Wealth
The Richest Women in America in One Graphic
The Richest Women in America in One Graphic
The majority of the world’s billionaires hail from the United States.
But of the 724 American billionaires whose net worths are tracked daily by Forbes, only 86 are women. That’s just 12% of the country’s billionaires.
This visualization examines the select few who have made the cut into this prestigious list, using data compiled from Forbes’ real-time billionaires list.
Note: All data is as of November 1, 2021 unless otherwise stated.
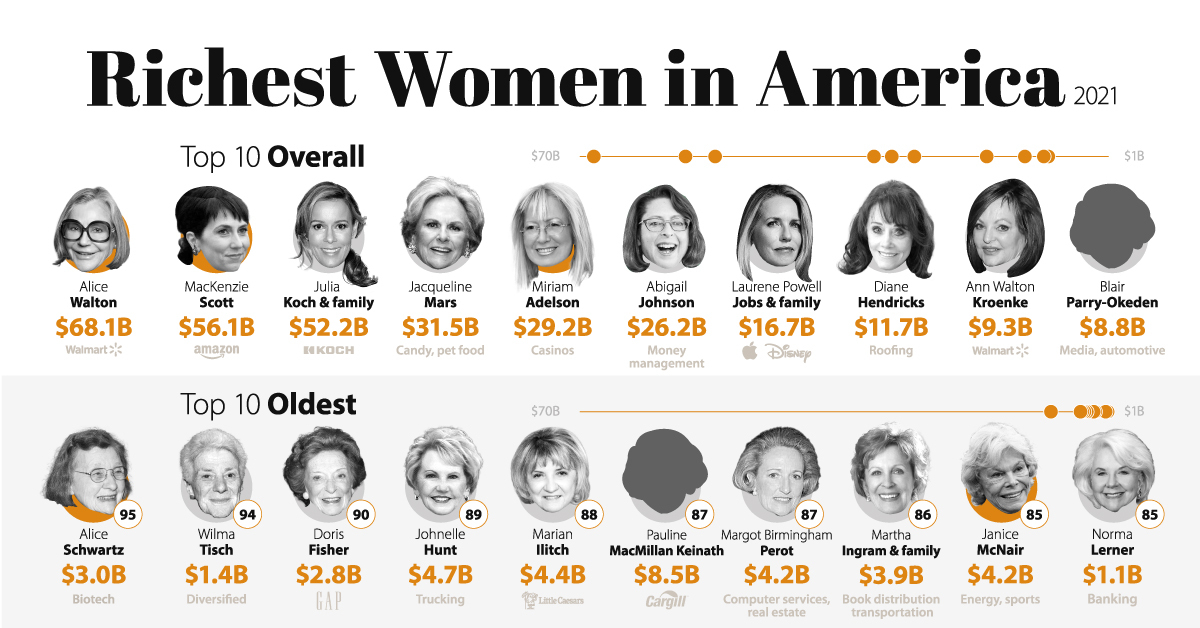
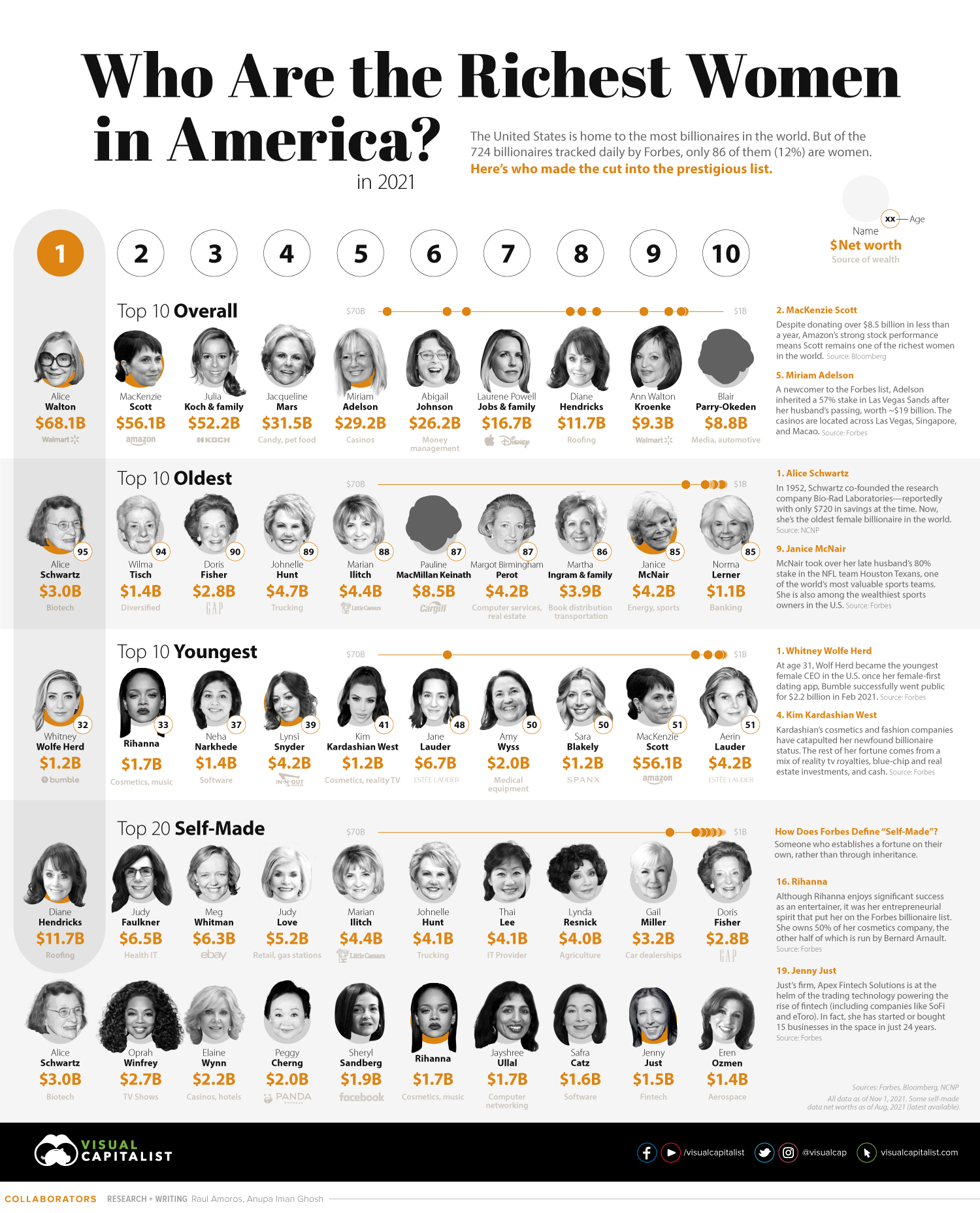
Top 10 Richest Women in America
Since 2020, MacKenzie Scott has donated over $8.5 billion and counting of her wealth. Yet, she still remains one of the richest women in the world. This is largely due to the Amazon shares that she received in her divorce settlement.
Amazon’s stock performance soared amid the pandemic, which resulted in the initial value of her shares ($38.3 billion) nearly doubling.
| Top 10 overall | Name | Net Worth | Age | Source of wealth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Alice Walton | $68.1 B | 72 | Walmart |
| #2 | MacKenzie Scott | $56.1 B | 51 | Amazon |
| #3 | Julia Koch & family | $52.2 B | 59 | Koch Industries |
| #4 | Jacqueline Mars | $31.5 B | 82 | Candy, pet food |
| #5 | Miriam Adelson | $29.2 B | 76 | Casinos |
| #6 | Abigail Johnson | $26.2 B | 59 | Money management |
| #7 | Laurene Powell Jobs & family | $16.7 B | 57 | Apple, Disney |
| #8 | Diane Hendricks | $11.7 B | 74 | Roofing |
| #9 | Ann Walton Kroenke | $9.3 B | 72 | Walmart |
| #10 | Blair Parry-Okeden | $8.8 B | 71 | Media, automotive |
Miriam Adelson inherited her late husband’s 57% stake (worth ~$19 billion) in Las Vegas Sands, making her one of the richest newcomers to the Forbes list. The casinos have locations across Las Vegas, Singapore, and Macao.
Several of the women in this top 10 list also share membership with some of the richest families in America—from the Walmart Waltons, to the Johnsons at the helm of Fidelity Investments and Fidelity International.
The Oldest Richest Women in America
The oldest female billionaire in the world, Alice Schwartz, is 95 years old. She co-founded Bio-Rad Laboratories with her husband, which operates in the life sciences research and clinical diagnostics markets. They started the company in 1952 with only $720 in the bank.
| Oldest | Name | Net Worth | Age | Source of wealth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Alice Schwartz | $3.0 B | 95 | Biotech |
| #2 | Wilma Tisch | $1.4 B | 94 | Diversified |
| #3 | Doris Fisher | $2.8 B | 90 | Gap |
| #4 | Johnelle Hunt | $4.7 B | 89 | Trucking |
| #5 | Marian Ilitch | $4.4 B | 88 | Little Caesars |
| #6 | Pauline MacMillan Keinath | $8.5 B | 87 | Cargill |
| #7 | Margot Birmingham Perot | $4.2 B | 87 | Computer services, real estate |
| #8 | Martha Ingram & family | $3.9 B | 86 | Book distribution, transportation |
| #9 | Janice McNair | $4.2 B | 85 | Energy, sports |
| #10 | Norma Lerner | $1.1 B | 85 | Banking |
After her husband’s passing in 2018, Janice McNair (aged 85) took over his 80% stake in the NFL team Houston Texans, which ranks highly as one of the world’s most valuable sports teams. This also subsequently catapulted her position as being among the wealthiest sports owners in the country.
The Youngest Richest Women in America
In the online dating era, Whitney Wolfe Herd has made a name for herself. The female-first dating app she co-founded, Bumble, grew into a formidable competitor for her former employer, Match Group (which owns Tinder and OkCupid, among others).
At age 31, Wolfe Herd became the youngest self-made female CEO in the country after Bumble’s $2.2 billion IPO in February 2021.
| Youngest | Name | Net Worth | Age | Source of wealth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Whitney Wolfe Herd | $1.2 B | 32 | Dating app |
| #2 | Rihanna | $1.7 B | 33 | Cosmetics, music |
| #3 | Neha Narkhede | $1.4 B | 37 | Software |
| #4 | Lynsi Snyder | $4.2 B | 39 | In-N-Out Burger |
| #5 | Kim Kardashian West | $1.2 B | 41 | Cosmetics, reality TV |
| #6 | Jane Lauder | $6.7 B | 48 | Estée Lauder |
| #7 | Amy Wyss | $2.0 B | 50 | Medical equipment |
| #8 | Sara Blakely | $1.2 B | 50 | Spanx |
| #9 | MacKenzie Scott | $56.1 B | 51 | Amazon |
| #10 | Aerin Lauder | $4.2 B | 51 | Cosmetics |
Wearing many hats from influencer to entrepreneur, socialite Kim Kardashian West’s cosmetics and fashion companies (KKW Beauty and shapewear line Skims) have catapulted her to a newfound billionaire status. She has a set of diverse revenue streams, from reality TV royalties to blue-chip and real estate investments.
Top 20 Self-Made Richest Women in America
The self-made label is an additional fascinating avenue to explore. Forbes defines this category as people who establish a fortune independently, rather than partly or wholly through inheritance.
One of the newest entrants into this mix is Rihanna. She already enjoyed significant success as an entertainer, with her claim to fame being one of the best-selling artists of the 2010s. However, it was her entrepreneurial spirit that put her on the Forbes list in August 2021. Rihanna owns 50% of her cosmetics company, Fenty Beauty. The other half is run by Bernard Arnault, who is among the world’s top billionaires.
Here is the rest of the top 20 self-made richest women in America:
| Self-Made | Name | Net Worth | Age | Source of wealth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Diane Hendricks | $11.7 B | 74 | Roofing |
| #2 | Judy Faulkner | $6.5 B | 77 | Health IT |
| #3 | Meg Whitman | $6.3 B | 65 | eBay |
| #4 | Judy Love | $5.2 B | 84 | Retail and gas stations |
| #5 | Marian Ilitch | $4.4 B | 88 | Little Caesars |
| #6 | Johnelle Hunt | $4.1 B | 89 | Trucking |
| #7 | Thai Lee | $4.1 B | 62 | IT Provider |
| #8 | Lynda Resnick | $4.0 B | 78 | Agriculture |
| #9 | Gail Miller | $3.2 B | 77 | Car dealerships |
| #10 | Doris Fisher | $2.8 B | 90 | Gap |
| #11 | Alice Schwartz | $3.0 B | 95 | Biotech |
| #12 | Oprah Winfrey | $2.7 B | 67 | Media |
| #13 | Elaine Wynn | $2.2 B | 79 | Casinos, hotels |
| #14 | Peggy Cherng | $2.0 B | 73 | Fast food (Panda Express) |
| #15 | Sheryl Sandberg | $1.9 B | 51 | |
| #16 | Rihanna | $1.7 B | 33 | Cosmetics, music |
| #17 | Jayshree Ullal | $1.7 B | 60 | Computer networking |
| #18 | Safra Catz | $1.6 B | 59 | Software |
| #19 | Jenny Just | $1.5 B | 53 | Fintech |
| #20 | Eren Ozmen | $1.4 B | 62 | Aerospace |
Source: Forbes, as of Aug 2021 (latest available)
For those paying attention to the rapid rise of the fintech industry, Jenny Just’s entry on this list will come as no surprise. Her firm, Apex Fintech Solutions powers the trading technology behind companies like SoFi and eToro. In fact, she has started or bought 15 businesses in the space in just 24 years.
As the richest women in America continue to make great strides, this list could look very different in coming years.
Money
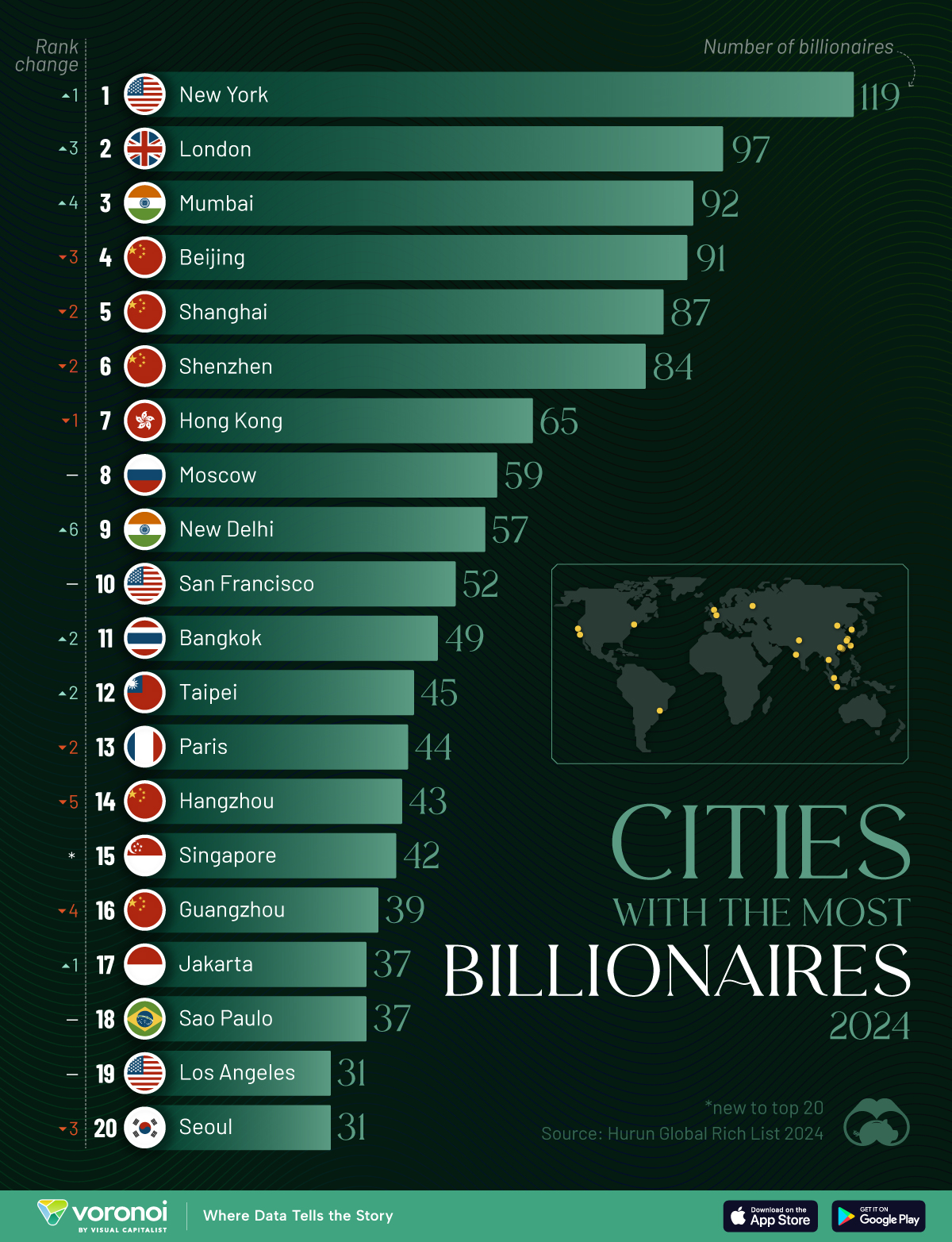
Charted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
Just two countries account for half of the top 20 cities with the most billionaires. And the majority of the other half are found in Asia.
Charted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Some cities seem to attract the rich. Take New York City for example, which has 340,000 high-net-worth residents with investable assets of more than $1 million.
But there’s a vast difference between being a millionaire and a billionaire. So where do the richest of them all live?
Using data from the Hurun Global Rich List 2024, we rank the top 20 cities with the highest number of billionaires in 2024.
A caveat to these rich lists: sources often vary on figures and exact rankings. For example, in last year’s reports, Forbes had New York as the city with the most billionaires, while the Hurun Global Rich List placed Beijing at the top spot.
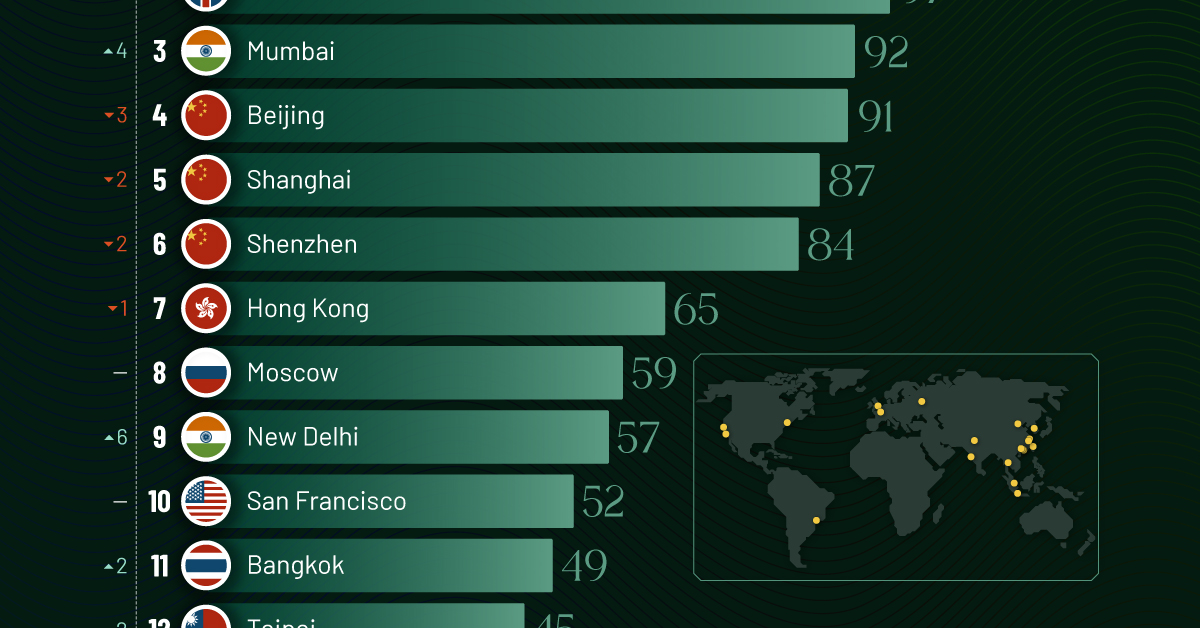
Ranked: Top 20 Cities with the Most Billionaires in 2024
The Chinese economy’s doldrums over the course of the past year have affected its ultra-wealthy residents in key cities.
Beijing, the city with the most billionaires in 2023, has not only ceded its spot to New York, but has dropped to #4, overtaken by London and Mumbai.
| Rank | City | Billionaires | Rank Change YoY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 New York | 119 | +1 |
| 2 | 🇬🇧 London | 97 | +3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Mumbai | 92 | +4 |
| 4 | 🇨🇳 Beijing | 91 | -3 |
| 5 | 🇨🇳 Shanghai | 87 | -2 |
| 6 | 🇨🇳 Shenzhen | 84 | -2 |
| 7 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | 65 | -1 |
| 8 | 🇷🇺 Moscow | 59 | No Change |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi | 57 | +6 |
| 10 | 🇺🇸 San Francisco | 52 | No Change |
| 11 | 🇹🇭 Bangkok | 49 | +2 |
| 12 | 🇹🇼 Taipei | 45 | +2 |
| 13 | 🇫🇷 Paris | 44 | -2 |
| 14 | 🇨🇳 Hangzhou | 43 | -5 |
| 15 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 42 | New to Top 20 |
| 16 | 🇨🇳 Guangzhou | 39 | -4 |
| 17T | 🇮🇩 Jakarta | 37 | +1 |
| 17T | 🇧🇷 Sao Paulo | 37 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇺🇸 Los Angeles | 31 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇰🇷 Seoul | 31 | -3 |
In fact all Chinese cities on the top 20 list have lost billionaires between 2023–24. Consequently, they’ve all lost ranking spots as well, with Hangzhou seeing the biggest slide (-5) in the top 20.
Where China lost, all other Asian cities—except Seoul—in the top 20 have gained ranks. Indian cities lead the way, with New Delhi (+6) and Mumbai (+3) having climbed the most.
At a country level, China and the U.S combine to make up half of the cities in the top 20. They are also home to about half of the world’s 3,200 billionaire population.
In other news of note: Hurun officially counts Taylor Swift as a billionaire, estimating her net worth at $1.2 billion.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries