Markets
Investing Megatrend: How Rapid Urbanization is Shaping the Future

How Rapid Urbanization is Shaping the Future
The world is constantly changing, and many of these shifts have the potential to alter the investment landscape.
While some of these changes can be temporary and fleeting, others can be powerful, transformative “megatrends” that shape how society is organized at a fundamental level.
One such megatrend that has been in place for decades is the rapid rate of population growth in urban areas — and while it’s been highly influential thus far, we’ve likely only seen the beginning of its formative impact on the global economy.
An Intro to Rapid Urbanization
Today’s infographic comes to us from iShares by BlackRock, and it highlights the case for rapid urbanization as being one of the most important overarching trends to watch in markets over the long term.
It’s a trend that originated in developed economies in the 21st century, as people transitioned from agricultural work to factory and service jobs.
| Region | Urban share of population (1900) | Urban share of population (2016) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 40% | 82% |
| Japan | 12% | 91% |
| Western Europe | 41% | 80% |
In these developed economies today, cities are major sources of innovation and wealth creation, and the World Bank estimates that over 80% of global GDP is now generated in cities.
A Global Shift
Over the coming decades, the large-scale role of cities will become even more amplified as rapid urbanization spills over to the rest of the world.
Billions of people — especially in Asia and Africa — will be seeking opportunities in cities over the coming decades. Between 2018 and 2050, the global urban population will increase from 55% to 68%, adding another 2.5 billion people to cities around the world.
| Rank | Country | Urban population growth (2018-2050) |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | India | 416 million people |
| #2 | China | 255 million people |
| #3 | Nigeria | 189 million people |
Nearly 90% of this growth will be in Africa and Asia, with India alone adding 416 million new people to its cities — more than any other country in the world over this timeframe.
The Dawn of the Megacity
People are not only flocking to cities, they are flocking to megacities — urban conglomerations with more than 10 million people.
In just 40 years, the total amount of megacities will quadruple, gaining nearly 600 million residents in the process:
| Year | # of Megacities | Population | % of Urban Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 10 | 153 million | 7% |
| 2010 | 23 | 370 million | 12% |
| 2030 | 41 | 730 million | 14% |
With billions of new people living in urban areas — and many of them living in megacities — we will have to rethink how our cities are designed and engineered.
And as this happens, the city as we know it will be revolutionized.
The Urban Opportunity
Rapid urbanization will create both opportunities and challenges for society, and a plethora of investment possibilities in the process.
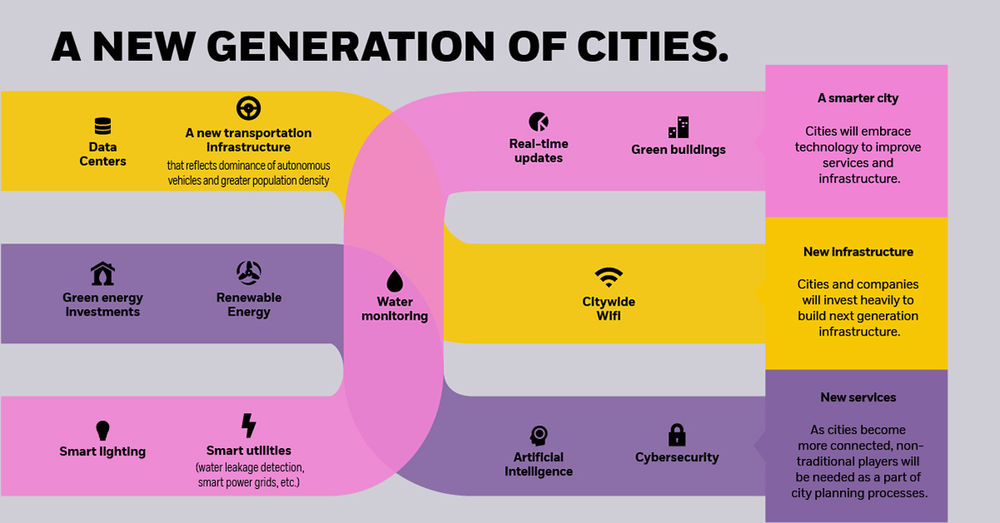
As global cities become more integrated with technology, new business models will emerge as cities become smarter, denser, and more connected.
These potential opportunities include:
- Smarter cities
Cities will embrace technology to improve services and infrastructure, adding tech-driven features like smart lighting or real-time traffic updates. - New infrastructure
Cities and companies will invest heavily to build next generation infrastructure, such as data centers, green energy, and citywide WiFi. - A focus on personal security
With higher crime rates in cities than rural areas, governments will employ elevated levels of surveillance on citizens in cities. Increasing connectivity means that every activity is logged and monitored. - New services
As cities become more connected, non-traditional players — such as cybersecurity experts or cleantech engineers — will be needed as a part of city planning processes. - No car ownership
A lack of space and the rise of autonomous cars will mean fewer people will own a car, preferring to use ‘summon-able’ services instead. - New healthcare systems
As population density grows to unprecedented levels, existing healthcare systems will need to be radically overhauled to deal with this influx.
Rapid urbanization will have a wide-ranging impact on global economics, demographics, and society as a whole.
As rapid urbanization and other megatrends collide and feed off each other, there’s no doubt that even more thematic investment opportunities will be created.
Markets
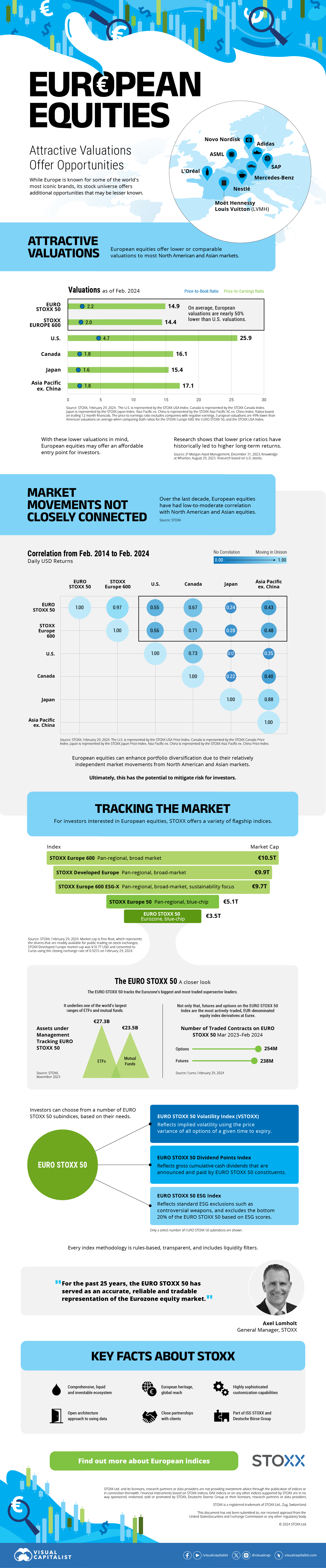
The European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
On average, the European stock market has valuations that are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations. But how can you access the market?
European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
Europe is known for some established brands, from L’Oréal to Louis Vuitton. However, the European stock market offers additional opportunities that may be lesser known.
The above infographic, sponsored by STOXX, outlines why investors may want to consider European stocks.
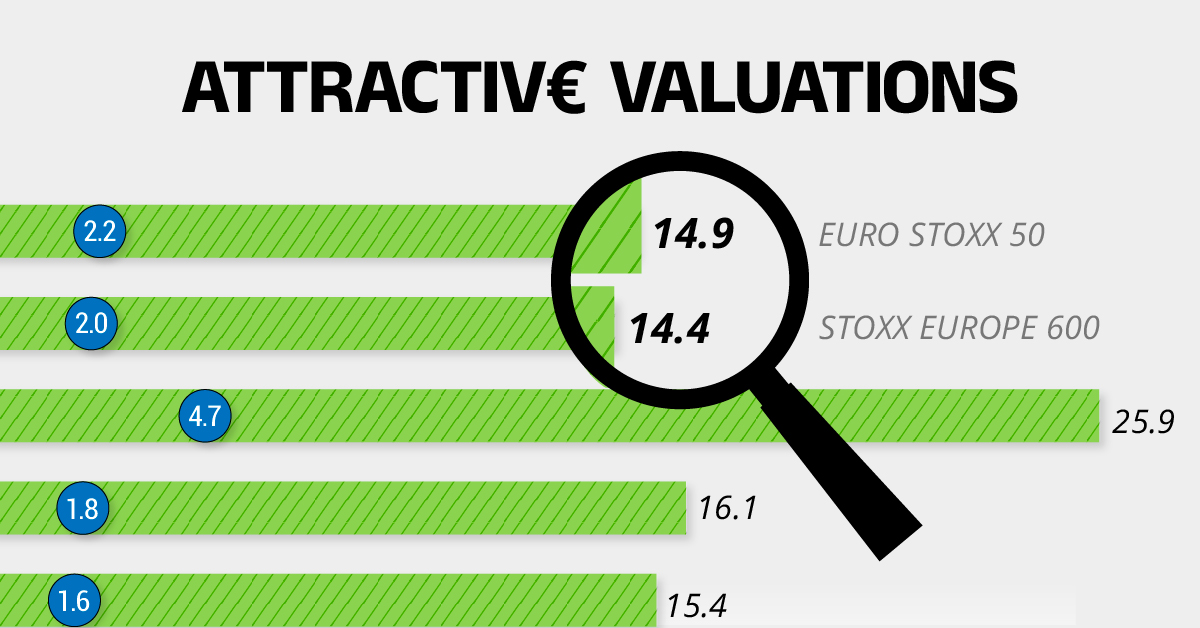
Attractive Valuations
Compared to most North American and Asian markets, European stocks offer lower or comparable valuations.
| Index | Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Price-to-Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 14.9 | 2.2 |
| STOXX Europe 600 | 14.4 | 2 |
| U.S. | 25.9 | 4.7 |
| Canada | 16.1 | 1.8 |
| Japan | 15.4 | 1.6 |
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 17.1 | 1.8 |
Data as of February 29, 2024. See graphic for full index names. Ratios based on trailing 12 month financials. The price to earnings ratio excludes companies with negative earnings.
On average, European valuations are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations, potentially offering an affordable entry point for investors.
Research also shows that lower price ratios have historically led to higher long-term returns.
Market Movements Not Closely Connected
Over the last decade, the European stock market had low-to-moderate correlation with North American and Asian equities.
The below chart shows correlations from February 2014 to February 2024. A value closer to zero indicates low correlation, while a value of one would indicate that two regions are moving in perfect unison.
| EURO STOXX 50 | STOXX EUROPE 600 | U.S. | Canada | Japan | Asia Pacific ex. China |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| STOXX EUROPE 600 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.48 | |
| U.S. | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| Canada | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.40 | |||
| Japan | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 1.00 |
Data is based on daily USD returns.
European equities had relatively independent market movements from North American and Asian markets. One contributing factor could be the differing sector weights in each market. For instance, technology makes up a quarter of the U.S. market, but health care and industrials dominate the broader European market.
Ultimately, European equities can enhance portfolio diversification and have the potential to mitigate risk for investors.
Tracking the Market
For investors interested in European equities, STOXX offers a variety of flagship indices:
| Index | Description | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| STOXX Europe 600 | Pan-regional, broad market | €10.5T |
| STOXX Developed Europe | Pan-regional, broad-market | €9.9T |
| STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X | Pan-regional, broad market, sustainability focus | €9.7T |
| STOXX Europe 50 | Pan-regional, blue-chip | €5.1T |
| EURO STOXX 50 | Eurozone, blue-chip | €3.5T |
Data is as of February 29, 2024. Market cap is free float, which represents the shares that are readily available for public trading on stock exchanges.
The EURO STOXX 50 tracks the Eurozone’s biggest and most traded companies. It also underlies one of the world’s largest ranges of ETFs and mutual funds. As of November 2023, there were €27.3 billion in ETFs and €23.5B in mutual fund assets under management tracking the index.
“For the past 25 years, the EURO STOXX 50 has served as an accurate, reliable and tradable representation of the Eurozone equity market.”
— Axel Lomholt, General Manager at STOXX
Partnering with STOXX to Track the European Stock Market
Are you interested in European equities? STOXX can be a valuable partner:
- Comprehensive, liquid and investable ecosystem
- European heritage, global reach
- Highly sophisticated customization capabilities
- Open architecture approach to using data
- Close partnerships with clients
- Part of ISS STOXX and Deutsche Börse Group
With a full suite of indices, STOXX can help you benchmark against the European stock market.

Learn how STOXX’s European indices offer liquid and effective market access.

-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees