Politics
The Official and Ceremonial Vehicles of World Leaders
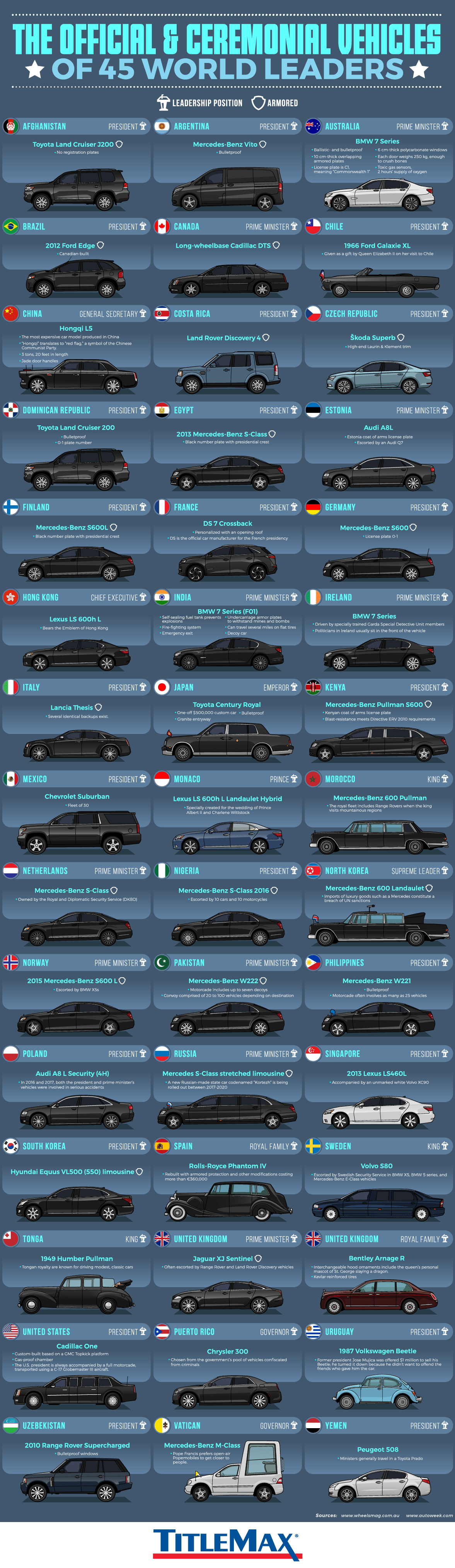
The Official and Ceremonial Vehicles of World Leaders
Transporting world leaders from A-to-B is a complex endeavor, usually accomplished using motorcades, escorts, roadblocks, and all sorts of bullet and bombproof vehicles. Incorporating that level of technological sophistication into a stylish vehicle worthy of transporting and head of state is no easy task.
Today’s graphic looks at official state vehicles, from the unparalleled Cadillac One that transports President Trump, to the understated ’87 Volkswagen Beetle driven by former Uruguayan president, Josè Mujica.
The Official Official Vehicle
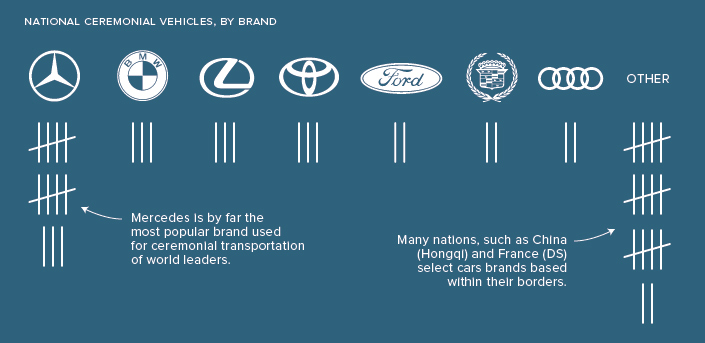
According to data from TitleMax, the overwhelming favorite car brand for world leaders is Mercedes–Benz, particularly the S-Class.
Many countries use luxury brands such as Mercedes–Benz and BMW to transport their heads of state, though it’s also a popular move select domestic brands for such an important and highly symbolic task. The United States, Japan, China, Germany, United Kingdom, France, and Sweden are all examples of countries that chose vehicles made by domestic brands.
Safety First
The United States spares little expense in keeping the president safe, and President Trump’s Cadillac One, nicknamed “The Beast“, is no exception.
As one would expect, the vehicle is heavily armored, with doors that weigh as much as the ones on a Boeing 757. There are also some unique features packed into the vehicle, such as tear gas launchers, and pints of blood that match the president’s blood type.
Australia’s Prime Minister, Malcolm Turnbull, rides in a BMW 7 Series that boasts some impressive safety features, including on-board oxygen supply and toxic gas sensors.
Old School Cool
While many nations fleets consist of modern luxury vehicles, some heads of state opt for vintage rides.
The former King of Tonga, George Tupou V, preferred traveling in vintage cars, such as a 1949 Humber Pullman and his customized London taxi.
An English taxi is extremely easy to get in and out of wearing a sword, a spiked helmet or spurs.
The Rolls-Royce Phantom IV is, in some ways, the quintessential vehicle for pomp and circumstance. Only 18 of the vehicles were made between 1950 and 1956, and all were purchased by royal families and heads of state. Three of these historical vehicles are still in use by the Spanish head of state for ceremonial occasions.
During special events, Chilean leaders cruise in a 1966 Ford Galaxie. The car, which has been in use for decades, was a gift from the Queen Elizabeth II.
Going Dutch
Prime Minister of the Netherlands, Mark Rutte, occasionally ditches his Mercedes–Benz S-Class to ride his bike to meetings. That may seem unusual in some parts of the world, but not in the Netherlands where nearly a quarter of the country’s population rides a bicycle on any given day.
Politics
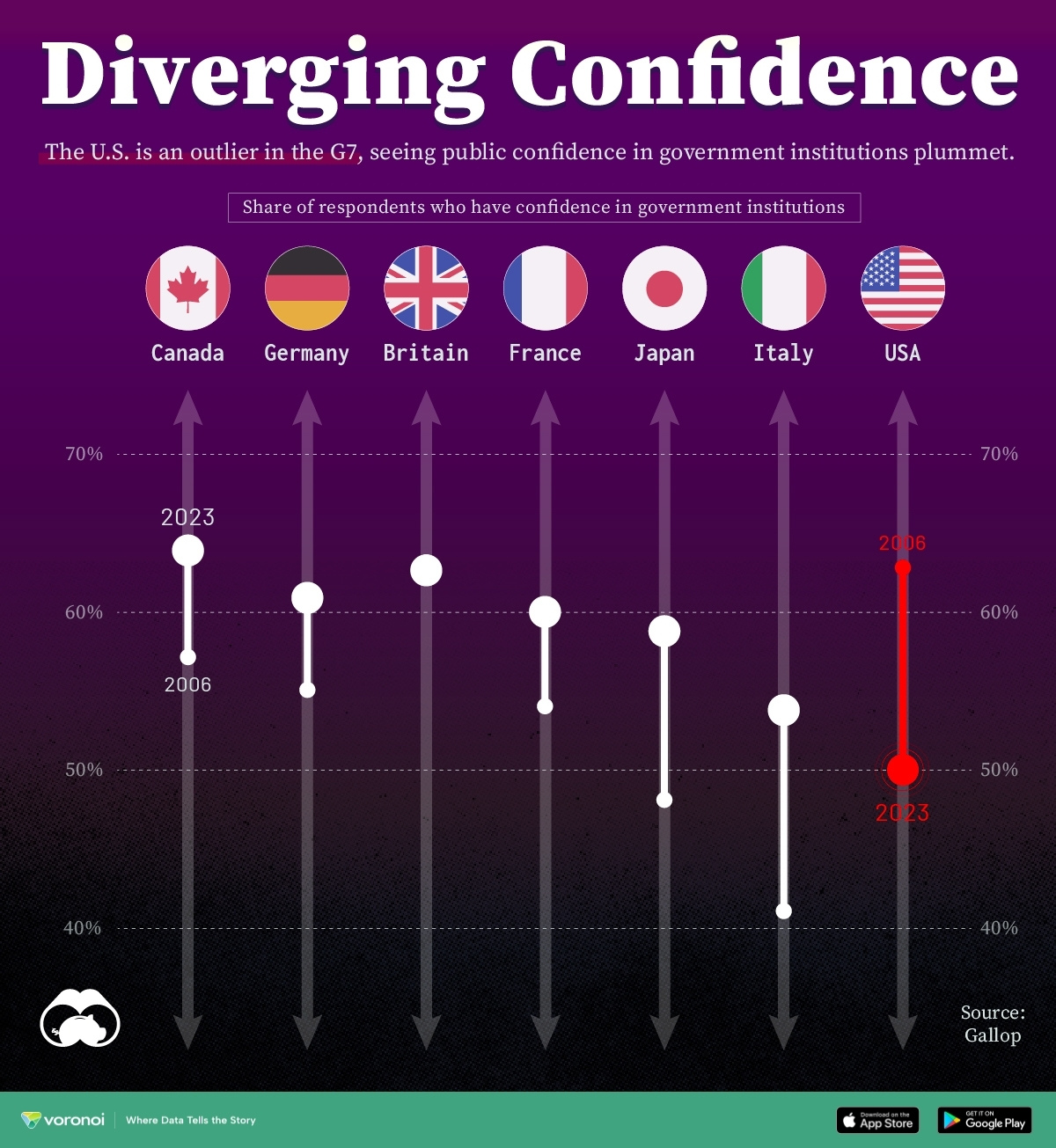
Charted: Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
How much do you trust the government and its various institutions? We look at data for G7 countries for the time period of 2006-2023.
Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
How much do you trust the government, and its various institutions?
It’s likely that your level of confidence probably depends on a wide range of factors, such as perceived competency, historical context, economic performance, accountability, social cohesion, and transparency.
And for these same reasons, trust levels in government institutions also change all the time, even in the world’s most developed countries: the G7.
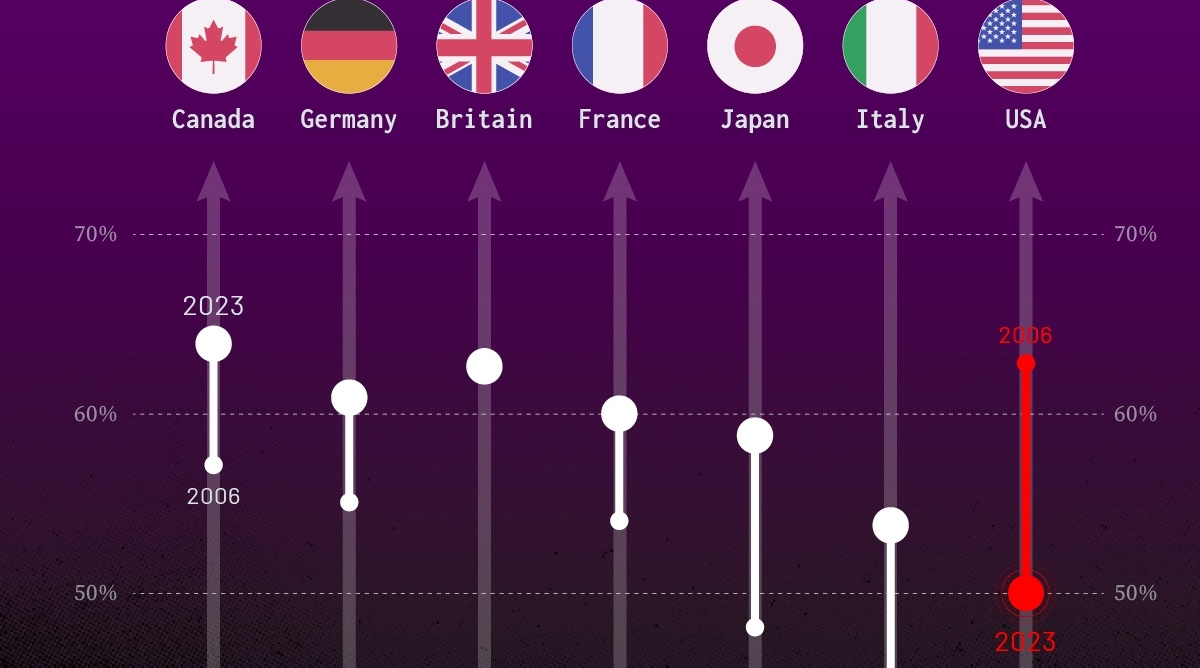
Confidence in Government by G7 Countries (2006-2023)
This chart looks at the changes in trust in government institutions between the years 2006 and 2023, based on data from a multi-country Gallup poll.
Specifically, this dataset aggregates confidence in multiple national institutions, including the military, the judicial system, the national government, and the integrity of the electoral system.
| Country | Confidence (2006) | Confidence (2023) | Change (p.p.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | 57% | 64% | +7 |
| Britain | 63% | 63% | +0 |
| Germany | 55% | 61% | +6 |
| France | 54% | 60% | +6 |
| Japan | 48% | 59% | +11 |
| Italy | 41% | 54% | +13 |
| United States | 63% | 50% | -13 |
What’s interesting here is that in the G7, a group of the world’s most developed economies, there is only one country bucking the general trend: the United States.
Across most G7 countries, confidence in institutions has either improved or stayed the same between 2006 and 2023. The largest percentage point (p.p.) increases occur in Italy and Japan, which saw +13 p.p. and +11 p.p. increases in trust over the time period.
In the U.S., however, confidence in government institutions has fallen by 13 p.p. over the years. What happened?
Key Figures on U.S. Trust in Institutions
In 2006, the U.S. was tied with the UK as having the highest confidence in government institutions, at 63%.
But here’s where the scores stand in 2023, across various institutions:
| 🇺🇸 Institutions | Confidence (2023) |
|---|---|
| Military | 81% |
| Judiciary | 42% |
| National Government | 30% |
| Elections | 44% |
| Overall | 49% |
Based on this data, it’s clear that the U.S. lags behind in three key indicators: confidence in the national government, confidence in the justice system, and confidence in fair elections. It ranked in last place for each indicator in the G7.
One other data point that stands out: despite leading the world in military spending, the U.S. is only the third most confident in its military in the G7. It lags behind France (86%) and the United Kingdom (83%).
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
-

 Uranium2 weeks ago
Uranium2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Debt2 weeks ago
Debt2 weeks agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands1 week ago
Brands1 week agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023