Technology
Tesla’s Valuation Surpasses Ford and GM Combined
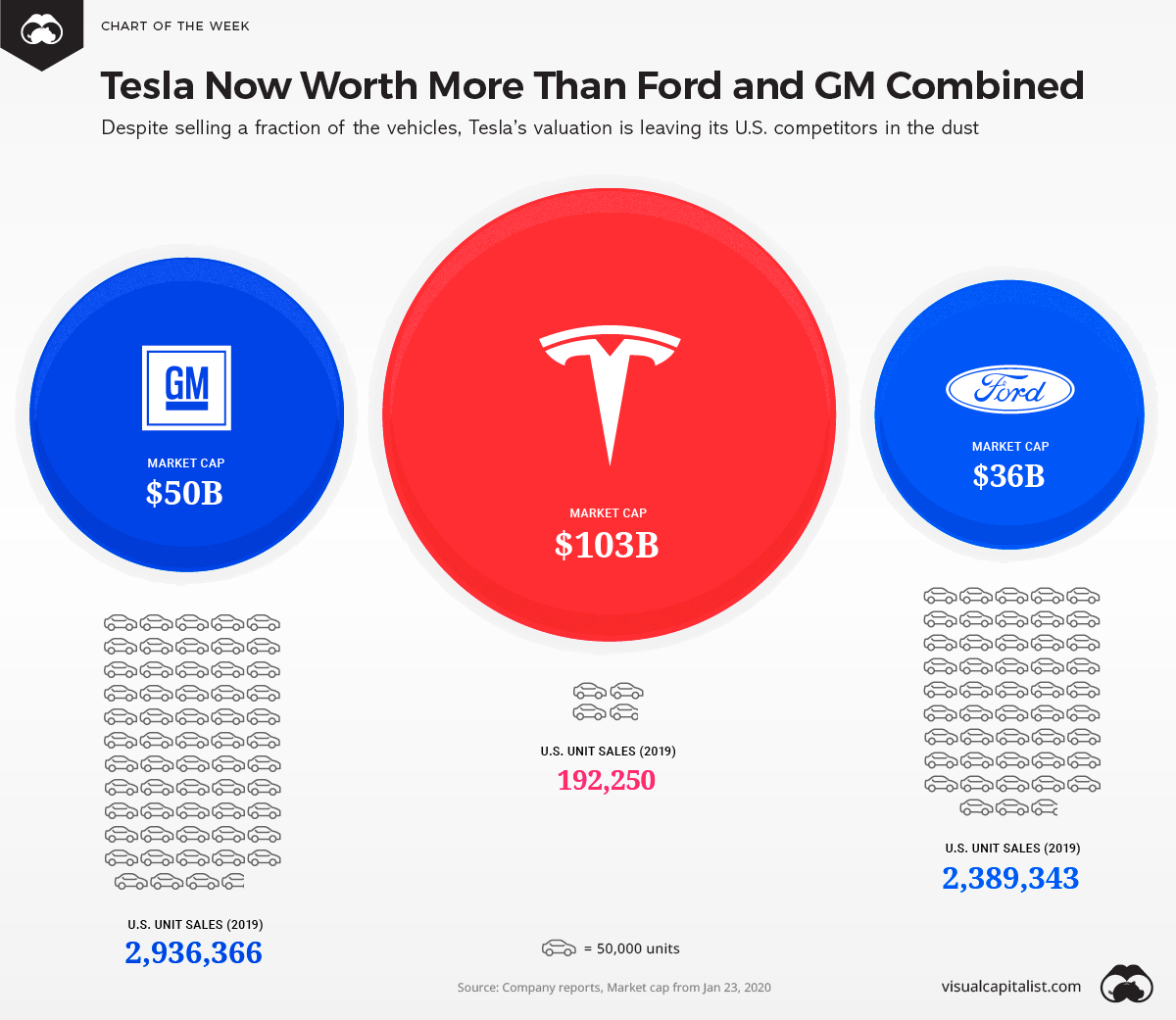
Chart: Tesla is Worth More than Ford and GM Combined
Tesla has been on a roller coaster ride of market sentiment in recent years, but the electric car company is starting off the new decade on a high note.
The company is not only America’s most valuable automaker, it’s now worth more than Ford and GM combined.
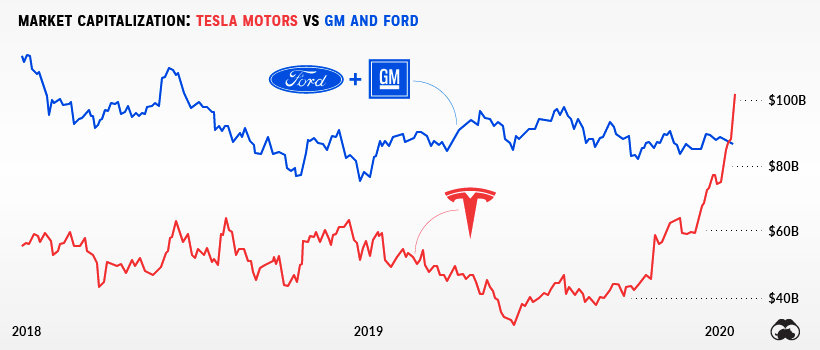
Tesla’s valuation has already surpassed the $100 billion mark – a significant milestone for a company that produces a fraction of the vehicles of its direct competitors.
Here’s a comparison of the top selling models in the U.S. for Ford, GM, and Tesla.
| Rank | Model | Unit Sales (Q4 2019) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ford F-Series | 233,952 |
| 2 | Chevrolet Silverado | 163,311 |
| 3 | Chevrolet Equinox | 92,092 |
| 4 | GMC Sierra | 68,722 |
| 5 | Ford Explorer | 51,284 |
| 6 | Ford Escape | 47,587 |
| 7 | Tesla Model 3 | 47,275 |
| 8 | Ford Edge | 37,621 |
| 9 | Ford Transit | 36,885 |
| 10 | Chevrolet Malibu | 34,314 |
A quick glance at this list is revealing. Though Tesla’s Model 3 put up strong sales numbers, it’s still only a small percentage of vehicles sold by U.S. automakers.
So, what’s driving Tesla’s meteoric growth, and is it sustainable? Below, we’ll take a high-level look at the bull and bear cases for the company.
The Bull Case for Tesla Motors
Tesla posted losses of $1.1 billion in the first half of 2019, but since then, the company has turned the situation around in dramatic fashion.
The automaker had a surprising third quarter with not only record deliveries of 97,000 cars, but also a profit of $143 million. Deliveries broke yet another record in Q4 2019, totaling 112,000 vehicles. These announcements helped improve market sentiment, sending the company’s stock back on an upward trajectory heading into 2020.

Here are three reasons some analysts and media are still bullish on Tesla:
1. Tapping into the World’s Largest Electric Car Market
For a long time, foreign companies looking to manufacture products in China couldn’t do so without working through a domestic partner. Recently though, Tesla became the first major benefactor of a policy change, becoming the first wholly foreign-owned automaker in China.
Gigafactory 3 in Shanghai was completed in October, and was built in just 10 months – an impressive feat. Furthermore, cars have already begun rolling off the assembly lines, as Tesla targets an annual production of 150,000 Model 3s.
Perhaps the best part for a company with historically volatile earnings: Tesla claims the facility was 65% cheaper to build than its production plant in the U.S.
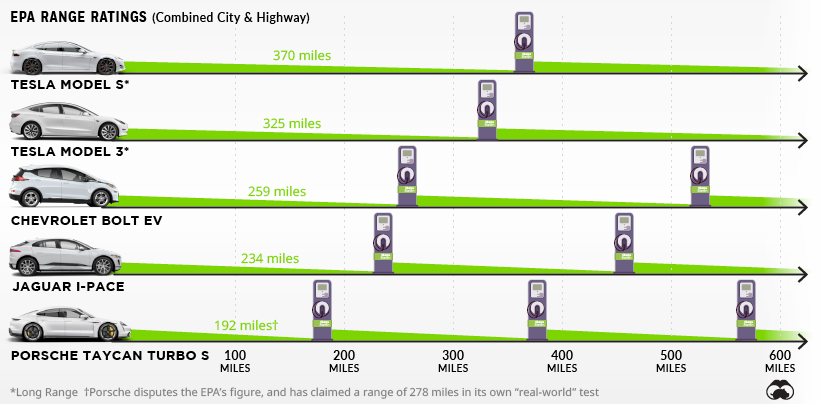
2. Still the Range King
2019 saw many of the more established automakers take their first swings at Tesla.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) handed out official range ratings for several new electric cars, but none could unseat the king:
3. Musk’s Megaphone
Few CEOs capture the attention of media quite like Elon Musk. While his actions can sometimes have unintended consequences for the company – the infamous “funding secured” tweet, for example – Elon Musk’s massive reach allows the company to sell vehicles without spending a dime on advertising.
By contrast, in 2018, Ford and GM spent $2.3 billion and $3.1 billion respectively on advertising in the U.S. alone.
The Bear Case for Tesla Motors
While the second half of 2019 has given Tesla bulls much to celebrate, many investors are remaining vigilant, if not skeptical.

1. Stiff Competition in China
Tapping into the world’s largest EV market is a double-edged sword for Tesla, as they face an onslaught of domestic and foreign competitors.
The Chinese government has also generously supported its own EV industry, handing out over $60 billion in subsidies to over 400 companies. Tesla will be competing against state-owned enterprises like BAIC, one of the largest players in the Chinese EV market.
Western automakers are also gaining a foothold in China as well. Volkswagen and its Chinese joint-venture partner, SAIC Motor, will begin producing cars at two factories in China in the autumn of 2020.
The German automotive giant has also forged partnerships with Chinese battery manufacturers, including China’s biggest battery company Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL).
2. Getting Ratio’d
Tesla has an extremely high premium on earnings when compared with its more established counterparts in the auto industry.
| Company | Ticker | Enterprise Multiple* (last 12 months) |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota | NYSE: TM | 8.4x |
| GM | NYSE: GM | 10.0x |
| Ford | NYSE: F | 14.5x |
| Tesla | NASDAQ: TSLA | 50.2x |
The enterprise multiple (EV/EBITDA) measures the dollars in enterprise value for each dollar of earnings. The ratio is commonly used to determine if a company is undervalued or overvalued compared to peers.
The Bottom Line is… the Bottom Line
Of course, Tesla’s future will be dictated by variables more complex than can be summed up in a tidy pro/con list.
Musk has shown a willingness to sacrifice profitability in the name of growth – Tesla has yet to prove it can deliver consistent, quarterly profits.
It’s hard to be profitable with that level of growth. We could slow it down, but then that would not be good for sustainability and the cause of electric vehicles.
– Elon Musk
After reporting a record number of deliveries in the final quarter of 2019, there’s no doubt that true believers and short sellers alike will be watching the company’s January 29, 2020, earnings call with much anticipation.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees