Sponsored
The Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
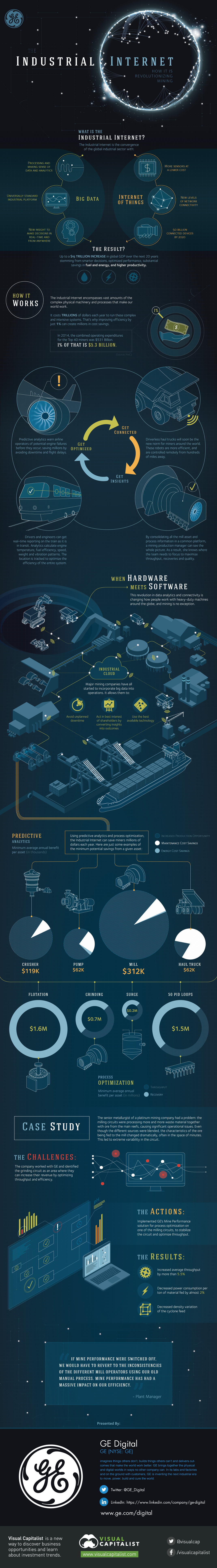
The Industrial Internet and How It Is Revolutionizing Mining
Today’s infographic was done in conjunction with GE Digital
The Industrial Internet is the convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things.
Big Data: New insight to make decisions in real-time is made possible by combining the ability to process and make sense of large amounts of data with a universally standard industrial platform.
Internet of Things: By 2020, 50 billion devices will be connected to the web. Many of these will be sensors, which can now be produced at a lower cost, creating new levels of network connectivity between machines and people.
The result of this convergence will be up to a $15 trillion increase in global GDP over the next 20 years stemming from smarter decisions, optimized performance, higher productivity, and substantial savings in fuel and energy.
How the Industrial Internet works
The Industrial Internet encompasses vast amounts of the complex physical machinery and processes that make our world work. It costs trillions of dollars each year to run these intensive systems. That’s why improving efficiency by just 1% can create millions in cost savings.
For example: the combined operating expenditures for the Top 40 miners in 2014 were $531 billion. 1% of that is $5.3 billion in potential savings.
Examples of the Industrial Internet in motion:
- Predictive analytics warn airline operators of potential engine failures before they occur, saving millions by avoiding downtime and flight delays
- Driverless haul trucks will soon be the new norm for miners around the world. These robots are more efficient, and are controlled remotely from hundreds of miles away.
- Drivers and engineers can get real-time reporting on a train as it is in transit. Analytics calculate engine temperature, fuel efficiency, speed, weight, and vibration patterns. The location is tracked to optimize the efficiency of the entire system.
- By consolidating all the mill asset and process information in a common platform, a mining production manager can see the whole picture. As a result, she knows where the team needs to focus to maximize throughput, recoveries, and quality.
When Hardware Meets Software
The revolution in data analytics and connectivity is changing how people work with heavy-duty machines around the globe, and mining is no exception.
Major mining companies have all started to incorporate big data into operations through the industrial cloud. This allows them to avoid unplanned downtime, to act in the best interest of shareholders by converting insights into outcomes, and to use the best available technology.
Using predictive analytics and process optimization, the industrial internet can save miners millions of dollars each year.
Here are just some examples of the minimum potential savings from a given asset per year using predictive analytics:
- Crusher: $119,000
- Pump: $62,000
- Mill: $312,000
- Haul truck: $62,000
Here are just some examples of the minimum potential savings gained per year by optimizing entire processes:
- Flotation: $1.6 million
- Grinding: $0.7 million
- Surge: $0.2 million
- 50 PID Loops: $1.5 million
Case Study
The senior metallurgist of a platinum mining company had a problem: the milling circuits were processing more and more waste material together with ore from the main reefs, causing significant operational issues. Even though the different sources were blended, the characteristics of the ore being fed to the mill changed dramatically, often in the space of minutes. This led to extreme variability in the circuit.
The Challenge: The company believed that it was losing potential revenue as a result of sub-optimal throughput and efficiency in the milling circuits.
The Action: Implemented GE’s Mine Performance solution for process optimization on one of the milling circuits, to stabilize the circuit and optimize throughput.
The Results:
- Increased average throughput by more than 5.5%
- Decreased power consumption per ton of material fed by almost 2%
- Decreased density variation of the cyclone feed
Sponsored
Accelerating a Net-Zero Future with Carbon Credits
To reach net-zero by 2050, trillions in annual investment will be required. Here’s how carbon credits help close this funding gap.
Accelerating a Net-Zero Future with Carbon Credits
Achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement is critical, yet national climate pledges fall short.
To reach net-zero by 2050, immediate action and $9.2 trillion in annual investment is required, or about 7-9% of global GDP. This would be $3.5 trillion annually more than today, which in 2020 was equal to roughly:
- 50% of corporate profits
- 25% of tax revenues
- 7% of household spending
This infographic sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation shows how carbon credits can help accelerate a net-zero future by funding climate action.
Closing the Funding Gap With Carbon Credits
Carbon credits play a vital role in channelling finance to help close this funding gap. Here are some ways in which carbon credits can be used:
- Unabated Emissions: Compensate for unabated or residual emissions while prioritizing mitigation on a science-based pathway.
- Accelerate Global Transition: For beyond value chain mitigation to accelerate the global transition to net-zero.
- Sustainability Goals: Achieve sustainability goals beyond climate action e.g. preserving biodiversity and valuable ecosystems.
Thanks to a growing number of initiatives listed below, 2023 is anticipated to bring greater credibility and transparency to the carbon credit market.
- The Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market
- Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi)
- Climate Action Data Trust
- Voluntary Carbon Markets Integrity Initiative
Not Every Carbon Credit is Equal
Identifying high-quality carbon credits is important because not every type of credit offers the same scope of benefits. Carbon credit buyers look for credits that offer tangible benefits that go beyond CO₂ reduction or removal, such as:
- Advancing Sustainable Development Goals
- Creating jobs in local communities
- Protecting biodiversity
- Providing education and job training
Often, credits that offer these types of benefits command a price premium.
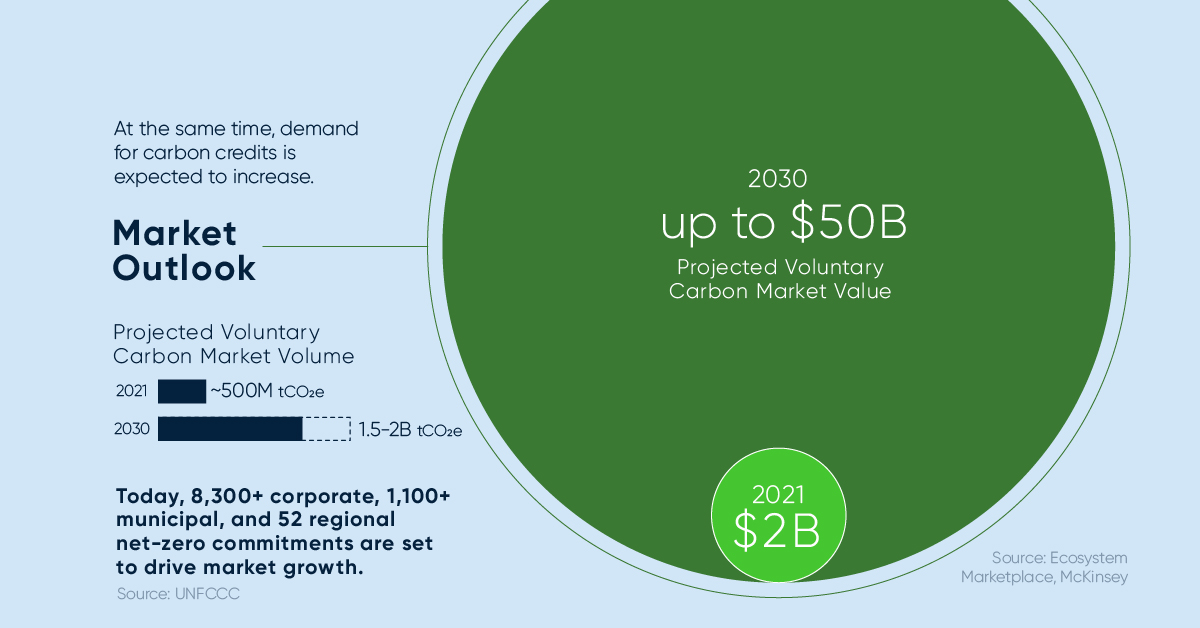
At the same time, demand for carbon credits is expected to increase. Within the decade, the value of the voluntary carbon market could grow from $2 billion up to $50 billion.
Voluntary carbon markets refer to the transactions in which carbon credits are purchased by corporate and other buyers that voluntarily (not required by a regulatory act) want to compensate for their emissions or advance sustainability goals.
| 2021 | 2030 (estimated) | |
|---|---|---|
| Voluntary Carbon Market Value | $2B | Up to $50B |
| Voluntary Carbon Market Volume | ~500M tCO₂e | 1.5-2B tCO₂e |
Source: Ecosystem Marketplace, McKinsey, UNFCCC
Today, over 8,300 corporate, 1,100 municipal, and 52 regional net-zero commitments are set to drive market growth.
Carbon Streaming’s Innovative Approach to Climate Action
Carbon Streaming is a publicly listed company that invests capital in high integrity carbon credit projects on a global scale. It uses the proven, flexible streaming model to create long-term partnerships.
This model aligns interests to benefit all stakeholders.
| Project Partners | Carbon Streaming | Credit Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| Delivers upfront cash to project Ongoing payments for life of project Sales channel to monetize carbon credits Maximum value sought for credit sales with a revenue share structure Ability to create or accelerate tangible co-benefits | Recurring credits received throughout the term No responsibility for operating or capital costs Potential value appreciation with purchase terms set upfront Independent verification Established buffer pools | Majority of purchase price flows to projects and local communities Investment-grade due diligence Diverse and long-term supply of credits Credits with additional sustainable benefits Access to new project types as portfolio grows |
Carbon Streaming’s growing portfolio of carbon credits includes over 20 projects across six different project types in 12 countries that aim to accelerate a net-zero future.
Transformative Year Ahead
By the end of 2023, carbon credits are expected to be issued from 10 or more projects.
Importantly, all of Carbon Streaming’s carbon projects aim to advance multiple UN Sustainable Development Goals. Carbon Streaming intends to continue growing and diversifying its portfolio while selling carbon credits received to maximize value for all stakeholders.
>>>Interested in learning more about Carbon Streaming? Click here to learn more.

-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology…
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees