Energy
Video: Preparing For The Energy Needs Of The Future
We’re living in a time of unprecedented change.
Our snail mail has turned to email. We’ve traded our TVs and radios for Netflix and iTunes. Instead of going to the store down the street, we do our shopping online, and we can even pay with crypto instead of cash.
Our world is transforming, and so is the energy industry.
The Changing Energy Industry
Today’s animation comes to us from California ISO, and it shows the challenges faced by the energy industry as they plan ahead for the energy needs of the future.
As the world grows more environmentally conscious, the energy sector faces new demands:
Environmental
Environmental concerns have brought clean energy systems to center stage, as we look for ways to reduce our dependence on greenhouse gases and preserve our planet for future generations. The push to eliminate fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions means we need to find ways to power coal-dependent sectors with renewable energy.
Technology
As new technologies emerge, they provide us with revolutionary ways to approach energy storage and efficiency, while bringing different types of renewable energies within our reach.
Decentralization
Energy grids have become less centralized over time, as grids move away from power plants in favor of distributed energy sources. Groupings of smaller energy sources are less vulnerable to failure, and provide reliable, cost effective energy options for consumers.
Economics
Economic demands push for competitive pricing and consumer rates, as they impact economic viability and promote healthy investment in the energy sector.
Politics
Renewable energy policies are progressing at the highest levels, as governments around the world set ambitious renewable energy goals for their nation.
Consumer Expectations
Consumers are no longer mere users of electricity, but informed producers. Through rooftop solar energy collection and the development of microgrids, consumers now have the option to gather energy reserves through their own clean energy systems and feed this back into the grid, making a positive impact on their communities.
With all these competing influences, the global energy industry now faces the challenge of creating a system capable of meeting the energy demands of our changing world.
Where to from here?
Planning for the energy needs of the future is no easy task. It’s a challenge to ensure reliable energy provision for consumers, leveraging emerging technology while hedging against disruptive factors like natural disasters which impact energy infrastructure.
There is no single solution, but a network of interconnected solutions working together can improve strengthen green energy provision as our world continues to evolve.
Energy
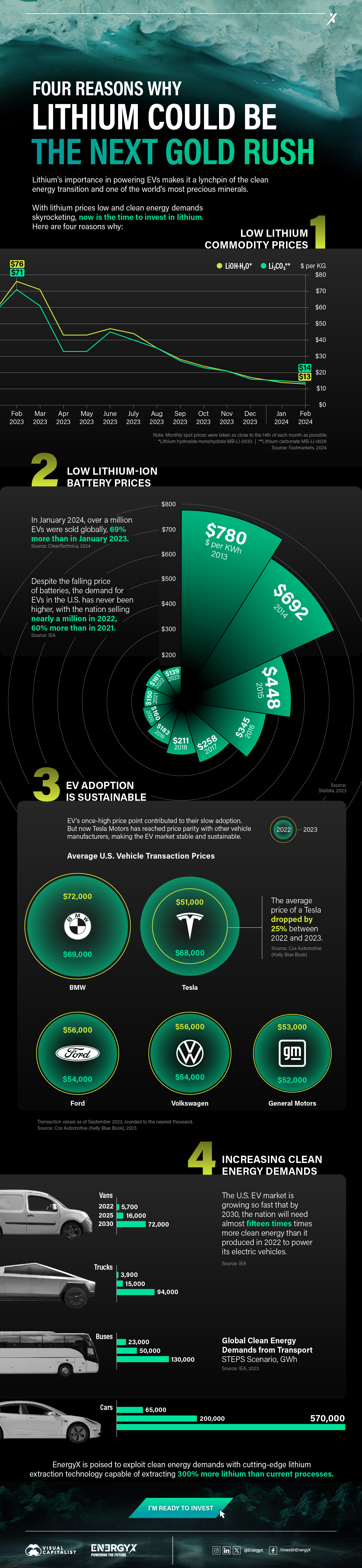
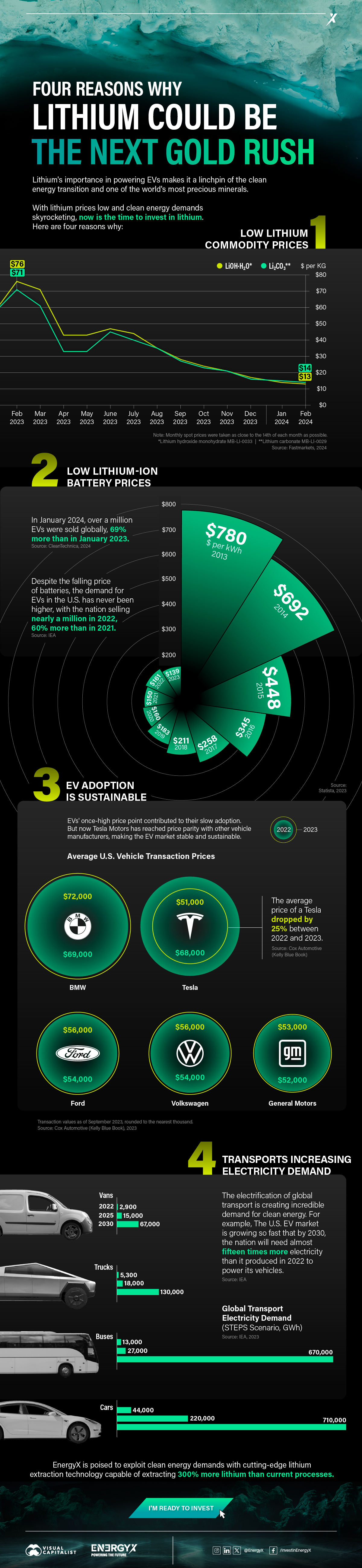
Charted: 4 Reasons Why Lithium Could Be the Next Gold Rush
Visual Capitalist has partnered with EnergyX to show why drops in prices and growing demand may make now the right time to invest in lithium.
4 Reasons Why You Should Invest in Lithium
Lithium’s importance in powering EVs makes it a linchpin of the clean energy transition and one of the world’s most precious minerals.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnered with EnergyX to explore why now may be the time to invest in lithium.
1. Lithium Prices Have Dropped
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating an investment is ensuring that the asset’s value is higher than its price would indicate. Lithium is integral to powering EVs, and, prices have fallen fast over the last year:
| Date | LiOH·H₂O* | Li₂CO₃** |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2023 | $76 | $71 |
| March 2023 | $71 | $61 |
| Apr 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| May 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| June 2023 | $47 | $45 |
| July 2023 | $44 | $40 |
| Aug 2023 | $35 | $35 |
| Sept 2023 | $28 | $27 |
| Oct 2023 | $24 | $23 |
| Nov 2023 | $21 | $21 |
| Dec 2023 | $17 | $16 |
| Jan 2024 | $14 | $15 |
| Feb 2024 | $13 | $14 |
Note: Monthly spot prices were taken as close to the 14th of each month as possible.
*Lithium hydroxide monohydrate MB-LI-0033
**Lithium carbonate MB-LI-0029
2. Lithium-Ion Battery Prices Are Also Falling
The drop in lithium prices is just one reason to invest in the metal. Increasing economies of scale, coupled with low commodity prices, have caused the cost of lithium-ion batteries to drop significantly as well.
In fact, BNEF reports that between 2013 and 2023, the price of a Li-ion battery dropped by 82%.
| Year | Price per KWh |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $139 |
| 2022 | $161 |
| 2021 | $150 |
| 2020 | $160 |
| 2019 | $183 |
| 2018 | $211 |
| 2017 | $258 |
| 2016 | $345 |
| 2015 | $448 |
| 2014 | $692 |
| 2013 | $780 |

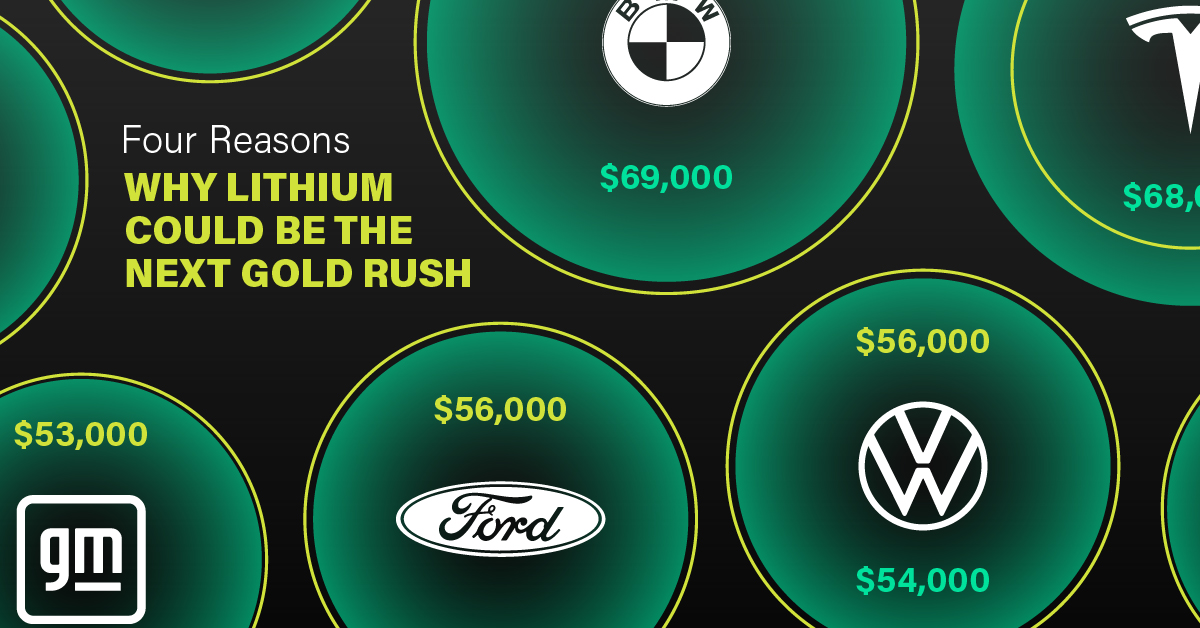
3. EV Adoption is Sustainable
One of the best reasons to invest in lithium is that EVs, one of the main drivers behind the demand for lithium, have reached a price point similar to that of traditional vehicle.
According to the Kelly Blue Book, Tesla’s average transaction price dropped by 25% between 2022 and 2023, bringing it in line with many other major manufacturers and showing that EVs are a realistic transport option from a consumer price perspective.
| Manufacturer | September 2022 | September 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| BMW | $69,000 | $72,000 |
| Ford | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| Volkswagon | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| General Motors | $52,000 | $53,000 |
| Tesla | $68,000 | $51,000 |
4. Electricity Demand in Transport is Growing
As EVs become an accessible transport option, there’s an investment opportunity in lithium. But possibly the best reason to invest in lithium is that the IEA reports global demand for the electricity in transport could grow dramatically by 2030:
| Transport Type | 2022 | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buses 🚌 | 23,000 GWh | 50,000 GWh | 130,000 GWh |
| Cars 🚙 | 65,000 GWh | 200,000 GWh | 570,000 GWh |
| Trucks 🛻 | 4,000 GWh | 15,000 GWh | 94,000 GWh |
| Vans 🚐 | 6,000 GWh | 16,000 GWh | 72,000 GWh |
The Lithium Investment Opportunity
Lithium presents a potentially classic investment opportunity. Lithium and battery prices have dropped significantly, and recently, EVs have reached a price point similar to other vehicles. By 2030, the demand for clean energy, especially in transport, will grow dramatically.
With prices dropping and demand skyrocketing, now is the time to invest in lithium.
EnergyX is poised to exploit lithium demand with cutting-edge lithium extraction technology capable of extracting 300% more lithium than current processes.

-

 Lithium6 days ago
Lithium6 days agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.
-

 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoThe World’s Biggest Oil Producers in 2023
Just three countries accounted for 40% of global oil production last year.
-
 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoHow Much Does the U.S. Depend on Russian Uranium?
Currently, Russia is the largest foreign supplier of nuclear power fuel to the U.S.
-
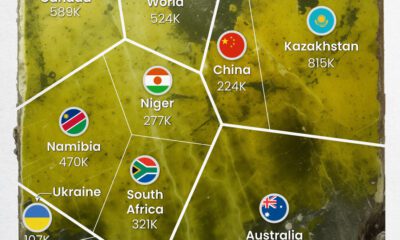
 Uranium2 months ago
Uranium2 months agoCharted: Global Uranium Reserves, by Country
We visualize the distribution of the world’s uranium reserves by country, with 3 countries accounting for more than half of total reserves.
-
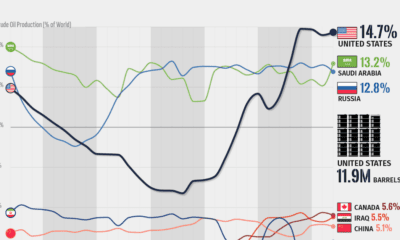
 Energy3 months ago
Energy3 months agoVisualizing the Rise of the U.S. as Top Crude Oil Producer
Over the last decade, the United States has established itself as the world’s top producer of crude oil, surpassing Saudi Arabia and Russia.
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue