Mining
How to Avoid Common Mistakes With Mining Stocks (Part 5: Funding Strength)
A mining company’s past projects and funding strength are interlinked, and can provide clues as to its potential success.
A good track record can provide better opportunities to raise capital, but the company must still ensure it times its financing with the market, protects its shareholders, and demonstrates value creation from the funding it receives.
Part 5: The Role of Funding Strength
We’ve partnered with Eclipse Gold Mining on an infographic series to show you how to avoid common mistakes when evaluating and investing in mining exploration stocks.
Part 5 of the series highlights six things to keep in mind when analyzing a company’s project history and funding ability.

View all five parts of the series:
- 1. Common mistakes made with the team
- 2. Common mistakes made with the business plan
- 3. Common mistakes with the jurisdiction of the project
- 4. Common mistakes with the project and technical risks
- 5. Common mistakes with raising money
Part 5: Raising Capital and Funding Strength
So what must investors evaluate when it comes to funding strength?
Here are six important areas to cover.
1. Past Project Success: Veteran vs. Recruit
A history of success in mining helps to attract capital from knowledgeable investors. Having an experienced team provides confidence and opens up opportunities to raise additional capital on more favorable terms.
Veteran:
- A team with past experience and success in similar projects
- A history of past projects creating value for shareholders
- A clear understanding of the building blocks of a successful project
A company with successful past projects instills confidence in investors and indicates the company knows how to make future projects successful, as well.
2. Well-balanced Financing: Shareholder Friendly vs. Banker Friendly
Companies need to balance between large investors and protecting retail shareholders. Management with skin in the game ensures they find a balance between serving the interests of both of these unique groups.
Shareholder Friendly:
- Clear communication with shareholders regarding the company’s financing plans
- High levels of insider ownership ensures management has faith in the company’s direction, and is less likely to make decisions which hurt shareholders
- Share dilution is done in a limited capacity and only when it helps finance new projects that will create more value for shareholders
Mining companies need to find a balance between keeping their current shareholders happy while also offering attractive financing options to attract further investors.
3. A Liquid Stock: Hot Spot vs. Ghost Town
Lack of liquidity in a stock can be a major problem when it comes to attracting investment. It can limit investments from bigger players like funds and savvy investors. Investors prefer liquid stocks that are easily traded, as this allows them to capitalize on market trends.
Hot Spot:
- A liquid stock ensures shareholders are able to buy and sell shares at their expected price
- More liquid stocks often trade at better valuations than their illiquid counterparts
- High liquidity can help avoid price crashes during times of market instability
Liquidity makes all the difference when it comes to attracting investors and ensuring they’re comfortable holding a company’s stock.
4. Timing the Market: On Time vs. Too Late or Too Early
Raising capital at the wrong time can result in little interest from investors. Companies in tune with market cycles can raise capital to capture rising interest in the commodity they’re mining.
Being On Time:
- Raising capital near the start of a commodity’s bull market can attract interest from speculators looking to capitalize on price trends
- If timed well, the attention around a commodity can attract investors
- Well-timed financing will instill confidence in shareholders, who will be more likely to hold onto their stock
- Raising capital at the right time during bull markets is less expensive for the company and reduces risk for investors
Companies need to time when they raise capital in order to maximize the amount raised.
5. Where is the Money Going? Money Well Spent vs. Well Wasted
How a company spends its money plays a crucial role in whether the company is generating more value or just keeping the lights on. Investors should always try to determine if management is simply in it for a quick buck, or if they truly believe in their projects and the quality of the ore the company is mining.
Money Well Spent:
- Raised capital goes towards expanding projects and operations
- Efficient use of capital can increase revenue and keep shareholders happy with dividend hikes and share buybacks
- By showing tangible results from previous investments, a company can more easily raise capital in the future
Raised capital needs to be allocated wisely in order to support projects and generate value for shareholders.
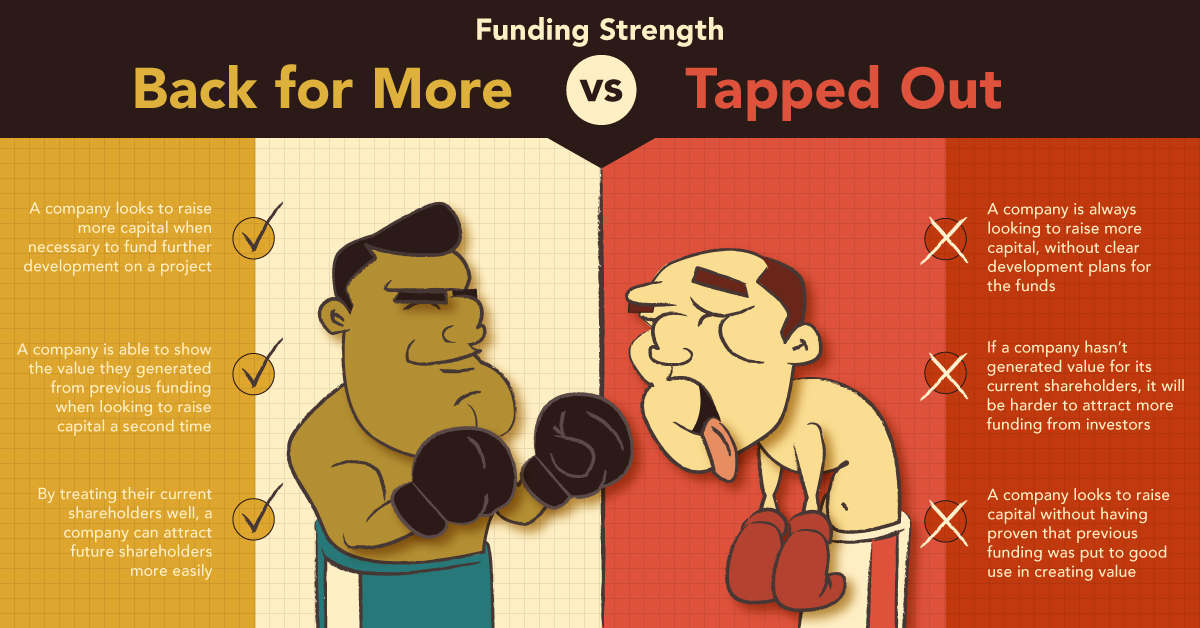
6. Additional Capital: Back for More vs. Tapped Out
Mining is a capital intensive process, and unless the company has access to a treasure trove, funding is crucial to advancing any project. Companies that demonstrate consistency in their ability to create value at every stage will find it easier to raise capital when it’s necessary.
Back For More:
- Raise more capital when necessary to fund further development on a project
- Able to show the value they generated from previous funding when looking to raise capital a second time
- Attract future shareholders easily by treating current shareholders well
Every mining project requires numerous financings. However, if management proves they spend capital in a way that creates value, investors will likely offer more funding during difficult or unexpected times.
Wealth Creation and Funding Strength
Mining companies that develop significant assets can create massive amounts of wealth, but often the company will not see cash flow for years. This is why it is so important to have funding strength: an ability to raise capital and build value to harvest later.
It is a challenging process to build a mining company, but management that has the ability to treat their shareholders and raise money can see their dreams built.
Lithium
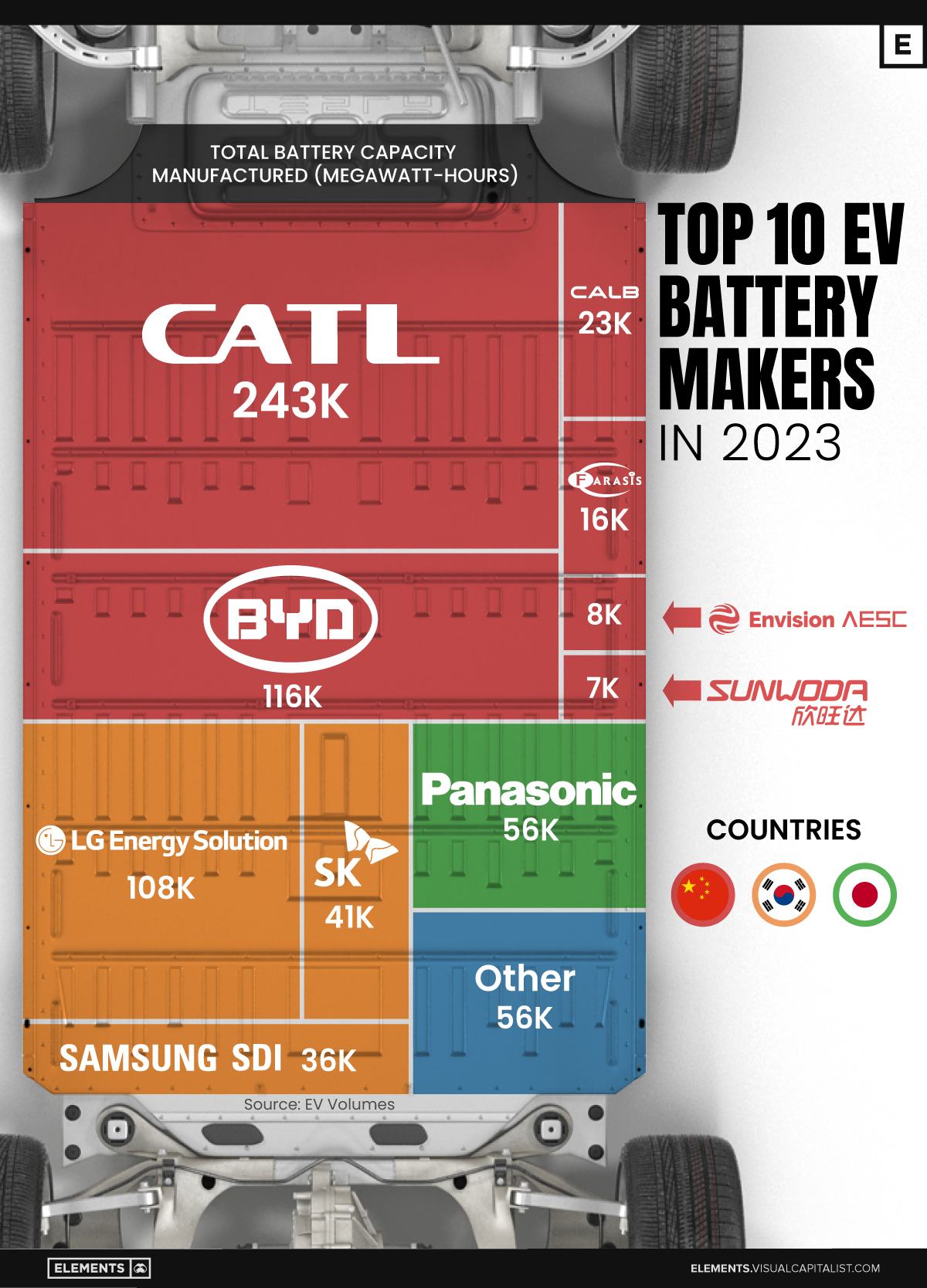
Ranked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts from the U.S. and EU to secure local domestic supply, all major EV battery manufacturers remain based in Asia.
In this graphic we rank the top 10 EV battery manufacturers by total battery deployment (measured in megawatt-hours) in 2023. The data is from EV Volumes.
Chinese Dominance
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has swiftly risen in less than a decade to claim the title of the largest global battery group.
The Chinese company now has a 34% share of the market and supplies batteries to a range of made-in-China vehicles, including the Tesla Model Y, SAIC’s MG4/Mulan, and various Li Auto models.
| Company | Country | 2023 Production (megawatt-hour) | Share of Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL | 🇨🇳 China | 242,700 | 34% |
| BYD | 🇨🇳 China | 115,917 | 16% |
| LG Energy Solution | 🇰🇷 Korea | 108,487 | 15% |
| Panasonic | 🇯🇵 Japan | 56,560 | 8% |
| SK On | 🇰🇷 Korea | 40,711 | 6% |
| Samsung SDI | 🇰🇷 Korea | 35,703 | 5% |
| CALB | 🇨🇳 China | 23,493 | 3% |
| Farasis Energy | 🇨🇳 China | 16,527 | 2% |
| Envision AESC | 🇨🇳 China | 8,342 | 1% |
| Sunwoda | 🇨🇳 China | 6,979 | 1% |
| Other | - | 56,040 | 8% |
In 2023, BYD surpassed LG Energy Solution to claim second place. This was driven by demand from its own models and growth in third-party deals, including providing batteries for the made-in-Germany Tesla Model Y, Toyota bZ3, Changan UNI-V, Venucia V-Online, as well as several Haval and FAW models.
The top three battery makers (CATL, BYD, LG) collectively account for two-thirds (66%) of total battery deployment.
Once a leader in the EV battery business, Panasonic now holds the fourth position with an 8% market share, down from 9% last year. With its main client, Tesla, now sourcing batteries from multiple suppliers, the Japanese battery maker seems to be losing its competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, the global EV battery market size is projected to grow from $49 billion in 2022 to $98 billion by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights.
-

 Brands6 days ago
Brands6 days agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue