Technology
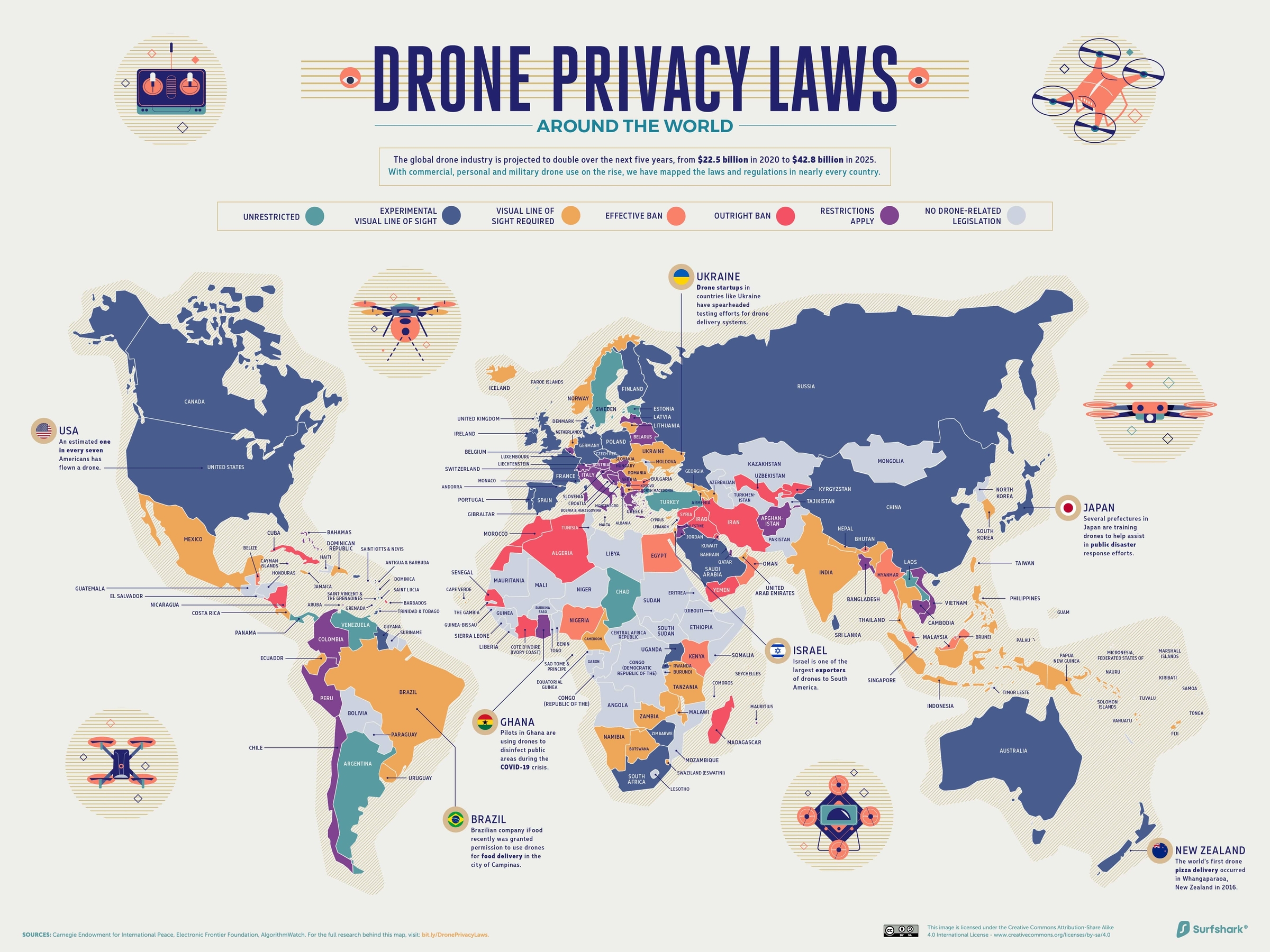
Mapped: Drone Privacy Laws Around the World
View the full-resolution version of this infographic
Mapped: Drone Privacy Laws Around the World
View the high-resolution of the infographic by clicking here.
From Olympic opening ceremonies to public safety, drone applications have come a long way.
In fact, their modern applications are set to almost double the total value of the commercial drone market from $22.5 billion to $42.8 billion between 2020-2025, at a 13.8% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
Naturally, such diverse and complex uses can go quickly awry if not monitored and regulated correctly by governments—yet in some cases, it’s because of governments that drones’ uses border on sinister.
This in-depth map from Surfshark explores the murky guidelines surrounding drone privacy laws around the world, and some case studies of how they’re used in every region.
How Are Drone Privacy Laws Classified?
According to the map researchers, drone and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) regulations typically fall into one of the following buckets:
- Outright ban
- Effective ban
- Visual line of sight required
Pilots need to be able to see the drones at all times, and must usually obtain a license or permit - Experimental visual line of sight
Pilots can let the drone fly outside their field of vision e.g. during a race - Restrictions apply
Drones need to be registered, and/or additional observers are required - Unrestricted
When drones are flown around private property and airports, and under 500 feet (150 meters) - No drone-related legislation
Categories are assigned based on legislation as of October 2020.
Clearly, there is some overlap among these categories. They are highly dependent on judgment calls made by specific legal authorities, and change based on what a drone is being used for.
Explore the drone privacy laws in your specific country here:
| Country/Territory | Continent | Drone Legal Status (Oct. 2020) |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Asia | Unrestricted |
| Albania | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Algeria | Africa | Outright ban |
| Andorra | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Angola | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Antigua and Barbuda | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Argentina | South America | Unrestricted |
| Armenia | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Aruba | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Australia | Oceania | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Austria | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Azerbaijan | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Bahamas, The | North America | Unrestricted |
| Bahrain | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Bangladesh | Asia | Unrestricted |
| Barbados | North America | Outright ban |
| Belarus | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Belgium | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Belize | North America | Effective ban |
| Benin | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Bermuda | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Bhutan | Asia | Effective ban |
| Bolivia | South America | No drone-related legislation |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Botswana | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Brazil | South America | Visual line of sight required |
| Brunei Darussalam | Asia | Outright ban |
| Bulgaria | Europe | Effective ban |
| Burkina Faso | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Burundi | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Cabo Verde | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Cambodia | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Cameroon | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Canada | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Cayman Islands | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Central African Republic | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Chad | Africa | Unrestricted |
| Chile | South America | Visual line of sight required |
| China | Asia | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Colombia | South America | Visual line of sight required |
| Comoros | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Congo, Dem. Rep. | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Congo, Rep. | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Costa Rica | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Cote d'Ivoire | Africa | Outright ban |
| Croatia | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Cuba | North America | Outright ban |
| Curacao | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Cyprus | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Czech Republic | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Denmark | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Djibouti | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Dominica | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Dominican Republic | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Ecuador | South America | Visual line of sight required |
| Egypt, Arab Rep. | Africa | Effective ban |
| El Salvador | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Equatorial Guinea | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Eritrea | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Estonia | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Ethiopia | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Faroe Islands | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Fiji | Oceania | Visual line of sight required |
| Finland | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| France | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Gabon | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Gambia, The | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Georgia | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Germany | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Ghana | Africa | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Gibraltar | Europe | Effective ban |
| Greece | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Greenland | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Grenada | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Guam | Oceania | Unrestricted |
| Guatemala | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Guinea | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Guinea-Bissau | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Guyana | South America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Haiti | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Honduras | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Hong Kong SAR, China | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Hungary | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Iceland | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| India | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Indonesia | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Iran, Islamic Rep. | Asia | Outright ban |
| Iraq | Asia | Outright ban |
| Ireland | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Israel | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Italy | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Jamaica | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Japan | Asia | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Jordan | Asia | Unrestricted |
| Kazakhstan | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Kenya | Africa | Effective ban |
| Kiribati | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Korea, Dem. People’s Rep. | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Korea, Rep. | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Kosovo | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Kuwait | Asia | Outright ban |
| Kyrgyz Republic | Asia | Outright ban |
| Lao PDR | Asia | Unrestricted |
| Latvia | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Lebanon | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Lesotho | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Liberia | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Libya | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Liechtenstein | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Lithuania | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Luxembourg | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Macao SAR, China | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Madagascar | Africa | Outright ban |
| Malawi | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Malaysia | Asia | Effective ban |
| Maldives | Asia | Effective ban |
| Mali | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Malta | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Marshall Islands | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Mauritania | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Mauritius | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Mexico | North America | Visual line of sight required |
| Micronesia, Fed. Sts. | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Moldova | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Monaco | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Mongolia | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Montenegro | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Morocco | Africa | Outright ban |
| Mozambique | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Myanmar | Asia | Effective ban |
| Namibia | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Nauru | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Nepal | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Netherlands | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| New Caledonia | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| New Zealand | Oceania | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Nicaragua | North America | Outright ban |
| Niger | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Nigeria | Africa | Effective ban |
| North Macedonia | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Norway | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Oman | Asia | Effective ban |
| Pakistan | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Palau | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Panama | North America | Unrestricted |
| Papua New Guinea | Oceania | Visual line of sight required |
| Paraguay | South America | No drone-related legislation |
| Peru | South America | Visual line of sight required |
| Philippines | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Poland | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Portugal | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Puerto Rico | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Qatar | Asia | Unrestricted |
| Romania | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Russian Federation | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Rwanda | Africa | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Samoa | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| San Marino | Europe | No drone-related legislation |
| Sao Tome and Principe | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Saudi Arabia | Asia | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Senegal | Africa | Outright ban |
| Serbia | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Seychelles | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Sierra Leone | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Singapore | Asia | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Sint Maarten (Dutch part) | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Slovak Republic | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| Slovenia | Europe | Outright ban |
| Solomon Islands | Oceania | Visual line of sight required |
| Somalia | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| South Africa | Africa | Experimental visual line of sight |
| South Sudan | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Spain | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Sri Lanka | Asia | Experimental visual line of sight |
| St. Kitts and Nevis | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| St. Lucia | North America | Unrestricted |
| St. Martin (French part) | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| St. Vincent and the Grenadines | North America | No drone-related legislation |
| Sudan | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Suriname | South America | No drone-related legislation |
| Swaziland | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Sweden | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Switzerland | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Syrian Arab Republic | Asia | Outright ban |
| Taiwan | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Tajikistan | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Tanzania | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Thailand | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| Timor-Leste | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Togo | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Tonga | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Trinidad and Tobago | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Tunisia | Africa | No drone-related legislation |
| Turkey | Europe | Unrestricted |
| Turkmenistan | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | North America | Unrestricted |
| Tuvalu | Oceania | No drone-related legislation |
| Uganda | Africa | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Ukraine | Europe | Visual line of sight required |
| United Arab Emirates | Asia | Visual line of sight required |
| United Kingdom | Europe | Experimental visual line of sight |
| United States | North America | Experimental visual line of sight |
| Uruguay | South America | Visual line of sight required |
| Uzbekistan | Asia | Outright ban |
| Vanuatu | Oceania | Visual line of sight required |
| Venezuela, RB | South America | Unrestricted |
| Vietnam | Asia | Unrestricted |
| Yemen, Rep. | Asia | No drone-related legislation |
| Zambia | Africa | Visual line of sight required |
| Zimbabwe | Africa | Experimental visual line of sight |
So How Are Drones Used Worldwide?
The myriad of drone uses are literally and metaphorically up in the air—while they originated in military needs, drone uses now range from hobbies such as aerial photography to supporting disaster relief.
The following regional maps show privacy laws in closer detail, while also highlighting interesting case studies on how drones are used.
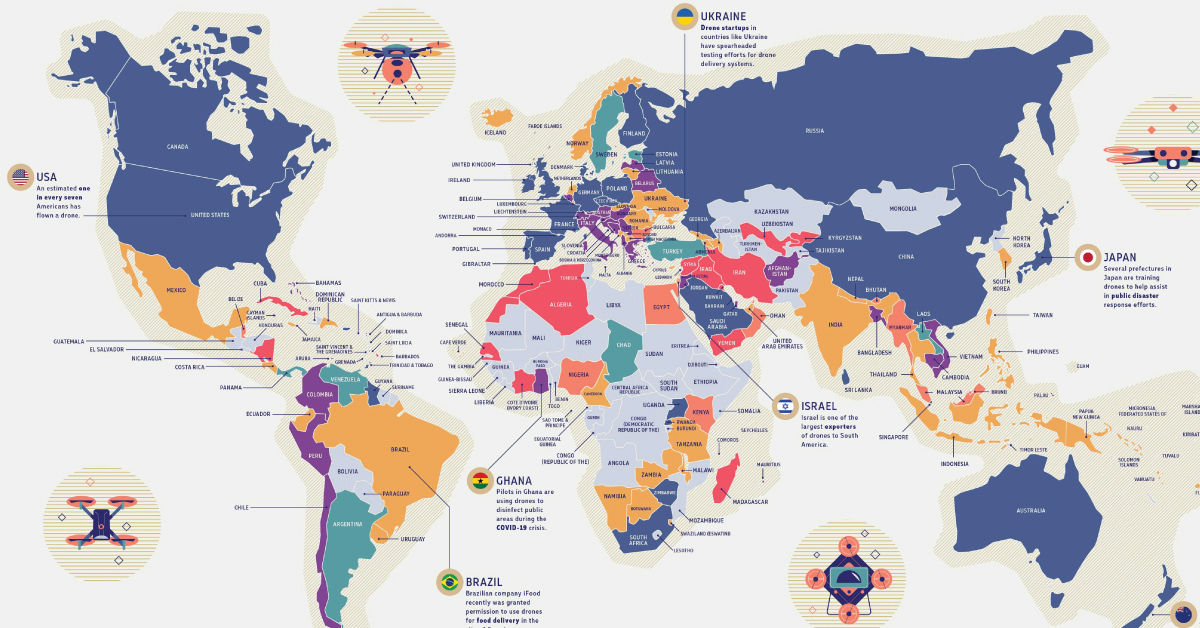
North America
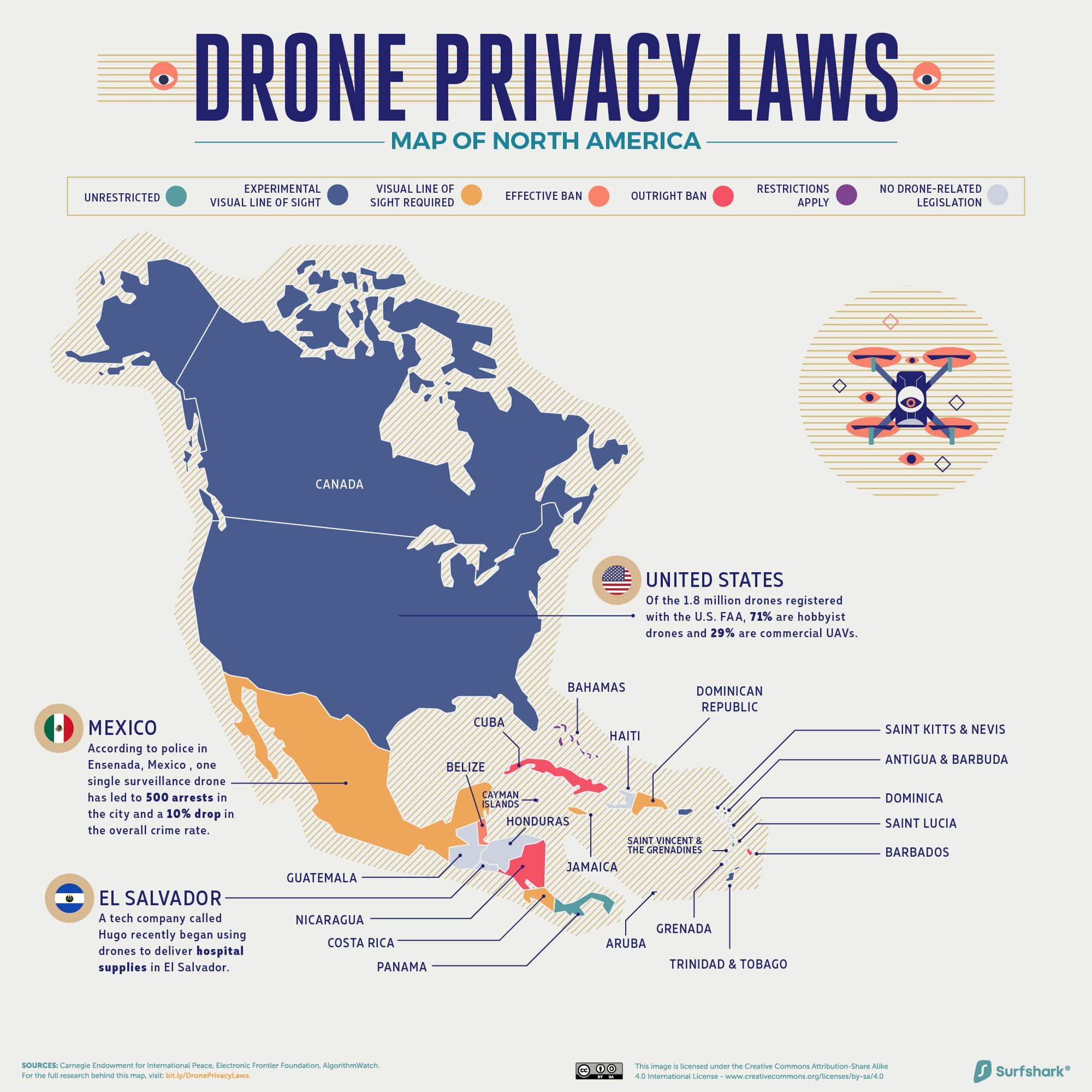
Click here for the high-resolution version of this graphic.
According to the latest drone numbers, 70.5% of registered U.S. drones are recreational, but these proportions may soon decline in favor of commercial uses. As of December 2020, civilian drones are allowed to fly over populated areas, a step towards fulfilling their potential in package delivery.
Meanwhile, countries like Mexico are beginning to rely on drones to combat crime, with good results. In the city of Ensenada, a single drone’s surveillance patrol resulted in a 10% drop in overall crime rates in 2018. Drones are increasingly being used to monitor illicit activity such as drug trafficking routes.
South America
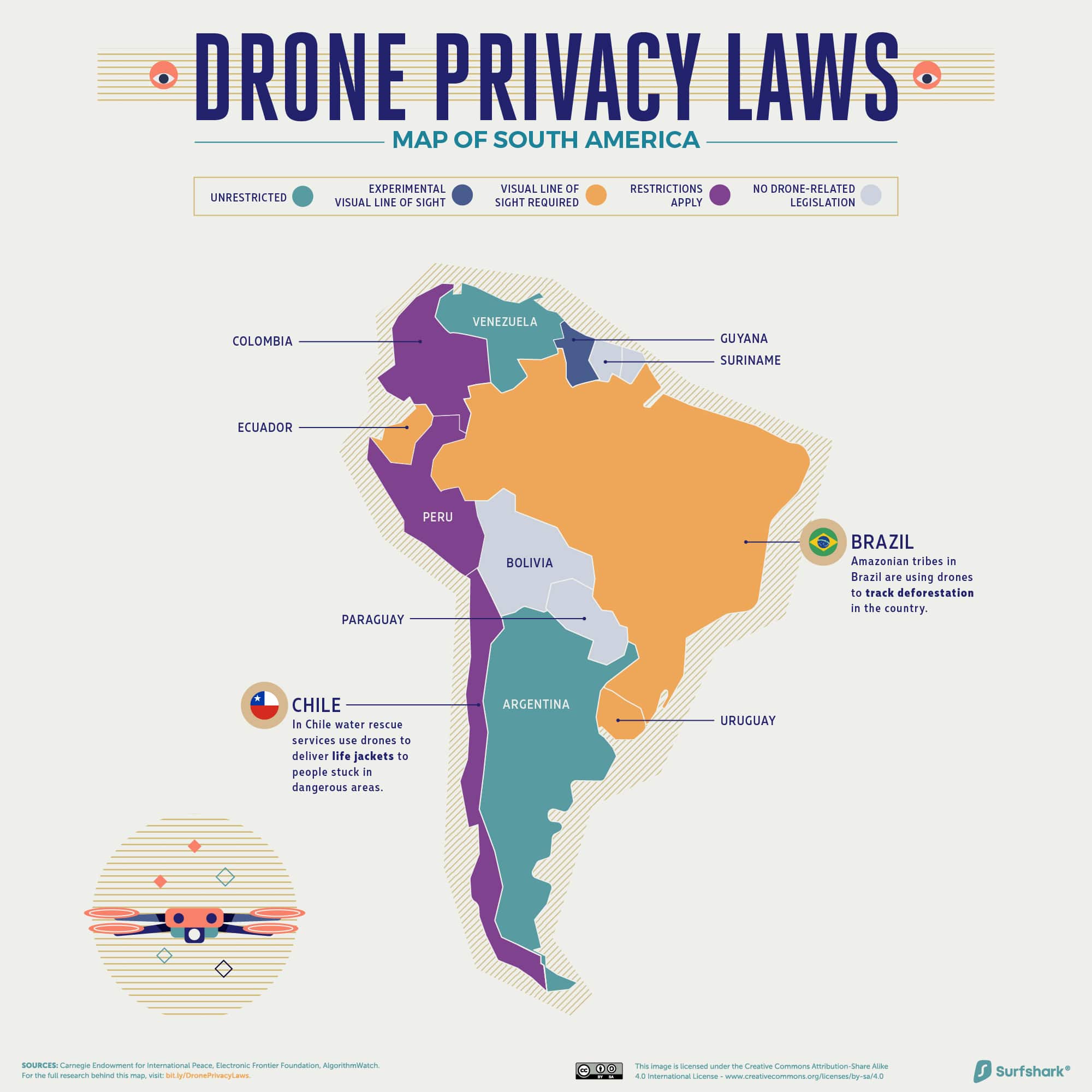
Click here for the high-resolution version of this graphic.
Interestingly, the environmental applications of drones come into play in the Amazon rainforest. An indigenous tribe in Brazil is using drones to track levels of deforestation and forest fires—and presenting that data evidence to authorities to urge them to act.
Across the continent, drones are also in place to deliver everything from hospital supplies to life jackets in Chile and El Salvador.
Europe
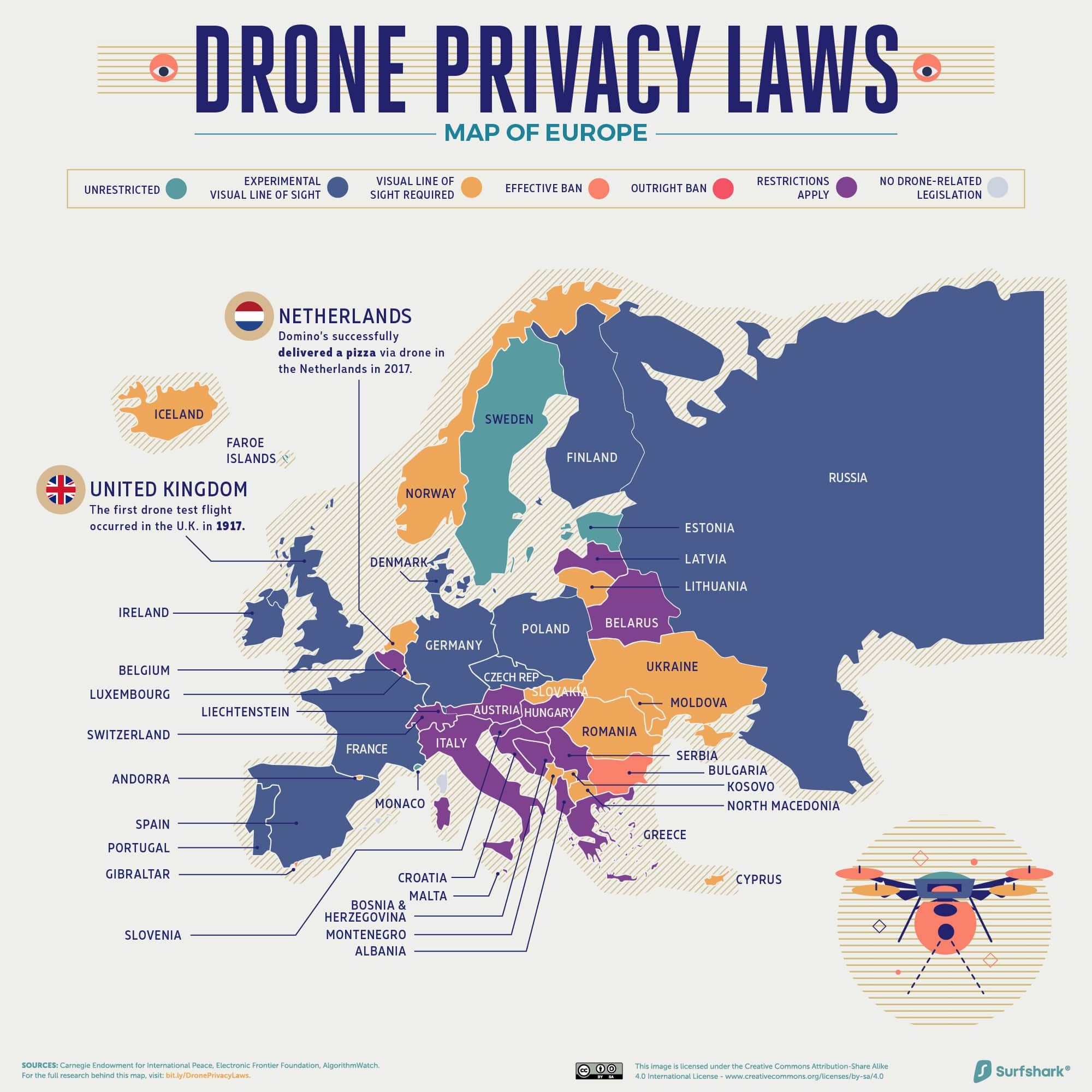
Click here for the high-resolution version of this graphic.
The first unmanned, radio-controlled aircraft test flight occurred in the United Kingdom in 1917. The Kettering Aerial Target (or “The Bug”) carried 180 pounds of explosives and became the basis for modern missiles.
While Europe has some of the most liberal drone privacy laws today, that doesn’t mean they’re lenient. Even among countries that allow experimental visual lines of sight (such as Finland and Portugal), special permissions are required.
Middle East and Central Asia
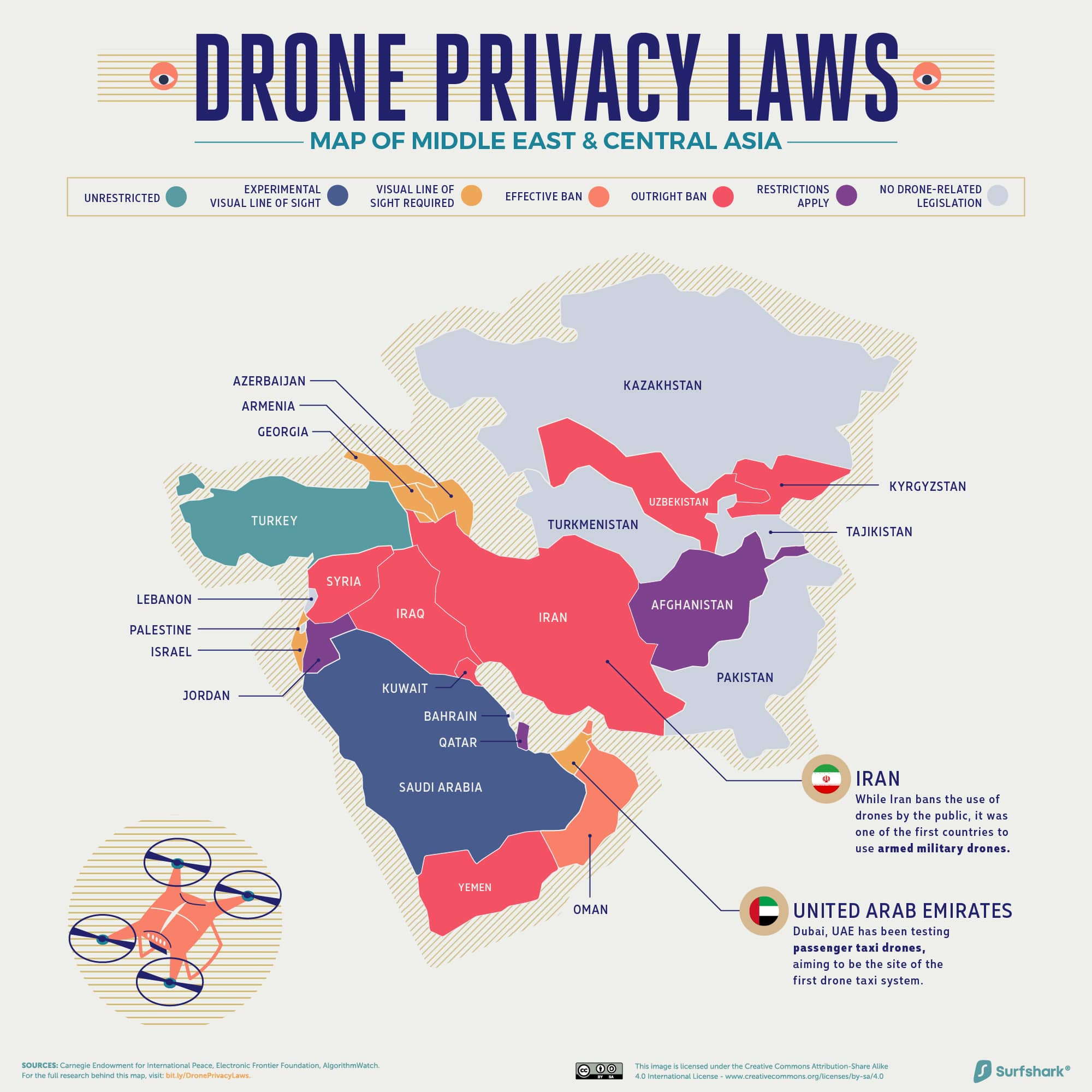
Click here for the high-resolution version of this graphic.
The military applications of drones persist in this region. Iran was one of the first to use armed drones and continues to do so, while simultaneously banning their public use.
Neighboring Turkey also relies on kamikaze drones, augmented by AI and facial recognition, to strengthen border security.
Rest of Asia and Oceania
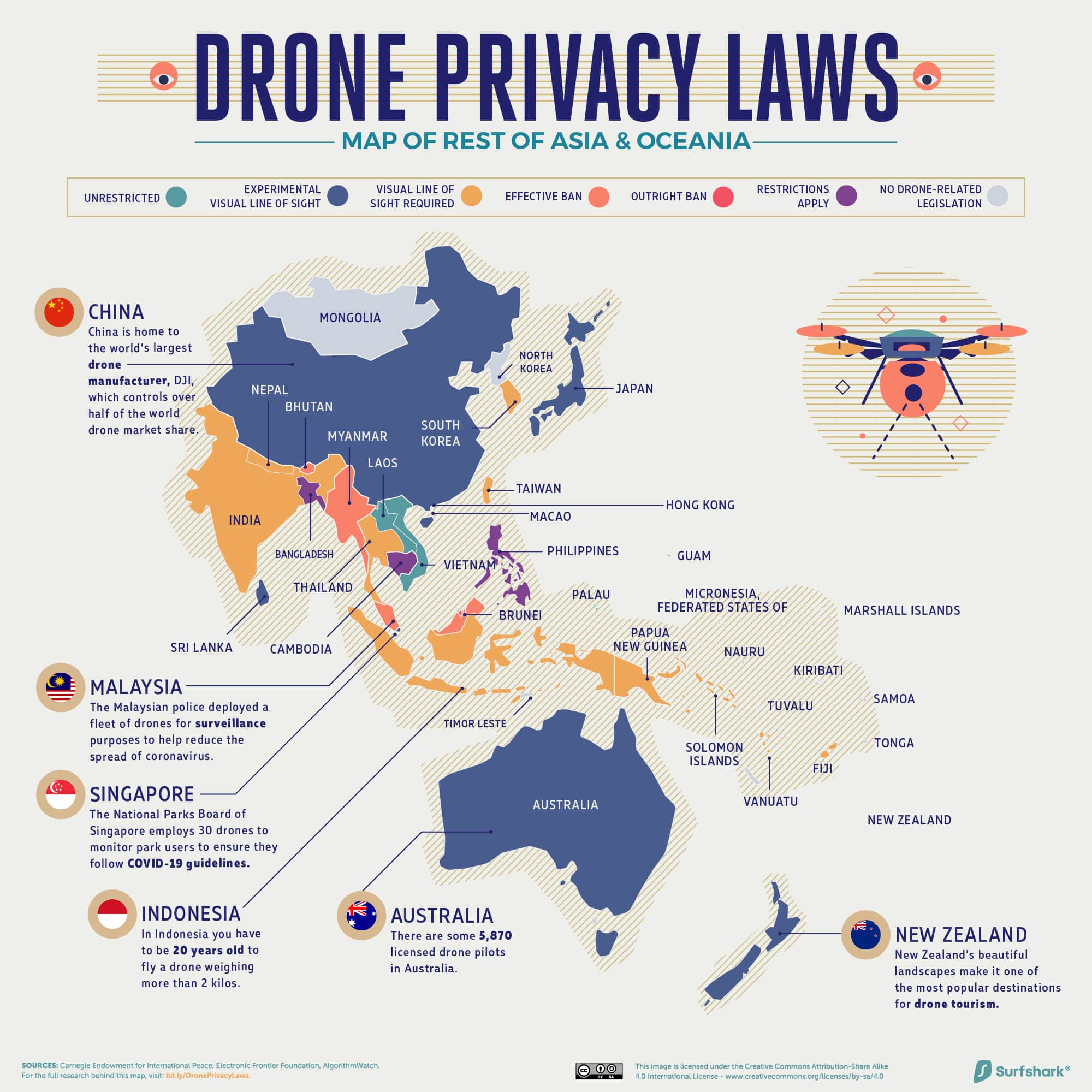
Click here for the high-resolution version of this graphic.
China-based DJI is the world’s largest drone manufacturer, dominating 70% of the global market. Across Asia, drones have been in use for mass surveillance, particularly in China. In recent times, drones also track compliance with strict COVID-19 guidelines in Malaysia and Singapore.
Meanwhile, in Japan, Nokia is testing out a drone network to provide a more rapid response to future natural disasters. The relief capabilities include disseminating more real-time updates and monitoring evacuation progress.
Africa
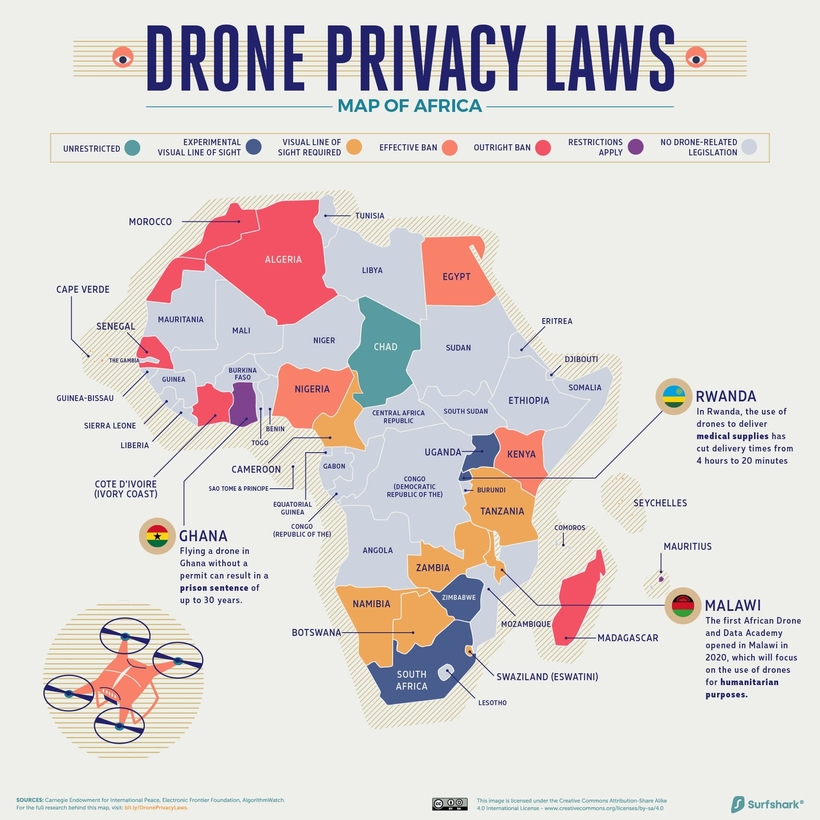
Click here for the high-resolution version of this graphic.
While many parts of Africa haven’t developed any drone-related laws yet, promising innovation is rearing its head. Medical drones are already saving lives in Rwanda, delivering supplies in as little as 15 minutes.
In the same vein, the pioneer African Drone and Data Academy (ADDA) opened in Malawi. The academy promotes drone usage for humanitarian and disaster preparedness, and aims to equip individuals with the relevant skills.
Towards Greater Heights?
As the uses of drones evolve over time, so will their legal status and the privacy concerns surrounding them. However, the adoption of any technology is always accompanied by a certain level of skepticism.
With drones, it remains to be seen whether they’ll mostly occupy the role of a friend or a foe for years to come—and that power lies only in the hands of those who remotely control them.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees