Personal Finance
Charted: Retirement Age by Country
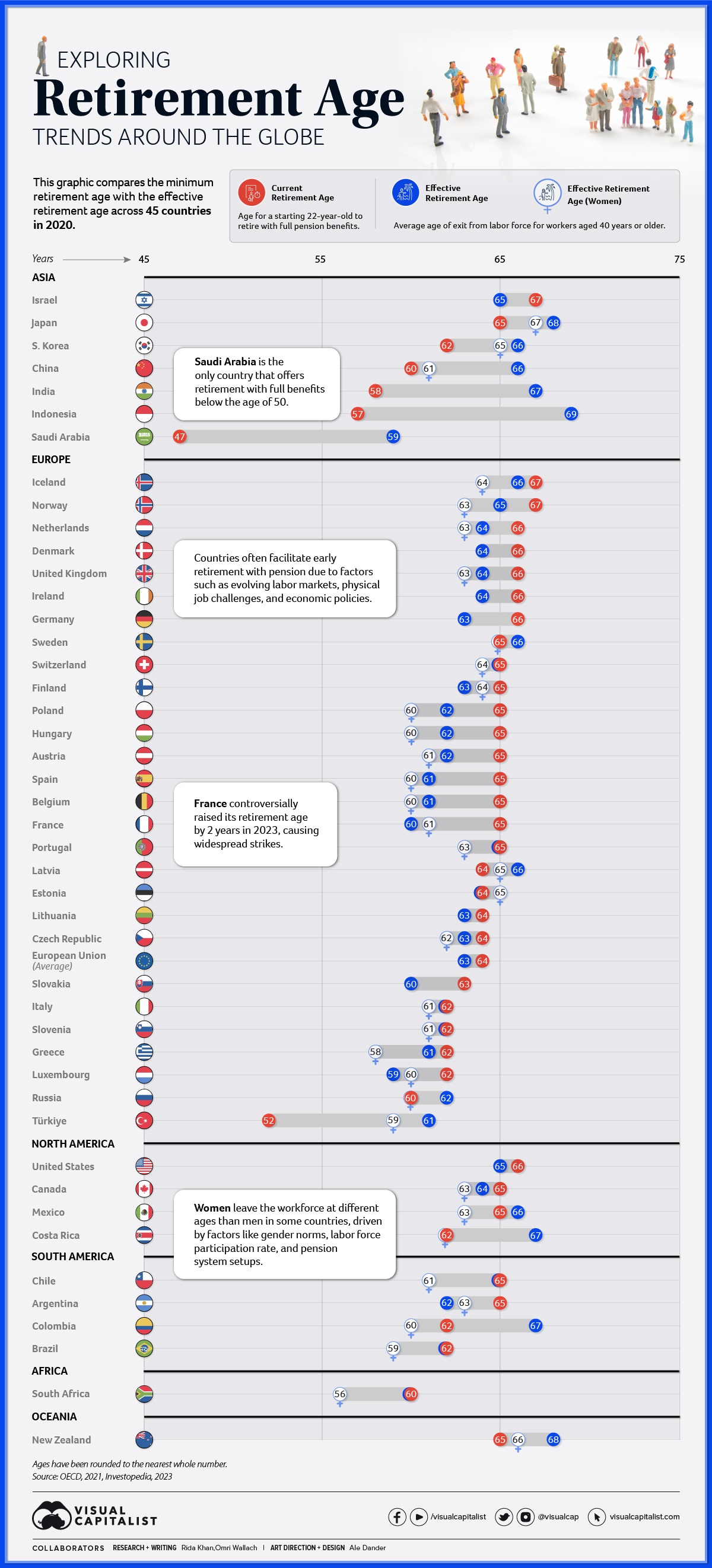
Charted: Retirement Age by Country
The retirement landscape can look completely different depending on what country you’re in. And charting the retirement age by country reveals a lot of differences in the the makeup of a labor force, both for economic and cultural reasons.
This graphic delves into the current and effective retirement ages across 45 nations in 2020, based on comprehensive data from the OECD 2021 report.
Defining Retirement Ages
Before we dive into the numbers, let’s clarify the measurements used by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- The current retirement age is the age at which individuals can retire without penalty to pension after completing a full career starting from age 22.
- The effective retirement age refers to the average age of exit from the labor force for workers aged 40 years or more.
Many countries have seen workers effectively retire earlier or later than the current retirement age. This variance can arise due to a multitude in factors including differences in career start ages, some industries offering earlier retirements or benefits for later commitments, or countries facilitating different workforce exits due to market demands and policies.
Some people also choose to retire early due to personal reasons or a lack of available work, receiving a smaller pension or in some cases forgoing it entirely. Likewise, some people choose to stay employed if they are able to find work.
Retirement Age by Country in 2020
Here’s a snapshot of the current and effective retirement ages by country in 2020:
| Country | Retirement age (Current) | Retirement age (Effective) | Retirement age (Women, Effective) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 65 | 62 | 61 |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 65 | 61 | 60 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 65 | 64 | 63 |
| 🇨🇱 Chile | 65 | 65 | 61 |
| 🇨🇴 Colombia | 62 | 67 | 60 |
| 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 62 | 67 | 62 |
| 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 64 | 63 | 62 |
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | 66 | 64 | N/A |
| 🇪🇪 Estonia | 64 | 64 | 65 |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 65 | 63 | 64 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 65 | 60 | 61 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 66 | 63 | N/A |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 62 | 61 | 58 |
| 🇭🇺 Hungary | 65 | 62 | 60 |
| 🇮🇸 Iceland | 67 | 66 | 64 |
| 🇮🇪 Ireland | 66 | 64 | N/A |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | 67 | 65 | N/A |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 62 | 62 | 61 |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 65 | 68 | 67 |
| 🇰🇷 Korea, Republic of | 62 | 66 | 65 |
| 🇱🇻 Latvia | 64 | 66 | 65 |
| 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 64 | 63 | N/A |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 62 | 59 | 60 |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | 65 | 66 | 63 |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 66 | 64 | 63 |
| 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 65 | 68 | 66 |
| 🇳🇴 Norway | 67 | 65 | 63 |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | 65 | 62 | 60 |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 65 | 65 | 63 |
| 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 63 | 60 | N/A |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 62 | 62 | 61 |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 65 | 61 | 60 |
| 🇸🇪 Sweden | 65 | 66 | 65 |
| 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 65 | 65 | 64 |
| 🇹🇷 Türkiye | 52 | 61 | 59 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 66 | 64 | 63 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 66 | 65 | N/A |
| 🇪🇺 European Union (Average) | 64 | 63 | N/A |
| 🇦🇷 Argentina | 65 | 62 | 63 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 62 | 62 | 59 |
| 🇨🇳 China (People's Republic of) | 60 | 66 | 61 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 58 | 67 | N/A |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 57 | 69 | N/A |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 62 | 62 | 60 |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 47 | 59 | N/A |
| 🇿🇦 South Africa | 60 | 60 | 56 |
Three countries had the highest current retirement age at 67 years, Iceland, Israel, and Norway, but all had slightly lower effective retirement ages on average. On the flip side, Saudi Arabia had the lowest current retirement age at only 47 years with full pension benefits. Only Türkiye at 52 years was close, and notably both had much higher effective retirement ages on average.
Discrepancies between different regions are clear across the board. Many Asian countries including China, India, and South Korea have official minimum retirement ages in the early 60s and late 50s, but see workers stay in the workforce well into their late 60s. Meanwhile, most European countries as well as the U.S. and Canada have more workers retire earlier than minimum retirement ages on average.
Almost all of the countries with measured effective retirement ages for women also saw them exit the workforce earlier than men. This can be the result of cultural gender norms, labor force participation rates, and even the setup of pension systems in different countries.
The five exceptions in the dataset where women retired later than men? Argentina, Estonia, Finland, France, and Luxembourg.
Looking to the Future
In 2023, France sparked controversy by raising its early retirement age by two years. This decision triggered widespread strikes and riots and ignited debates about the balance between economic sustainability and individual well-being.
Given aging demographics in many developed countries and a continued need for labor, this isn’t expected to be the only country to reassess retirement. The OECD projects a two-year increase in the average effective retirement age by the mid-2060s.
Personal Finance
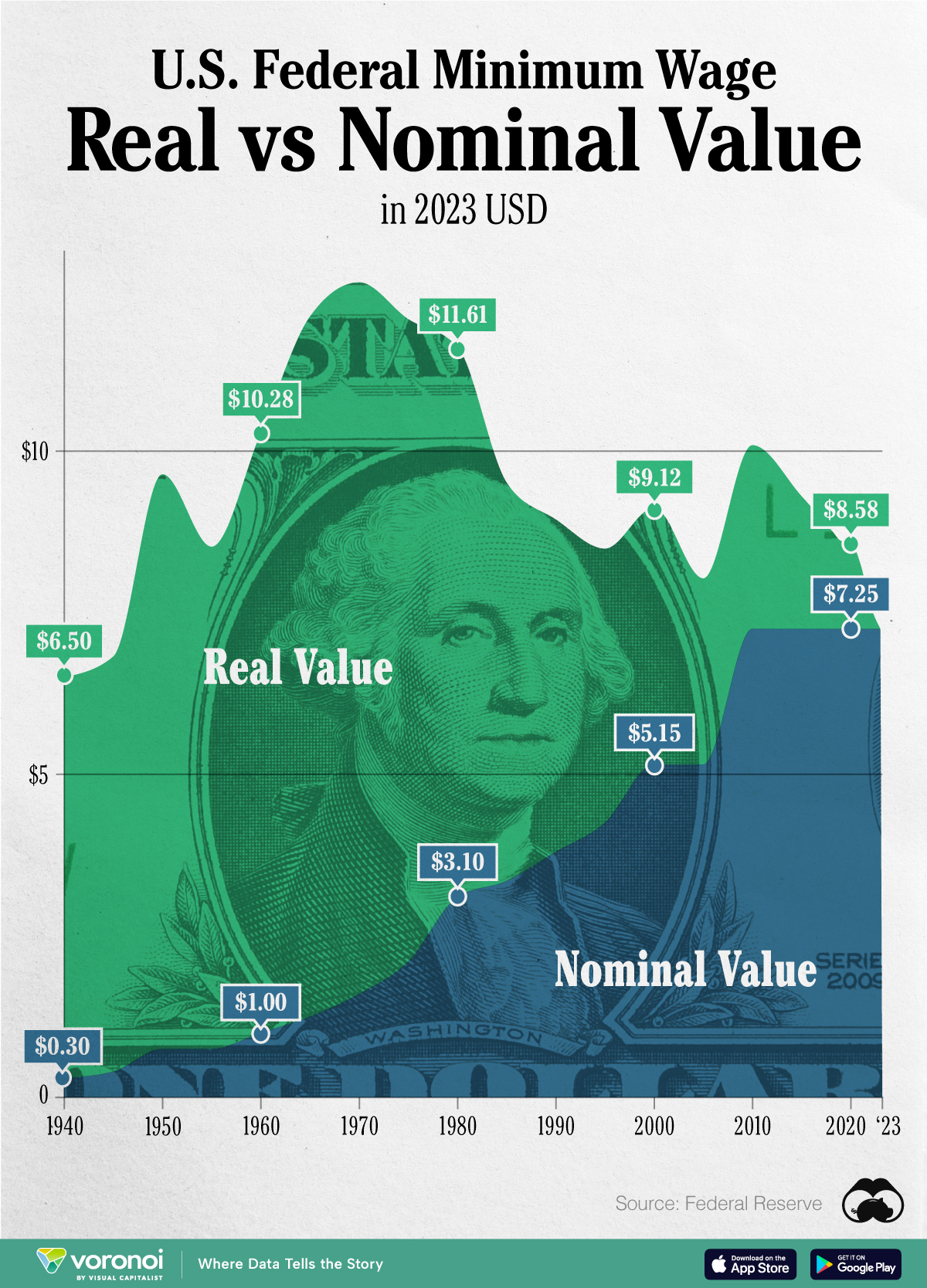
Chart: The Declining Value of the U.S. Federal Minimum Wage
This graphic compares the nominal vs. inflation-adjusted value of the U.S. minimum wage, from 1940 to 2023.

The Declining Value of the U.S. Federal Minimum Wage
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This graphic illustrates the history of the U.S. federal minimum wage using data compiled by Statista, in both nominal and real (inflation-adjusted) terms. The federal minimum wage was raised to $7.25 per hour in July 2009, where it has remained ever since.
Nominal vs. Real Value
The data we used to create this graphic can be found in the table below.
| Year | Nominal value ($/hour) | Real value ($/hour) |
|---|---|---|
| 1940 | 0.3 | 6.5 |
| 1945 | 0.4 | 6.82 |
| 1950 | 0.75 | 9.64 |
| 1955 | 0.75 | 8.52 |
| 1960 | 1 | 10.28 |
| 1965 | 1.25 | 12.08 |
| 1970 | 1.6 | 12.61 |
| 1975 | 2.1 | 12.04 |
| 1980 | 3.1 | 11.61 |
| 1985 | 3.35 | 9.51 |
| 1990 | 3.8 | 8.94 |
| 1995 | 4.25 | 8.49 |
| 2000 | 5.15 | 9.12 |
| 2005 | 5.15 | 8.03 |
| 2010 | 7.25 | 10.09 |
| 2015 | 7.25 | 9.3 |
| 2018 | 7.25 | 8.78 |
| 2019 | 7.25 | 8.61 |
| 2020 | 7.25 | 8.58 |
| 2021 | 7.25 | 8.24 |
| 2022 | 7.25 | 7.61 |
| 2023 | 7.25 | 7.25 |
What our graphic shows is how inflation has eroded the real value of the U.S. minimum wage over time, despite nominal increases.
For instance, consider the year 1960, when the federal minimum wage was $1 per hour. After accounting for inflation, this would be worth around $10.28 today!
The two lines converge at 2023 because the nominal and real value are identical in present day terms.
Many States Have Their Own Minimum Wage
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL), 30 states and Washington, D.C. have implemented a minimum wage that is higher than $7.25.
The following states have adopted the federal minimum: Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, New Hampshire, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Texas, Utah, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
Meanwhile, the states of Alabama, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, and Tennessee have no wage minimums, but have to follow the federal minimum.
How Does the U.S. Minimum Wage Rank Globally?
If you found this topic interesting, check out Mapped: Minimum Wage Around the World to see which countries have the highest minimum wage in monthly terms, as of January 2023.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees