Healthcare
How Does the COVID Delta Variant Compare?
How Does the COVID Delta Variant Compare?
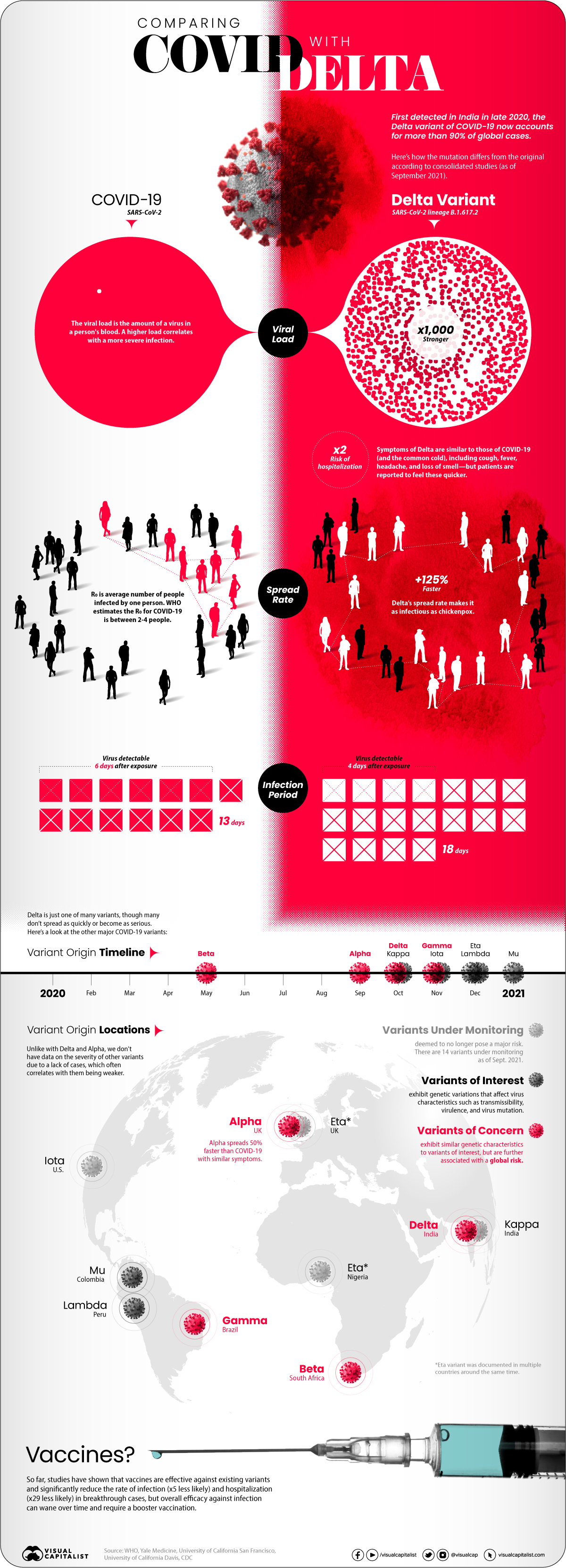
In late 2020, a variant of COVID-19 was detected in India that began to quickly spread.
Soon after it received the label “Delta,” it started to become the predominant strain of COVID-19 in countries of transmission. It spread faster than both the original disease and other variants, including “Alpha” that had taken hold in the UK.
Now the COVID-19 pandemic has essentially become the Delta pandemic, as the variant accounts for more than 90% of global cases.
But how does the COVID-19 Delta variant differ from the original disease? We consolidated studies as of September 2021 to highlight key differences between COVID-19 and the dominant variant. Sources include the CDC, Yale Medicine, and the University of California.
COVID-19 vs COVID-19 Delta Variant
At first glance, infections caused by the Delta variant are similar to the original COVID-19 disease. Symptoms reported from patients include cough, fever, headache, and a loss of smell.
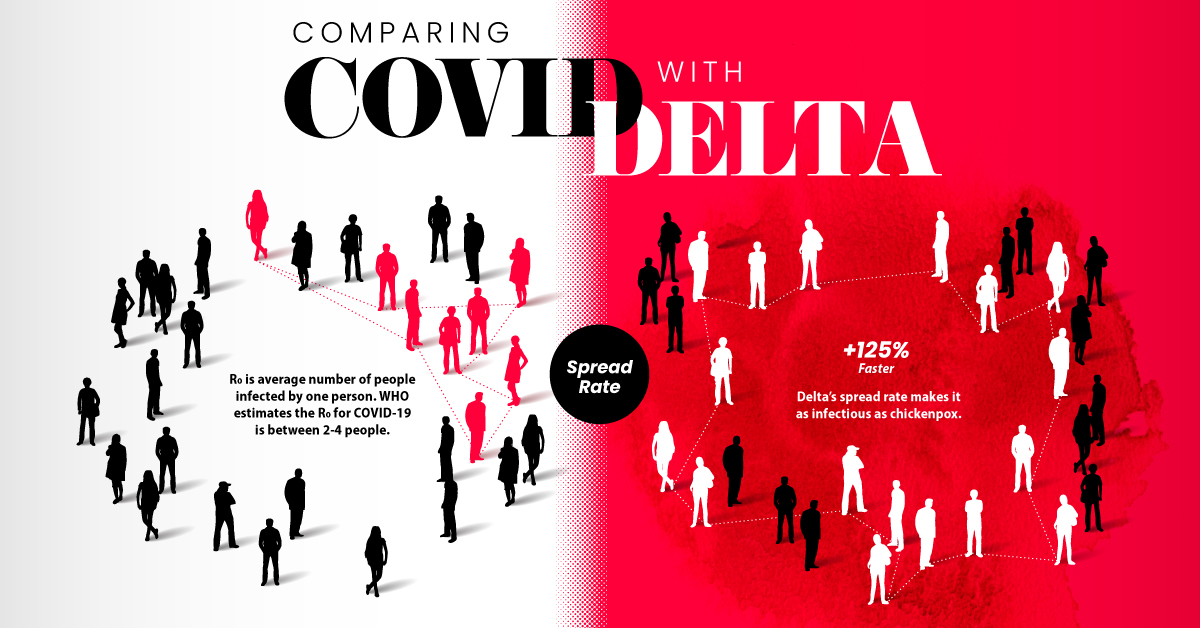
But studies showed that the difference was in how quickly and severely patients got sick:
- Spread rate: How quickly the infection spreads in a community (based on the R0 or basic reproductive number). The Delta variant spread 125% faster than the original disease, making it potentially as infectious as chickenpox.
- Viral load: How much of a virus is detectable in an infected person’s blood, with higher loads correlating with more severe infections. Delta infections had a 1000x higher viral load.
- Virus detectable: How long after exposure a virus is detectable in an infected person’s blood. Delta infections were found to be detectable four days after exposure, faster than the original disease (six days).
- Infectious period: How long an infected person has the capability to pass on the virus to other people, from the first time they were exposed. Delta infections were contagious for longer than traditional COVID-19 infections, at 18 days compared to 13 days.
- Risk of hospitalization: How much more or less likely is an infection going to require hospitalization for treatment? Infections caused by the Delta variant were twice as likely to cause hospitalization compared to the original disease.
One other important finding from studies was that the existing COVID-19 vaccines helped against Delta infections.
The CDC found that approved vaccines reduced the rate of infection by 5x and the rate of hospitalization by 29x in a breakthrough case. They also found that overall efficacy against infection can wane over time, however, and at-risk people might require a booster vaccine.
What About Other COVID-19 Variants?
Delta is just one of many COVID-19 variants tracked by health officials, but it’s the one we know the most about.
That’s because reliable statistics and information on diseases requires thousands of cases for comparisons. We know a lot about Delta (and the once-dominant UK strain Alpha) because of how widespread they became, but there haven’t been enough cases of other variants to reliably assess differences.
As of September 2021, WHO was tracking 20 COVID-19 variants around the world with different classifications based on potential severity:
- 14 Variants under monitoring (VUM): Variants that are deemed to not pose a major global health risk, or no longer pose one.
- 2 Variants of Interest (VOI): Variants that affect transmissibility, virulence, mutation, and other virus characteristics, and are spreading in clusters.
- 4 Variants of Concern (VOC): Have similar characteristics to VOI but are further associated with a global risk.
Most of the current variants of interest and concern were first identified and labeled in late 2020, though 2021 variants are showing up as well.
| Label | Designation | Documented Origin | Earliest Identified Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | Variant of Concern | UK | September 2020 |
| Beta | Variant of Concern | South Africa | May 2020 |
| Gamma | Variant of Concern | Brazil | November 2020 |
| Delta | Variant of Concern | India | October 2020 |
| Lambda | Variant of Interest | Peru | December 2020 |
| Mu | Variant of Interest | Colombia | January 2021 |
Should you be worried about all of these variants? For the most part, a lack of cases to provide clear information also reflects that they’re equivalent to or weaker than traditional COVID-19 infections.
But it’s important to note that our understanding of diseases and variants becomes more nuanced and accurate over time. As research continues over a longer timeline and over a wider database of cases, expect information on COVID-19 variants (and any disease) to become more concrete.
Healthcare
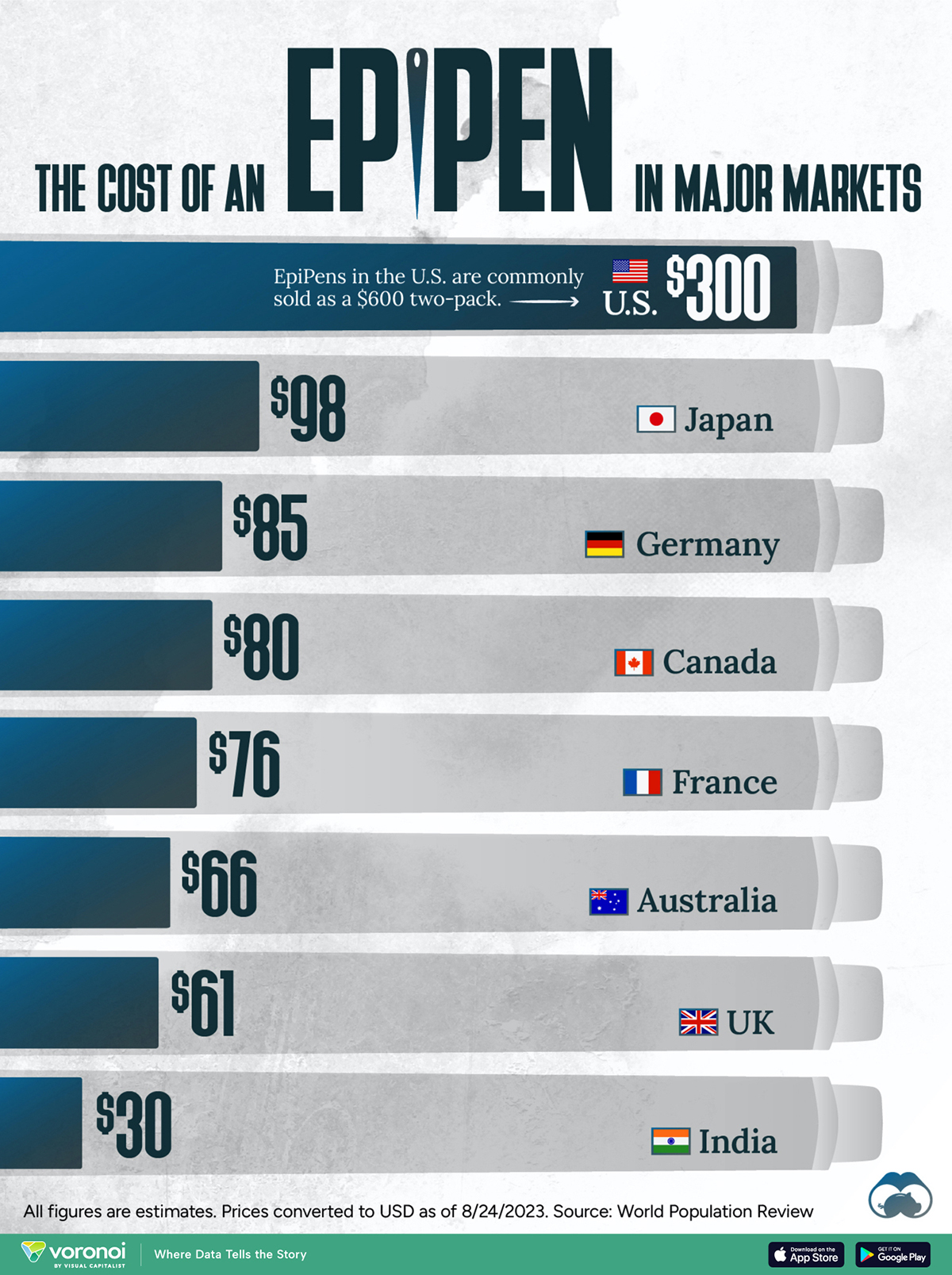
The Cost of an EpiPen in Major Markets
This visualization compares EpiPen prices around the world, with the U.S. having the highest prices by far.

The Cost of an EpiPen in Major Markets
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
EpiPens are auto-injectors containing epinephrine, a drug that can treat or reverse severe allergic reactions, potentially preventing death.
The global epinephrine market was valued at $1.75 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $4.08 billion by 2030. North America represents over 60% of the market.
EpiPens, however, can be prohibitively expensive in some regions.
In this graphic, we present estimated EpiPen prices in major global markets, compiled by World Population Review and converted to U.S. dollars as of August 2023.
Why are U.S. Prices so High?
The U.S. stands out as the most expensive market for EpiPens, despite over 1 million Americans having epinephrine prescriptions. After Mylan (now part of Pfizer) acquired the rights to produce EpiPens in the U.S. in 2007, the cost of a two-pack skyrocketed to $600, up from about $60.
| Country | Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 300* |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 98 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 85 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 76 |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | 66 |
| 🇬🇧 UK | 61 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 30 |
*Per unit cost. Commonly sold as a two-pack, meaning total cost is equal to $600
Former Mylan CEO Heather Bresch defended the price hikes to Congress, citing minimal profit margins. Mylan eventually settled with the U.S. government for a nine-figure sum.
Notably, EpiPens are available at a fraction of the cost in other developed countries like Japan, Germany, and Canada.
Making EpiPens More Affordable
Efforts to improve EpiPen affordability are underway in several U.S. states. For instance, the Colorado House approved a $60 price cap on epinephrine, now under review by the state Senate.
Similar measures in Rhode Island, Delaware, Missouri, and Vermont aim to ensure insurance coverage for epinephrine, which is not currently mandatory, although most health plans cover it.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees