Markets
5 Hidden Ways That Globalization is Changing
Globalization has been a powerful force in shaping modern human history.
The world economy has become increasingly connected and interdependent over recent decades, and conventional wisdom suggests that this will only continue in the years ahead.
But while it’s tempting to extrapolate the past effects of globalization into the future, such a leap may also be a mistake. That’s because there is growing evidence that globalization itself is quietly transforming – and how it ultimately evolves may be markedly different from what most business leaders might expect.
How Globalization is Changing
Today’s infographic highlights the most recent research about globalization from the McKinsey Global Institute, the business and economics research arm of McKinsey & Company.
Below are five major shifts that have gone mostly unnoticed, as well as the countries and companies that could benefit:

The findings of the report show that globalization is not static or constant, and that structural changes in the nature of globalization have been occurring in the background over the last decade or so.
>> View the Complete Report Here:
“Globalization in transition: The future of trade and value chains”
The impact that these shifts could have on the global economy is substantial: international trade already adds up to $22.4 trillion each year, or about 28% of global GDP. Even a minor change in this paradigm could affect the list of countries, corporations, and workers that stand to benefit.
The 5 Ways Globalization is Changing
The report looks into 23 different industry value chains in 43 different countries, representing 96% of global trade.
From that comprehensive data, five major structural shifts have been identified:
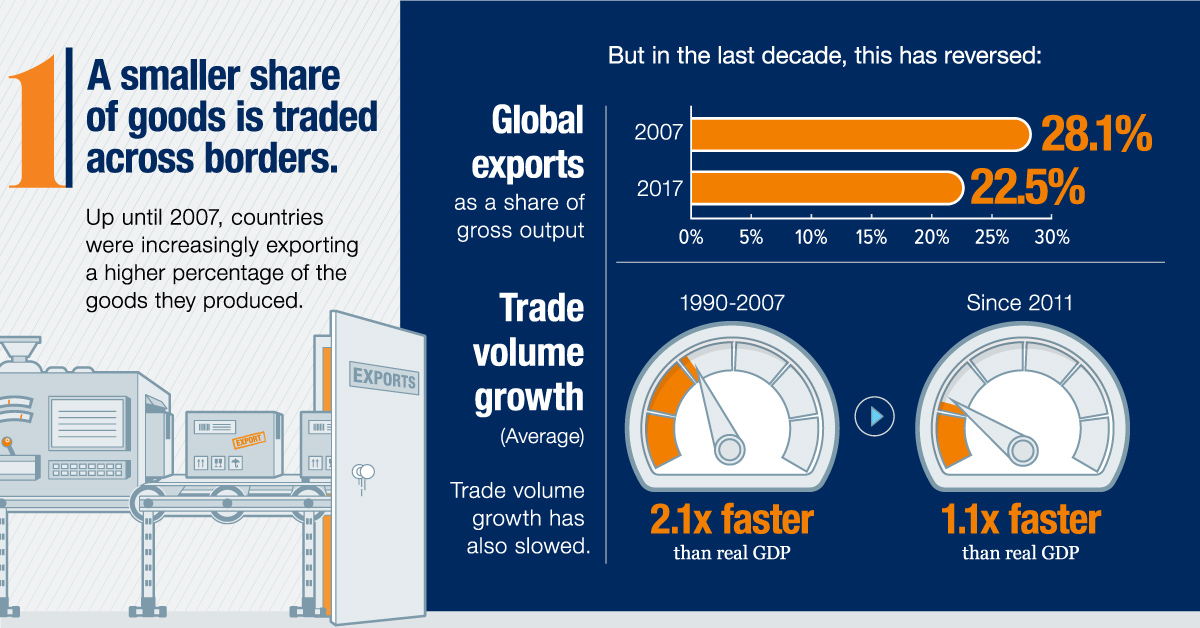
1. A smaller share of goods is traded across borders
Trade is still growing in absolute terms, but a smaller share of the physical goods made worldwide is now being traded. More specifically, during the span of 2007 to 2017, gross exports as a percentage of gross output decreased from 28.1% to 22.5% globally.
2. Services trade is growing 60% faster than goods trade
When we think of trade, we often focus on the trade of physical goods (i.e. autos, aerospace, oil). However, services are becoming increasingly important to the global economy – and if accounted for properly, it’s possible that the value of services is closer to $13.4 trillion, which is higher than the total goods trade.
3. Labor-cost arbitrage has become less important
It’s a common perception that trade flows are driven by companies searching for low-cost labor. However, in value chains today, only 18% of the goods trade is based strictly on labor-cost arbitrage.
4. R&D and innovation are becoming increasingly important
Companies are spending more on R&D and intangible assets such as brands, software, and IP as a percentage of overall revenue. This spending has increased from 5.4% to 13.1% of revenue over the period of 2000-2017.
5. Trade is becoming more concentrated within regions
The geography of global demand is changing as emerging markets consume a higher percentage of total goods. Since 2013, intraregional trade has increased by 2.7 percentage points – a reverse from the longstanding trend.
The mix of countries, companies, and workers that stand to gain in the next era is changing.
– McKinsey Global Institute
Why These Changes Matter
What types of countries are likely to benefit from these shifts, and which will face headwinds?
| Type of economy | Possible opportunities or challenges |
|---|---|
| Advanced economies | Strengths in innovation, services, and highly skilled talent put advanced economies in a strategic position to benefit from changes in globalization |
| Developing economies with close proximity to large consumer markets | As production moves closer to consumers, developing economies in close proximity can take advantage |
| Developing economies that are less connected | The window is narrowing for low-income countries to use labor-intensive exports as a development strategy |
Policy makers and business leaders must understand how the trade landscape is shifting so they can prepare for globalization’s next chapter and the opportunities and challenges it will present.
Economy
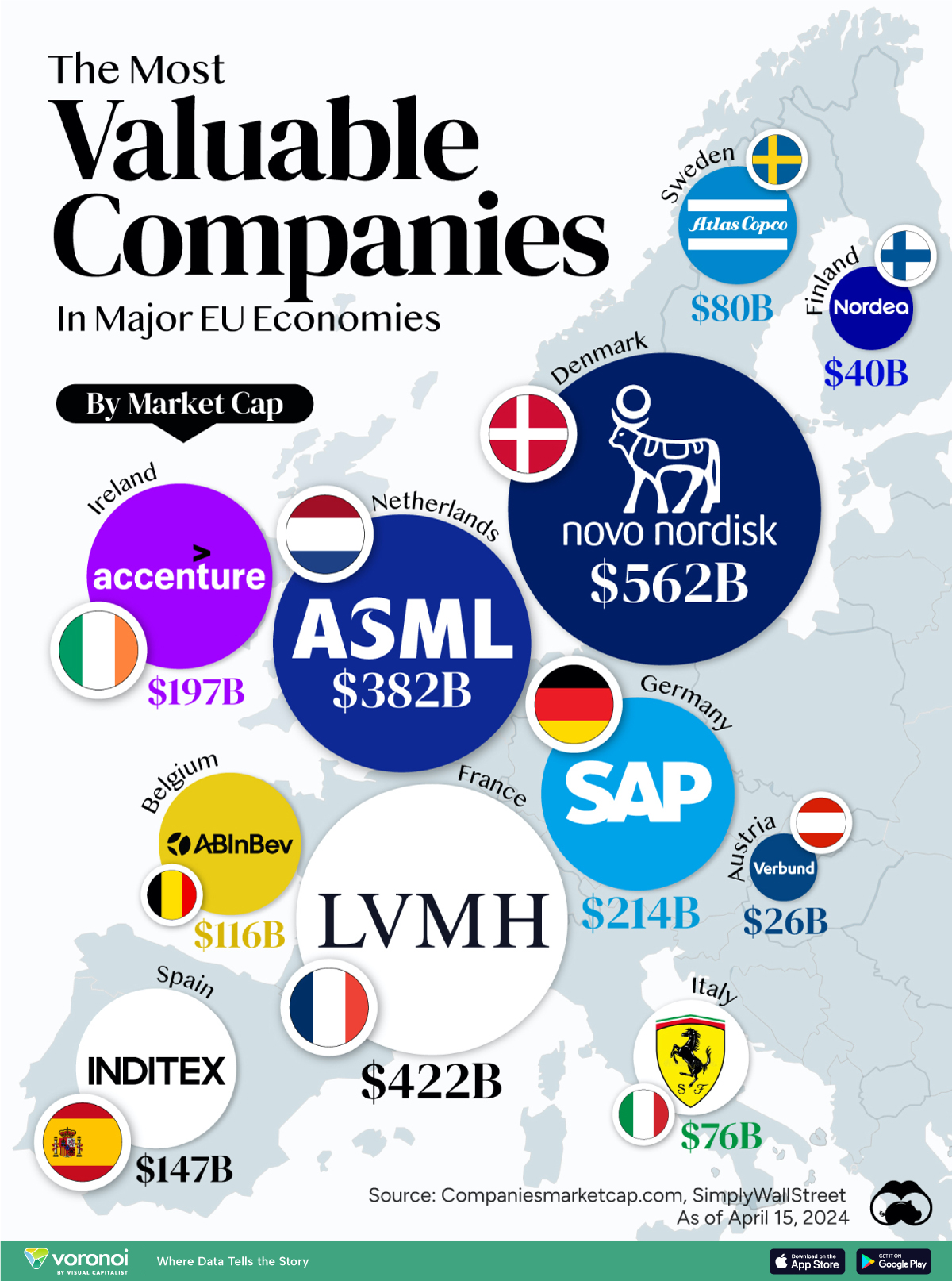
The Most Valuable Companies in Major EU Economies
From semiconductor equipment manufacturers to supercar makers, the EU’s most valuable companies run the gamut of industries.

Most Valuable Companies in the EU, by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
In this graphic, we mapped out the most valuable corporations in 11 major EU economies, based on their market capitalizations as of April 15th, 2024. All figures are in USD, and were sourced from Companiesmarketcap.com.
Novo Nordisk is currently worth more than $550 billion, making it Europe’s most valuable company by a wide margin. The pharmaceutical giant specializes in diabetes and weight-loss drugs. Demand for two of them, Ozempic and Wegovy, has surged due to their weight-loss capabilities, even causing nationwide shortages in the United States.
The following table includes an expanded list of the most valuable publicly-traded company in larger EU economies. Many of these were not included in the graphic due to space limitations.
| Country | Company | Sector | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | 💊 Novo Nordisk | Pharmaceuticals | $562B |
| 🇫🇷 France | 👜 LVMH | Luxury Goods | $422B |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 🔧 ASML | Semiconductor Equipment | $382B |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 💼 SAP | Enterprise Software | $214B |
| 🇮🇪 Ireland | 🖥️ Accenture | IT Services | $197B |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 👗 Inditex | Retail | $147B |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 🍻 Anheuser-Busch InBev | Beverages | $116B |
| 🇸🇪 Sweden | 🛠️ Atlas Copco | Industrial Equipment | $80B |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 🏎️ Ferrari | Automotive | $76B |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 🏦 Nordea Bank | Banking | $40B |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 🔌 Verbund AG | Energy | $26B |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 🏗️ Tenaris | Oil & Gas Equipment | $22B |
| 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 💡 CEZ Group | Energy | $20B |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | ⛽ PKN Orlen | Energy | $20B |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 🔌 EDP Group | Energy | $16B |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 🏦 Eurobank | Banking | $7B |
| 🇭🇺 Hungary | ⛽ MOL Group | Energy | $7B |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 🏦 Zagrebacka Banka | Banking | $6B |
| 🇷🇴 Romania | ⛽ Romgaz | Energy | $4B |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 💊 Krka | Pharmaceuticals | $4B |
Note: Figures are rounded and last updated on April 15th, 2024. Countries with top publicly-traded companies worth under $4 billion are excluded.
Luxury supergiant LVMH—which owns brands like Tiffany, Christian Dior, and TAG Heuer to name a few—is Europe’s second largest company by market cap, at $420 billion.
Rounding out the top three is ASML, which produces equipment crucial to chip manufacturers, worth $380 billion.
When looking at the region, there is a vast disparity between EU member states and their most valuable companies.
For example, as mentioned earlier, Denmark’s Novo Nordisk and France’s LVMH are worth between $400-550 billion each. Meanwhile, some countries don’t even have a single publicly-listed company that is worth over $1 billion.
In fact, only 12 EU countries (less than half of the union) are home to the top 100 most valuable companies within the bloc. An additional four countries are represented if you look at the list of the top 200 companies.
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Debt2 weeks ago
Debt2 weeks agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands1 week ago
Brands1 week agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010