Money
Student Loan Delinquencies are Sky High [Chart]
![Student Loan Delinquencies are Sky High [Chart]](https://www.visualcapitalist.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/student-loan-debt-chart.png)
Student Loan Delinquencies are Sky High [Chart]
Simple arithmetic shows one of these loans is not like the other
The Chart of the Week is a weekly Visual Capitalist feature on Fridays.
What do you get when you combine skyrocketing tuition costs, a lack of growth in high-paying jobs, moral hazard, and America’s largest-ever generation of students?
It’s a recipe for a mountain of $1.3 trillion in student loan debt – much of which is not being paid for.
Very Delinquent Students
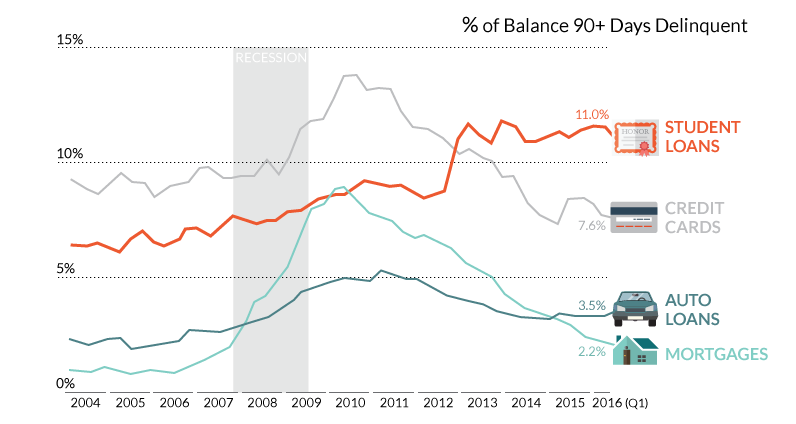
With many students graduating with high debt loads, a growing number of students are becoming delinquent on their loans. The most recent estimate by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York estimates the percent of 90+ day delinquent loans to now be at 11.0%.
This puts student loans at a higher delinquency rate than credit cards (7.6%), auto loans (3.5%), and mortgages (2.2%). It’s also particularly interesting because historically credit cards have had the highest rates among all types of consumer credit. Despite this, student loans “passed” credit cards in delinquency frequency at the end of 2012.
Why are student loans the most troubled form of consumer debt right now? It’s the result of a clear mismatch between supply and demand for college-educated workers.
The Overeducation Bubble
Have college graduates been oversold on the prospects of a college degree? Or is the market for high-paying jobs not materializing as expected in the current low-growth economy?
Either way, many college grads are punching below their weight in the job market. In a 2014 study, economists affiliated with the Federal Reserve Bank of New York found that up to 49% of recent college graduates aged 22 to 27 were working in careers that do not requite any college education.
Based on this and other factors, renowned investor Peter Thiel has called higher education to be a bubble:
If a college degree always means higher wages, then everyone should get a college degree. But how can everyone win a zero-sum tournament? No single path can work for everyone, and the promise of such an easy path is a sign of a bubble.
He’s backed up his opinion with the Thiel Fellowship, a $100,000 grant for would-be students who want to “build something” rather than sit in a classroom.
Some Students Left Behind
A recent survey shows that many graduates are regretting their choices around student debt and education. Roughly 57% of millennials now say they regret how much they borrowed, and over one-third of respondents said they wouldn’t have gone to college if they knew the true price tag.
Massive debt loads and the increasing student loan delinquency rate translate into real consequences for the economy. Many graduates are deferring having families or owning homes. One study even says that a modest student loan debt of $30,000 could cut $325,000 from a person’s 401(k) balance by retirement time.
Money
Charted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
Just two countries account for half of the top 20 cities with the most billionaires. And the majority of the other half are found in Asia.
Charted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Some cities seem to attract the rich. Take New York City for example, which has 340,000 high-net-worth residents with investable assets of more than $1 million.
But there’s a vast difference between being a millionaire and a billionaire. So where do the richest of them all live?
Using data from the Hurun Global Rich List 2024, we rank the top 20 cities with the highest number of billionaires in 2024.
A caveat to these rich lists: sources often vary on figures and exact rankings. For example, in last year’s reports, Forbes had New York as the city with the most billionaires, while the Hurun Global Rich List placed Beijing at the top spot.
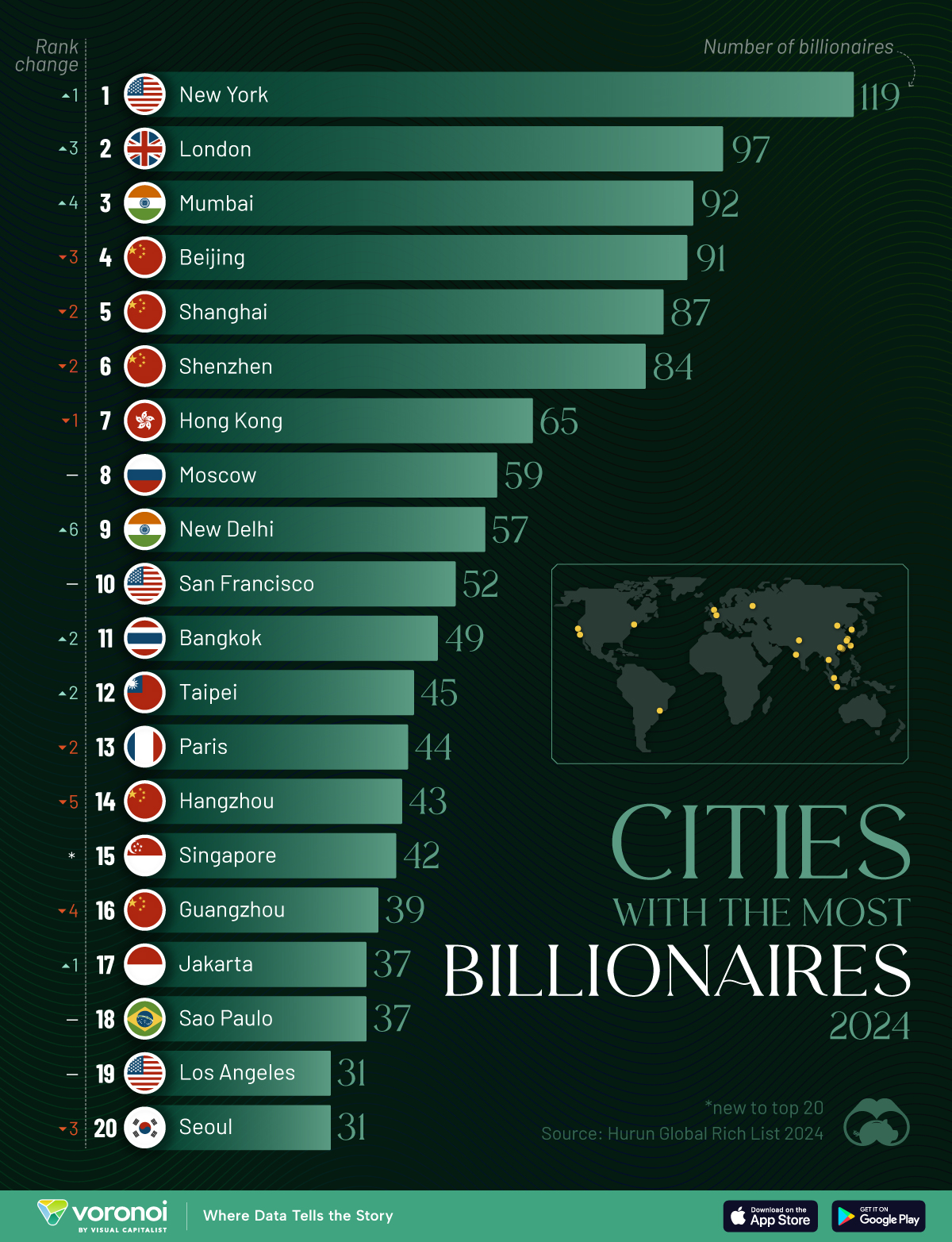
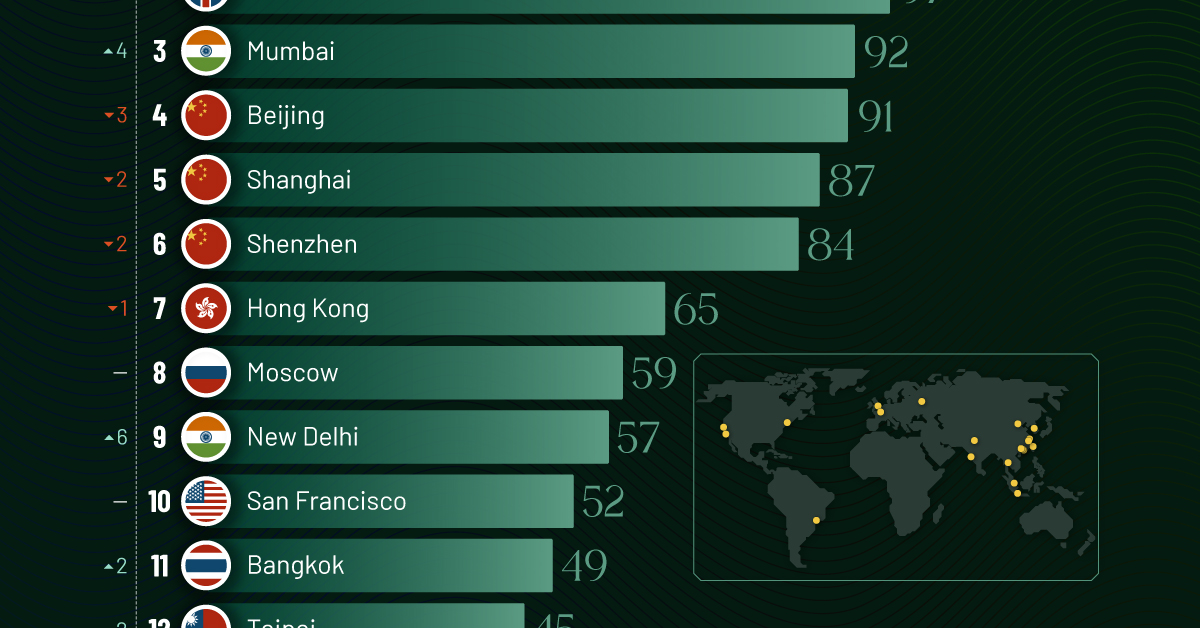
Ranked: Top 20 Cities with the Most Billionaires in 2024
The Chinese economy’s doldrums over the course of the past year have affected its ultra-wealthy residents in key cities.
Beijing, the city with the most billionaires in 2023, has not only ceded its spot to New York, but has dropped to #4, overtaken by London and Mumbai.
| Rank | City | Billionaires | Rank Change YoY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 New York | 119 | +1 |
| 2 | 🇬🇧 London | 97 | +3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Mumbai | 92 | +4 |
| 4 | 🇨🇳 Beijing | 91 | -3 |
| 5 | 🇨🇳 Shanghai | 87 | -2 |
| 6 | 🇨🇳 Shenzhen | 84 | -2 |
| 7 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | 65 | -1 |
| 8 | 🇷🇺 Moscow | 59 | No Change |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi | 57 | +6 |
| 10 | 🇺🇸 San Francisco | 52 | No Change |
| 11 | 🇹🇭 Bangkok | 49 | +2 |
| 12 | 🇹🇼 Taipei | 45 | +2 |
| 13 | 🇫🇷 Paris | 44 | -2 |
| 14 | 🇨🇳 Hangzhou | 43 | -5 |
| 15 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 42 | New to Top 20 |
| 16 | 🇨🇳 Guangzhou | 39 | -4 |
| 17T | 🇮🇩 Jakarta | 37 | +1 |
| 17T | 🇧🇷 Sao Paulo | 37 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇺🇸 Los Angeles | 31 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇰🇷 Seoul | 31 | -3 |
In fact all Chinese cities on the top 20 list have lost billionaires between 2023–24. Consequently, they’ve all lost ranking spots as well, with Hangzhou seeing the biggest slide (-5) in the top 20.
Where China lost, all other Asian cities—except Seoul—in the top 20 have gained ranks. Indian cities lead the way, with New Delhi (+6) and Mumbai (+3) having climbed the most.
At a country level, China and the U.S combine to make up half of the cities in the top 20. They are also home to about half of the world’s 3,200 billionaire population.
In other news of note: Hurun officially counts Taylor Swift as a billionaire, estimating her net worth at $1.2 billion.
-

 Science7 days ago
Science7 days agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023