Politics
Comparing U.S. Federal Spending with Revenue
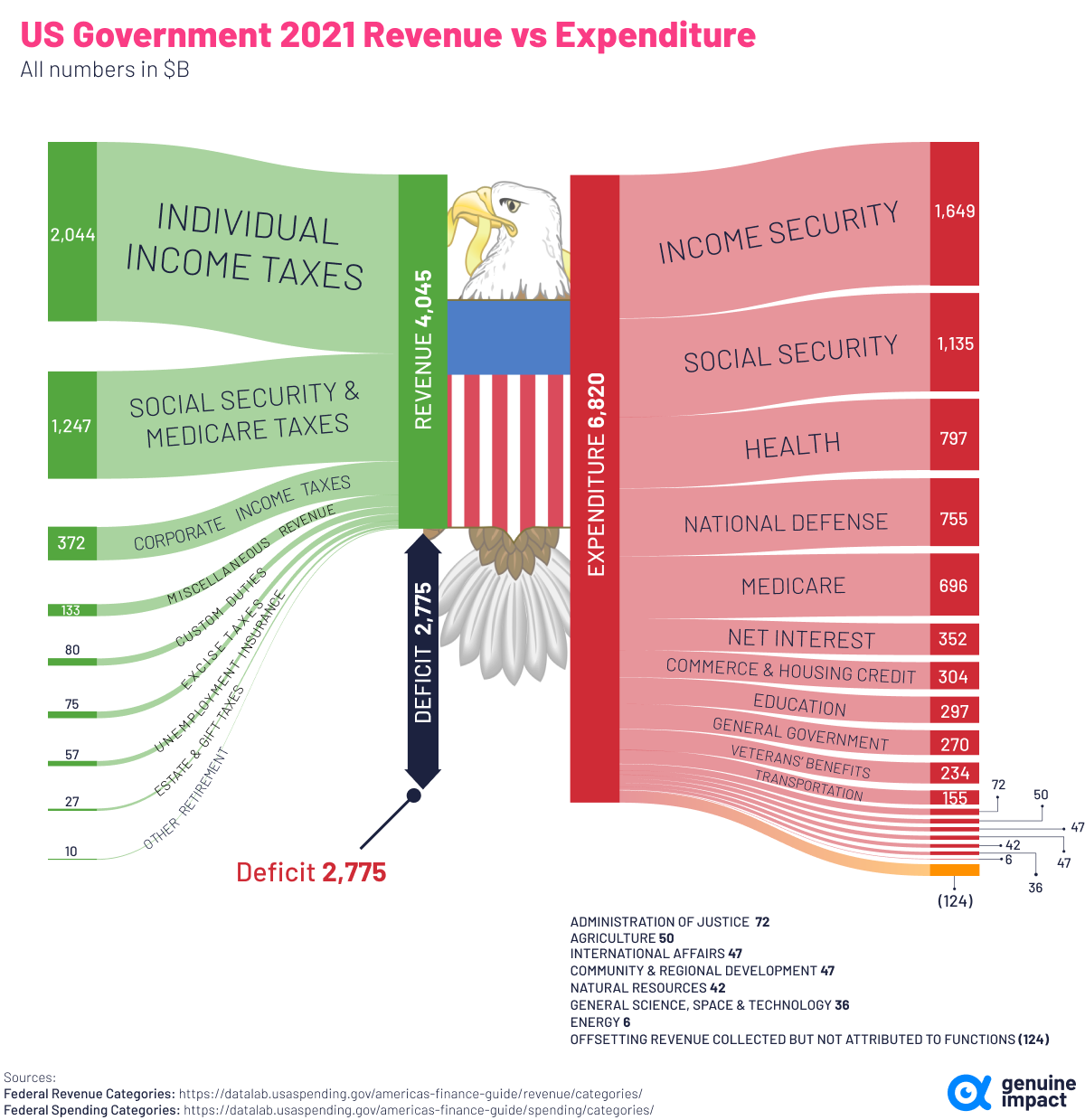
Comparing U.S. Federal Spending with Revenue
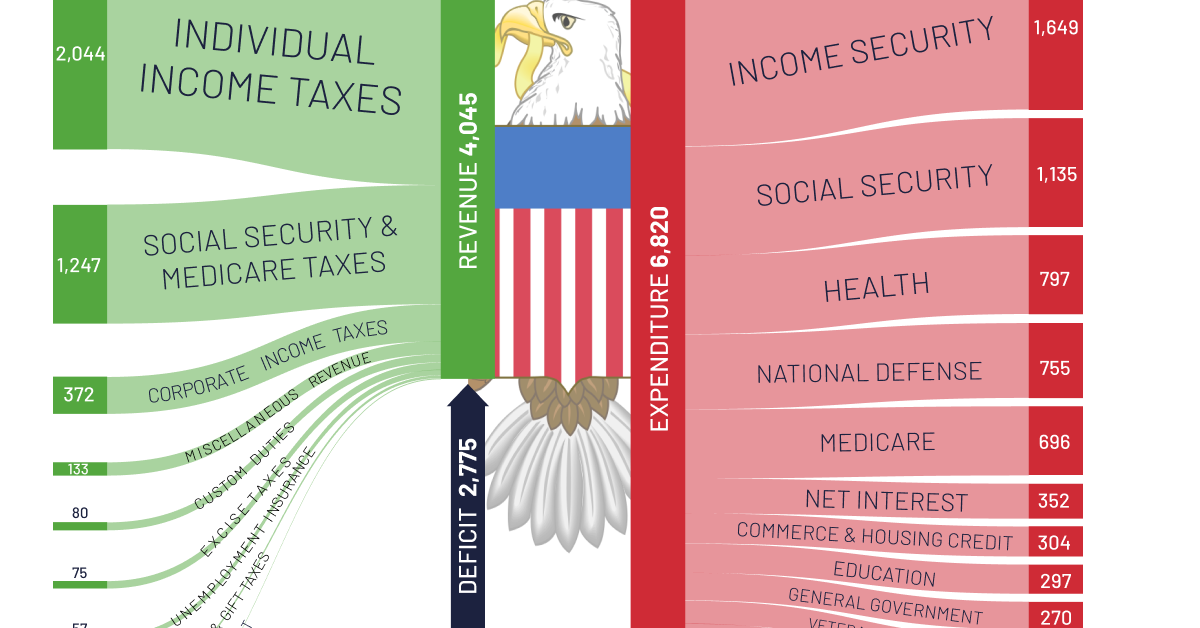
In 2021, the U.S. government spent $6.8 trillion on various expenditures and government-aided programs. Where was this money spent, and how much was covered by taxpayers’ dollars?
This graphic by Truman Du shows a breakdown of U.S. federal spending in 2021, as well as a breakdown of where the money came from, using data from USAspending.gov.
Money Comes and Goes
In 2021, U.S. government revenue totaled more than $4 trillion. About half of it came from individual income taxes, while about 30% came from Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Here’s a full breakdown of revenue sources in 2021:
| U.S. Government Revenue Source | 2021 Amount ($B) |
|---|---|
| Individual income taxes | $2,044 |
| Social security and medicare taxes | $1,247 |
| Corporate income taxes | $372 |
| Miscellaneous revenue | $133 |
| Custom duties | $80 |
| Excise taxes | $75 |
| Unemployment insurance | $57 |
| Estate and gift taxes | $27 |
| Other retirement | $10 |
| Total | $4,045 |
Despite the trillions in revenue generated, like most years, U.S. federal spending was higher in 2021, which put the federal government in a budget deficit of $2.7 trillion.
This was the second highest deficit on record, down from a peak of $3.1 trillion in 2020 during the height of the global pandemic.
After income and Social Security spending, health was the third-largest expenditure in 2021. Here’s a look at the full breakdown, and where spending was allocated last year:
| U.S. Government Spending Category | 2021 Amount ($B) |
|---|---|
| Income security | $1,649 |
| Social security | $1,135 |
| Health | $797 |
| National defense | $755 |
| Medicare | $697 |
| Net interest | $352 |
| Commerce and housing credit | $304 |
| Education | $297 |
| General government | $270 |
| Veterans benefits | $234 |
| Transportation | $155 |
| Administration of Justice | $72 |
| Agriculture | $50 |
| International affairs | $47 |
| Community and regional development | $47 |
| Natural resources | $42 |
| General science, space and technology | $36 |
| Energy | $6 |
| Offsetting revenue collected but not attributed to functions | ($124) |
| Total | $6,820 |
Spending is expected to curb further in 2022. According to the non-partisan Congressional Budget Office via AP News, the 2022 deficit is projected to drop to $1.15 trillion and will continue to decrease for the next three years.
U.S. National Debt
In March 2021, U.S. national debt reached an all-time high of $28 trillion. That includes intragovernmental holdings, which is about $6 trillion of debt owed within the government itself.
While overall debt is rising, the cost of servicing this debt has actually dropped in recent years thanks to record low interest rates.
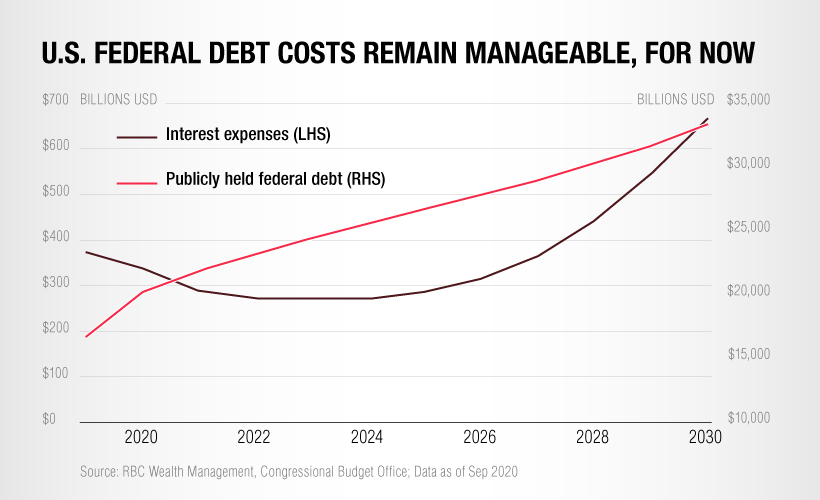
However, with interest rates on the rise again this year, servicing the existing national debt is becoming more expensive.
And eventually, when it comes time for the U.S. government to refinance its loans, a greater portion of the federal budget will need to be allocated to servicing debt, which will put a squeeze on other areas of spending.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
War
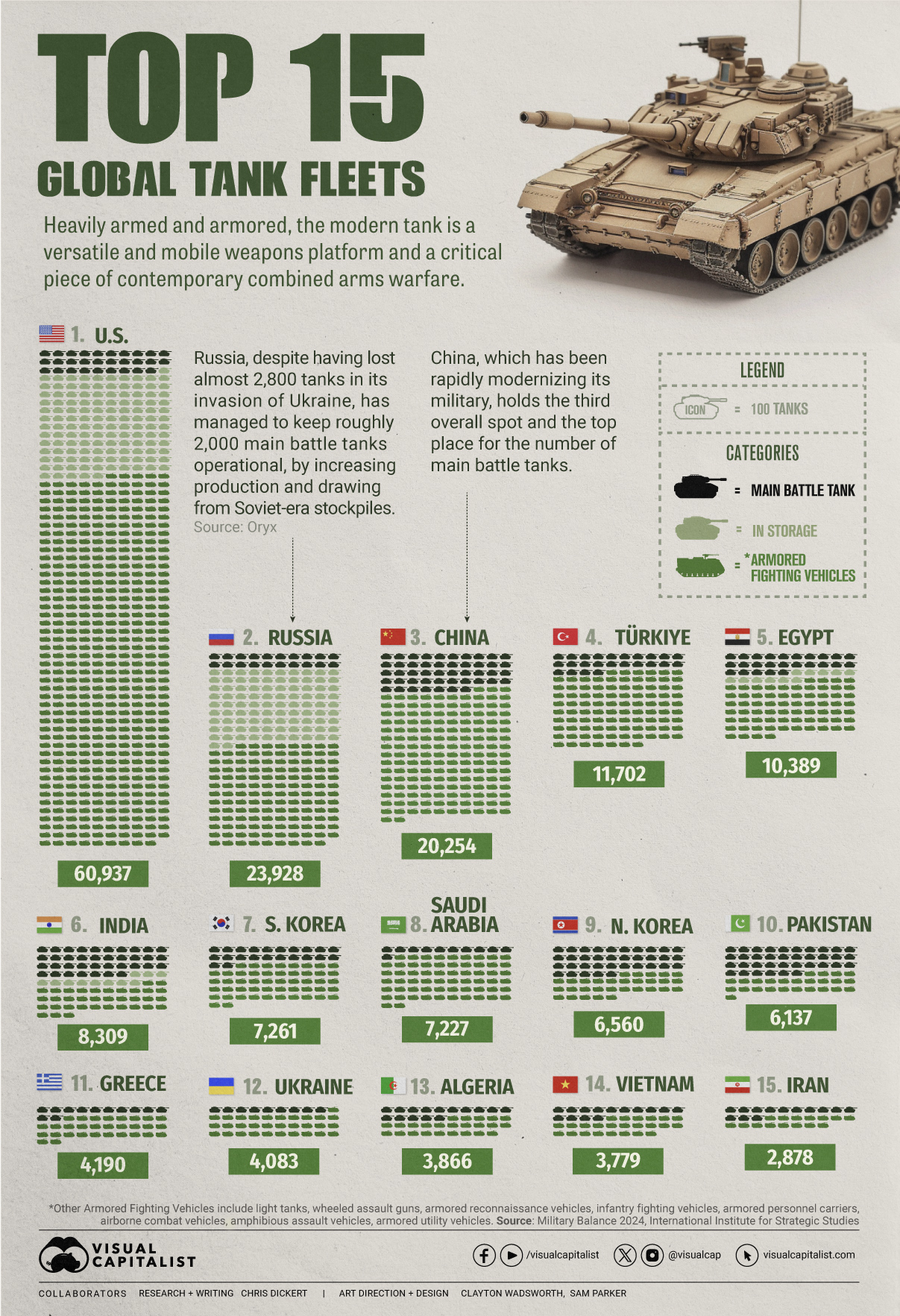
Visualized: Top 15 Global Tank Fleets
Heavily armed and armored, the modern tank is a versatile and mobile weapons platform, and a critical piece of contemporary warfare.

The Top 15 Global Tank Fleets
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Heavily armed and armored, the modern tank is a versatile and mobile weapons platform, and a critical piece of contemporary warfare.
This visualization shows the top 15 global tank fleets, using data from the 2024 Military Balance report from the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
Let’s take an in-depth look at the top three fleets:
1. United States
As the world’s pre-eminent military power, it’s perhaps no surprise that the United States also has the largest tank fleet, by a wide margin.
In total, they have just over 45,000 armored fighting vehicles in operation, along with 2,640 main battle tanks (MBTs), and 12,800 vehicles in storage, of which 2,000 are main battle tanks.
| Category | Vehicles | Global rank |
|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 2,640 | 4 |
| Armored reconnaissance | 1,745 | 1 |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 3,262 | 3 |
| Armored personnel carriers | 10,644 | 1 |
| Amphibious assault vehicles | 1,401 | 1 |
| Armored utility vehicles | 28,445 | 1 |
| Storage | 12,800 | 1 |
| Total | 60,937 | 1 |
The U.S. is internalizing the lessons from the ongoing invasion of Ukraine, where Western-supplied anti-tank weapons and massed Ukrainian artillery have been cutting Russian tanks to pieces. As a result, the U.S. recently canceled an upgrade of the M1 Abrams in favor of a more ambitious upgrade.
Meanwhile, the U.S. is nervously eyeing a more confident China and a potential clash over Taiwan, where air and naval forces will be critical. However, a recent war game showed that Taiwanese mechanized ground forces, kitted out with American-made tanks and armored fighting vehicles, were critical in keeping the island autonomous.
2. Russia
According to Oryx, a Dutch open-source intelligence defense website, at time of writing, Russia has lost almost 2,800 main battle tanks since invading Ukraine. Considering that in the 2022 edition of the Military Balance, Russia was estimated to have 2,927 MBTs in operation, those are some hefty losses.
Russia has been able to maintain about 2,000 MBTs in the field, in part, by increasing domestic production. Many defense plants have been taken over by state-owned Rostec and now operate around the clock. Russia is also now spending a full third of their budget on defense, equivalent to about 7.5% of GDP.
At the same time, they’ve also been drawing down their Soviet-era stockpiles, which are modernized before being sent to the front. Just how long they can keep this up is an open question; their stockpiles are large, but not limitless. Here is what their storage levels look like:
| Category | 2023 | 2024 | YOY change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 5,000 | 4,000 | -20.0% |
| Armored reconnaissance | 1,000 | 100 | -90.0% |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 4,000 | 2,800 | -30.0% |
| Armored personnel carriers | 6,000 | 2,300 | -61.7% |
| Total | 16,000 | 9,200 | -42.5% |
3. China
China holds the third overall spot and top place globally for the number of main battle tanks in operation. Untypically, the People’s Liberation Army has no armored vehicles in storage, which perhaps isn’t surprising when you consider that China has been rapidly modernizing its military and that stockpiles usually contain older models.
China also has one of the world’s largest fleets of armored fighting vehicles, second only to the United States. Breaking down that headline number, we can also see that they have the largest number of light tanks, wheeled guns, and infantry fighting vehicles.
| Category | Vehicles | Global rank |
|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 4,700 | 1 |
| Light tanks | 1,330 | 1 |
| Wheeled guns | 1,250 | 1 |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 8,200 | 1 |
| Armored personnel carriers | 3,604 | 5 |
| Airborne combat vehicles | 180 | 2 |
| Amphibious assault vehicles | 990 | 2 |
| Total | 20,254 | 3 |
This is equipment that would be integral if China were to make an attempt to reunify Taiwan with the mainland by force, where lightly armored mechanized units need to move with speed to occupy the island before Western allies can enter the fray. It’s worth noting that China also has one of the world’s largest fleets of amphibious assault vehicles.
End of the Tank?
Many commentators at the outset of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, were quick to predict the end of the tank, however, to paraphrase Mark Twain, reports of the tank’s demise are greatly exaggerated.
With the U.S. and China both developing remote and autonomous armored vehicles, tanks could be quite different in the future, but there is nothing else that matches them for firepower, mobility, and survivability on the modern battlefield today.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries