Mining
More Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Silver is one of the first metals that humans discovered and used. Its extensive use throughout history has linked its name to its monetary value. However, as we have advanced technologically, so have our uses for silver. In the future, silver will see a surge in demand from solar and electric vehicle (EV) technologies.
Part 1 and Part 2 of the Silver Series showcased its monetary legacy as a safe haven asset as a precious metal and why now is its time to shine.
Part 3 of the Silver Series comes to us from Endeavour Silver, and it outlines silver’s role in the new energy era and how it is more than just a precious metal.
A Sterling Reputation: Silver’s History in Technologies
Silver along with gold, copper, lead and iron, was one of the first metals known to humankind. Archaeologists have uncovered silver coins and objects dating from before 4,000 BC in Greece and Turkey. Since then, governments and jewelers embraced its properties to mint currency and craft jewelry.
This historical association between silver and money is recorded across multiple languages. The word silver itself comes from the Anglo-Saxon language, seolfor, which itself comes from ancient Germanic silabar.
Silver’s chemical symbol, “Ag”, is an abbreviation of the Latin word for silver, argentum. The Latin word originates from argunas, a Sanskrit word which means shining. The French use argent as the word for money and silver. Romans bankers and silver traders carried the name argentarius.
While silver’s monetary meanings still stand today, there have been hints of its use beyond money throughout history. For centuries, many cultures used silver containers and wares to store wine, water, and food to prevent spoilage.
During bouts of bubonic plague in Europe, children of wealthy families sucked on silver spoons to preserve their health, which gave birth to the phrase “born with a silver spoon in your mouth.”
Medieval doctors invented silver nitrate used to treat ulcers and burns, a practice that continues to this day. In the 1900s, silver found further application in healthcare. Doctors used to administer eye drops containing silver to newborns in the United States. During World War I, combat medics, doctors, and nurses would apply silver sutures to cover deep wounds.
Silver’s shimmer also made an important material in photography up until the 1970s. Silver’s reflectivity of light made it popular in mirror and building windows.
Now, a new era is rediscovering silver’s properties for the next generation of technology, making the metal more than precious.
Silver in the New Energy Era: Solar and EVs
Silver’s shimmering qualities foreshadowed its use in renewable technologies. Among all metals, silver has the highest electrical conductivity, making it an ideal metal for use in solar cells and the electronic components of electric vehicles.
Silver in Solar Photovoltaics
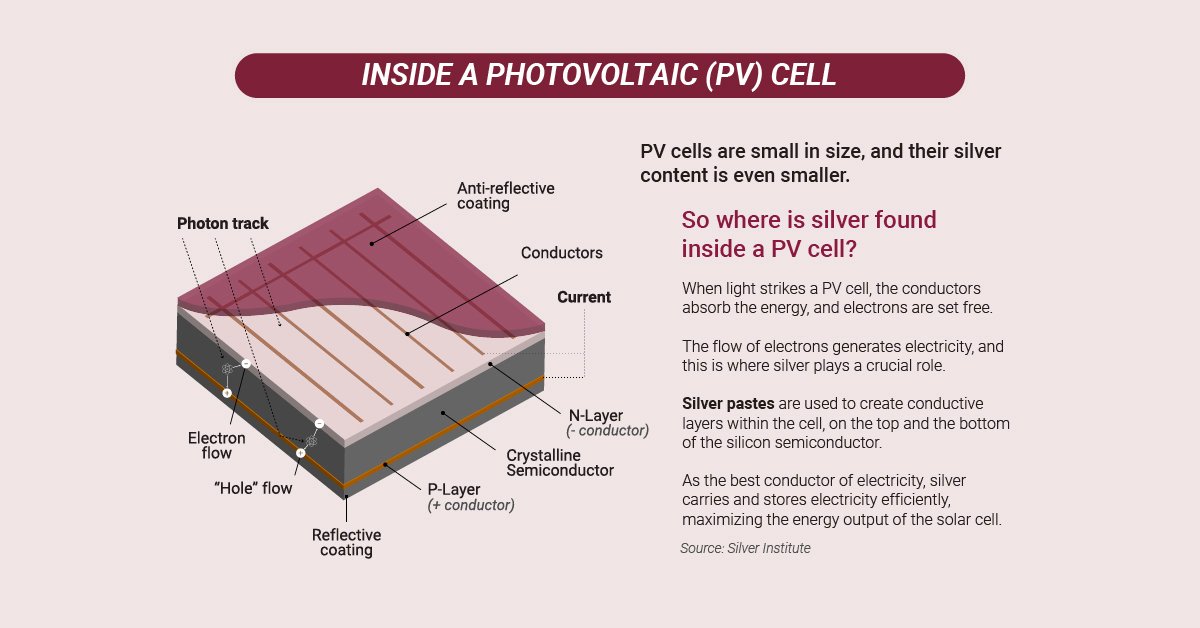
Conductive layers of silver paste within the cells of a solar photovoltaic (PV) cell help to conduct the electricity within the cell. When light strikes a PV, the conductors absorb the energy and electrons are set free.
Silver’s conductivity carries and stores the free electrons efficiently, maximizing the energy output of a solar cell. According to one study from the University of Kent, a typical solar panel can contain as much as 20 grams of silver.
As the world adopts solar photovoltaics, silver could see dramatic demand coming from this form of renewable energy.
Silver in Electric Vehicles
Silver’s conductivity and corrosion resistance makes its use in electronics critical, and electric vehicles are no exception. Virtually every electrical connection in a vehicle uses silver.
Silver is a critical material in the automotive sector, which uses over 55 million ounces of the metal annually. Auto manufacturers apply silver to the electrical contacts in powered seats and windows and other automotive electronics to improve conductivity.
A Silver Intensive Future
A green future will require metals and will redefine the role for many of them. Silver is no exception. Long known as a precious metal, silver also has industrial applications metal for an eco-friendly future.
Lithium
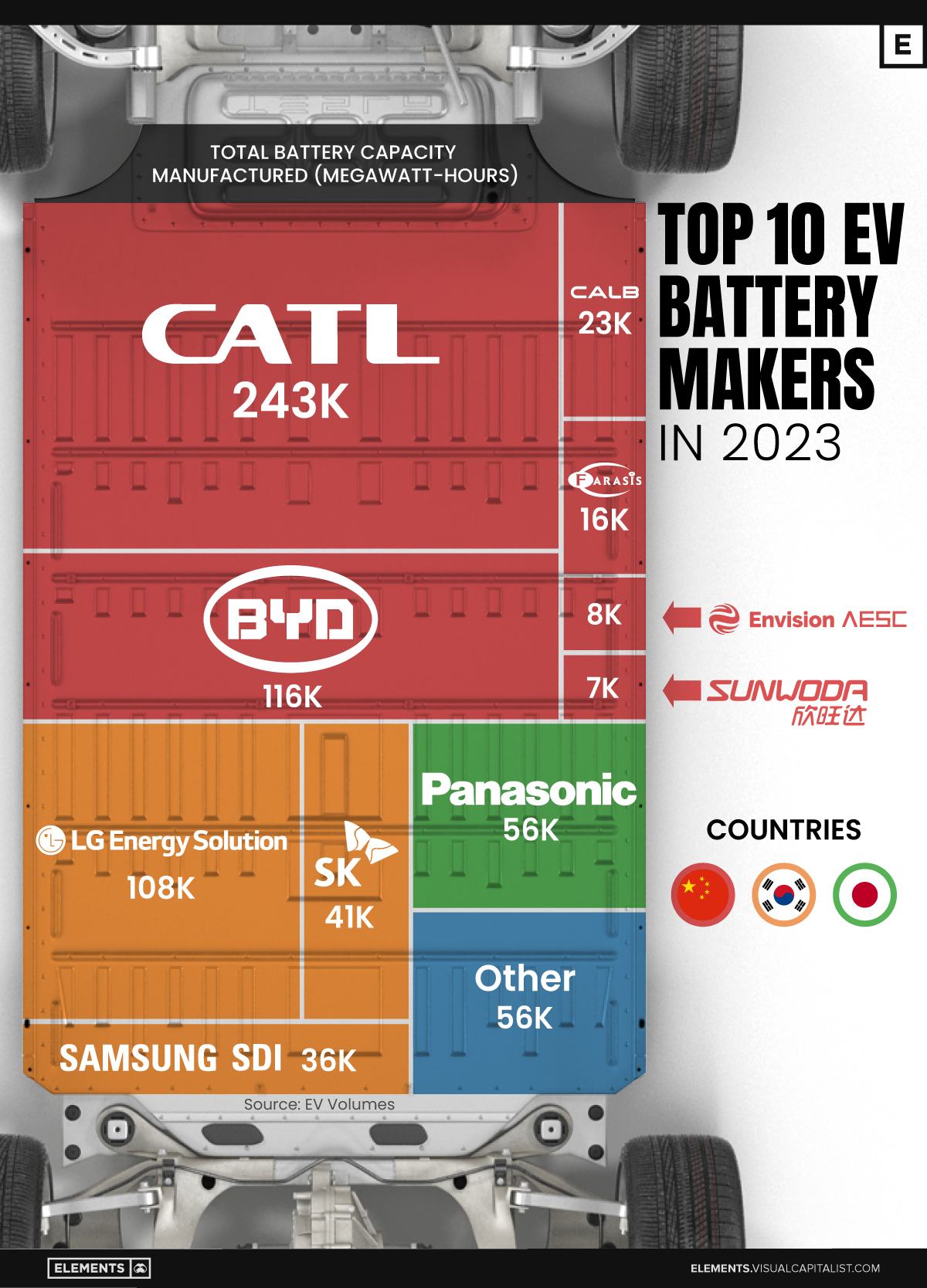
Ranked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
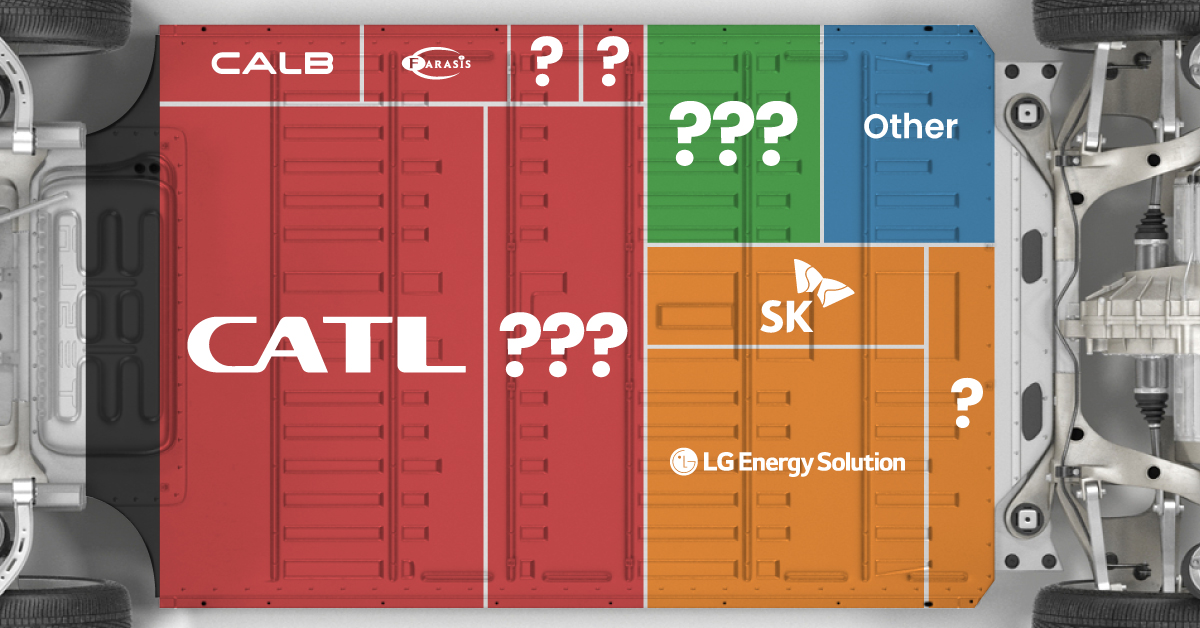
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts from the U.S. and EU to secure local domestic supply, all major EV battery manufacturers remain based in Asia.
In this graphic we rank the top 10 EV battery manufacturers by total battery deployment (measured in megawatt-hours) in 2023. The data is from EV Volumes.
Chinese Dominance
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has swiftly risen in less than a decade to claim the title of the largest global battery group.
The Chinese company now has a 34% share of the market and supplies batteries to a range of made-in-China vehicles, including the Tesla Model Y, SAIC’s MG4/Mulan, and various Li Auto models.
| Company | Country | 2023 Production (megawatt-hour) | Share of Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL | 🇨🇳 China | 242,700 | 34% |
| BYD | 🇨🇳 China | 115,917 | 16% |
| LG Energy Solution | 🇰🇷 Korea | 108,487 | 15% |
| Panasonic | 🇯🇵 Japan | 56,560 | 8% |
| SK On | 🇰🇷 Korea | 40,711 | 6% |
| Samsung SDI | 🇰🇷 Korea | 35,703 | 5% |
| CALB | 🇨🇳 China | 23,493 | 3% |
| Farasis Energy | 🇨🇳 China | 16,527 | 2% |
| Envision AESC | 🇨🇳 China | 8,342 | 1% |
| Sunwoda | 🇨🇳 China | 6,979 | 1% |
| Other | - | 56,040 | 8% |
In 2023, BYD surpassed LG Energy Solution to claim second place. This was driven by demand from its own models and growth in third-party deals, including providing batteries for the made-in-Germany Tesla Model Y, Toyota bZ3, Changan UNI-V, Venucia V-Online, as well as several Haval and FAW models.
The top three battery makers (CATL, BYD, LG) collectively account for two-thirds (66%) of total battery deployment.
Once a leader in the EV battery business, Panasonic now holds the fourth position with an 8% market share, down from 9% last year. With its main client, Tesla, now sourcing batteries from multiple suppliers, the Japanese battery maker seems to be losing its competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, the global EV battery market size is projected to grow from $49 billion in 2022 to $98 billion by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001