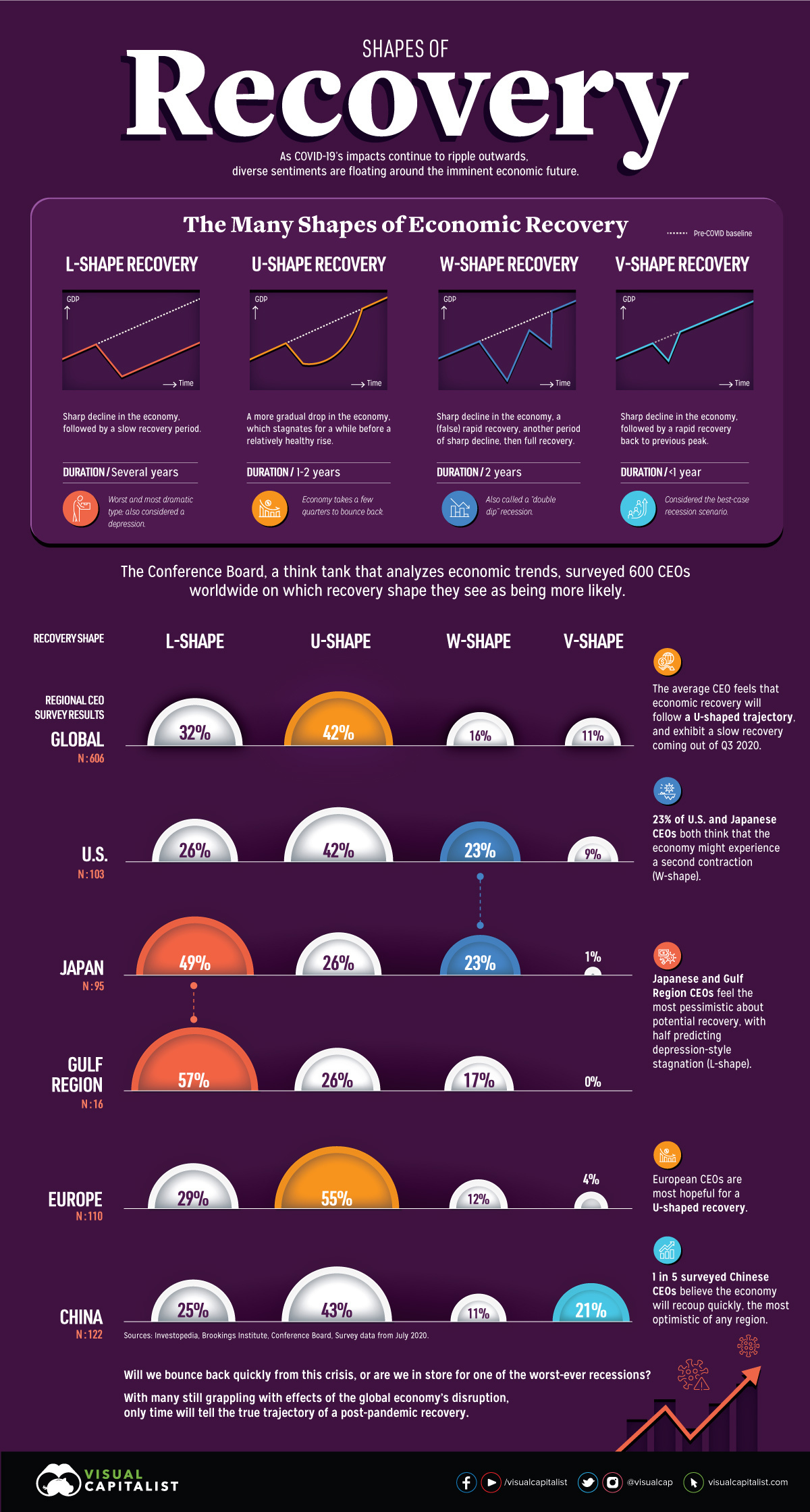
How CEOs Think The Economy Could Recover
The think tank The Conference Board surveyed over 600 CEOs worldwide, to uncover how they feel about the likelihood of each recovery shape playing out in the near future.
The average CEO felt that economic recovery will follow a U-shaped trajectory (42%), eventually exhibiting a slow recovery coming out of Q3 of 2020—a moderately optimistic view.
However, geography seems to play a part in these CEO estimates of how rapidly things might revert back to “normal”. Over half of European CEOs (55%) project a U-shaped recovery, which is significantly higher than the global average. This could be because recent COVID-19 hotspots have mostly shifted to other areas outside of the continent, such as the U.S., India, and Brazil.
Here’s how responses vary by region:
| Region | L-shape | U-shape | W-shape | V-shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global (N=606) | 32% | 42% | 16% | 11% |
| U.S. (N=103) | 26% | 42% | 23% | 9% |
| Europe (N=110) | 29% | 55% | 12% | 4% |
| China (N=122) | 25% | 43% | 11% | 21% |
| Japan (N=95) | 49% | 26% | 23% | 1% |
| Gulf Region (N=16) | 57% | 26% | 17% | - |
In the U.S. and Japan, 23% of CEOs expect a second contraction to occur, meaning that economic activity could undergo a W-shape recovery. Both countries have experienced quite the hit, but there are stark differences in their resultant unemployment rates—15% at its peak in the U.S., but a mere 2.6% in Japan.
In China, 21% of CEOs—or one in five—anticipate a quick, V-shaped recovery. This is the most optimistic outlook of any region, and with good reason. Although economic growth contracted by 6.8% in the first quarter, China has bounced back to a 3.2% growth rate in the second quarter.
Finally, Gulf Region CEOs feel the most pessimistic about potential economic recovery. In the face of an oil shock, 57% predict the economy will see an L-shaped recovery that could result in depression-style stagnation in years to come.
The Economic Recovery, According to Risk Analysts
At the end of the day, CEO opinions are all over the map on the potential shape of the economic recovery—and this variance likely stems from geography, cultural biases, and of course the status of their own individual countries and industries.
Despite this, portions of all cohorts saw some possibility of an extended and drawn-out recovery. Earlier in the year, risk analysts surveyed by the World Economic Forum had similar thoughts, projecting a prolonged recession as the top risk of the post-COVID fallout.
It remains to be seen whether this will ultimately indeed be the trajectory we’re in store for.
Markets
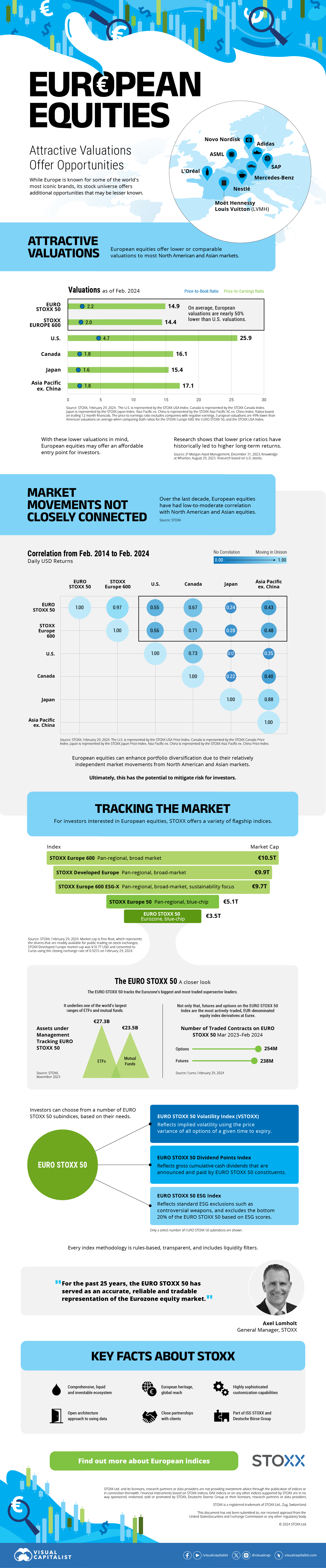
The European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
On average, the European stock market has valuations that are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations. But how can you access the market?
European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
Europe is known for some established brands, from L’Oréal to Louis Vuitton. However, the European stock market offers additional opportunities that may be lesser known.
The above infographic, sponsored by STOXX, outlines why investors may want to consider European stocks.
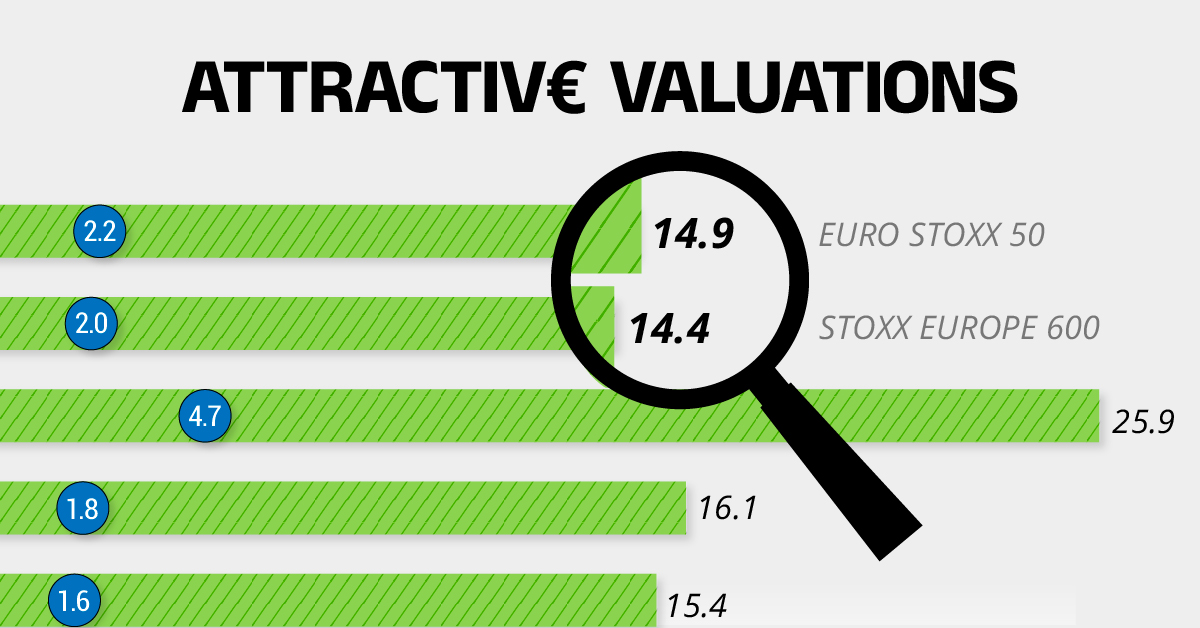
Attractive Valuations
Compared to most North American and Asian markets, European stocks offer lower or comparable valuations.
| Index | Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Price-to-Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 14.9 | 2.2 |
| STOXX Europe 600 | 14.4 | 2 |
| U.S. | 25.9 | 4.7 |
| Canada | 16.1 | 1.8 |
| Japan | 15.4 | 1.6 |
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 17.1 | 1.8 |
Data as of February 29, 2024. See graphic for full index names. Ratios based on trailing 12 month financials. The price to earnings ratio excludes companies with negative earnings.
On average, European valuations are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations, potentially offering an affordable entry point for investors.
Research also shows that lower price ratios have historically led to higher long-term returns.
Market Movements Not Closely Connected
Over the last decade, the European stock market had low-to-moderate correlation with North American and Asian equities.
The below chart shows correlations from February 2014 to February 2024. A value closer to zero indicates low correlation, while a value of one would indicate that two regions are moving in perfect unison.
| EURO STOXX 50 | STOXX EUROPE 600 | U.S. | Canada | Japan | Asia Pacific ex. China |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| STOXX EUROPE 600 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.48 | |
| U.S. | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| Canada | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.40 | |||
| Japan | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 1.00 |
Data is based on daily USD returns.
European equities had relatively independent market movements from North American and Asian markets. One contributing factor could be the differing sector weights in each market. For instance, technology makes up a quarter of the U.S. market, but health care and industrials dominate the broader European market.
Ultimately, European equities can enhance portfolio diversification and have the potential to mitigate risk for investors.
Tracking the Market
For investors interested in European equities, STOXX offers a variety of flagship indices:
| Index | Description | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| STOXX Europe 600 | Pan-regional, broad market | €10.5T |
| STOXX Developed Europe | Pan-regional, broad-market | €9.9T |
| STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X | Pan-regional, broad market, sustainability focus | €9.7T |
| STOXX Europe 50 | Pan-regional, blue-chip | €5.1T |
| EURO STOXX 50 | Eurozone, blue-chip | €3.5T |
Data is as of February 29, 2024. Market cap is free float, which represents the shares that are readily available for public trading on stock exchanges.
The EURO STOXX 50 tracks the Eurozone’s biggest and most traded companies. It also underlies one of the world’s largest ranges of ETFs and mutual funds. As of November 2023, there were €27.3 billion in ETFs and €23.5B in mutual fund assets under management tracking the index.
“For the past 25 years, the EURO STOXX 50 has served as an accurate, reliable and tradable representation of the Eurozone equity market.”
— Axel Lomholt, General Manager at STOXX
Partnering with STOXX to Track the European Stock Market
Are you interested in European equities? STOXX can be a valuable partner:
- Comprehensive, liquid and investable ecosystem
- European heritage, global reach
- Highly sophisticated customization capabilities
- Open architecture approach to using data
- Close partnerships with clients
- Part of ISS STOXX and Deutsche Börse Group
With a full suite of indices, STOXX can help you benchmark against the European stock market.

Learn how STOXX’s European indices offer liquid and effective market access.

-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees