Markets
How Normal Investors Can Use the Same Strategies as Hedge Funds
How Normal Investors Can Use the Same Strategies as Hedge Funds
In a Warren Buffett note from 2006, he credits the famous value investor Benjamin Graham as the co-creator of the first-ever hedge fund in the mid-1920s.
“It involved a partnership structure, a percentage-of-profits compensation arrangement for Ben as general partner, a number of limited partners and a variety of long and short positions,” Buffett’s letter says.
That means that hedge funds have been around for nearly a century – and they have almost exclusively existed as a vehicle for institutions and wealthy, private investors.
Alternative Investments
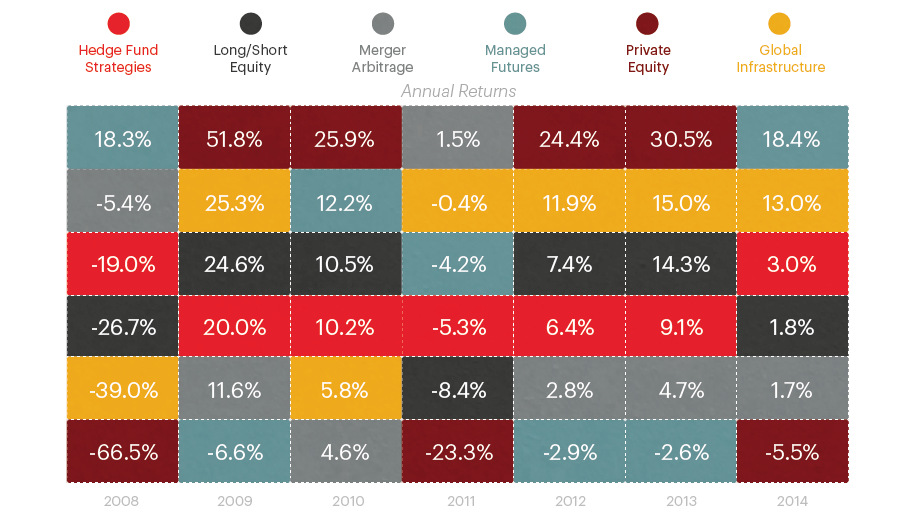
The initial use of the hedge fund was to “hedge” specific investments against the general volatility of the market. Despite this namesake, today hedge funds use a number of strategies to target gains.
While retail investors rarely had access to these types of strategies, today it is possible to buy mutual funds or ETFs that try to emulate similar tactics. These alternative investment funds, or alt-investments, come in mainly two varieties:
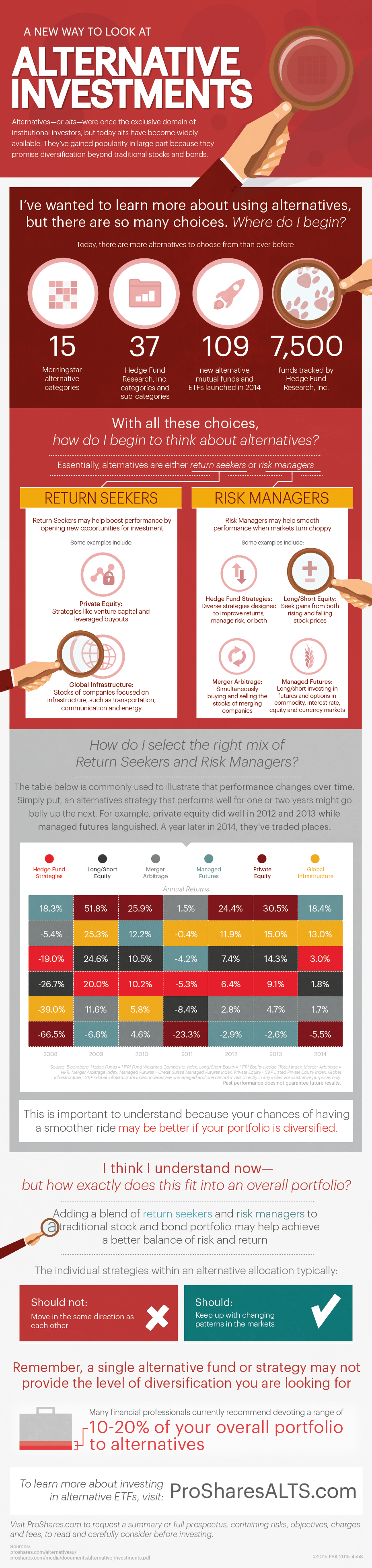
Return Seekers: Designed to help boost performance by opening up new opportunities to investment, such as private equity or global infrastructure.
Risk Managers: Designed to help smooth performance when markets turn choppy. Strategies include long/short equity, merger arbitrage, managed futures, and other hedge fund strategies.
Today’s Market
The key here, in our opinion, is that these strategies may allow investors to diversify out of traditional markets such as stocks and bonds.
The timing for alternative investments could be good as well, as the start to 2016 was the worst in history for markets and the average investor already lost 3.1% in 2015.
Although funds specializing in alt-investments typically have significant diversification benefits, they also usually come with higher fees in comparison to more traditional offerings. Investors should weigh the cost-benefit accordingly.
Original graphic by: ProShares
Economy
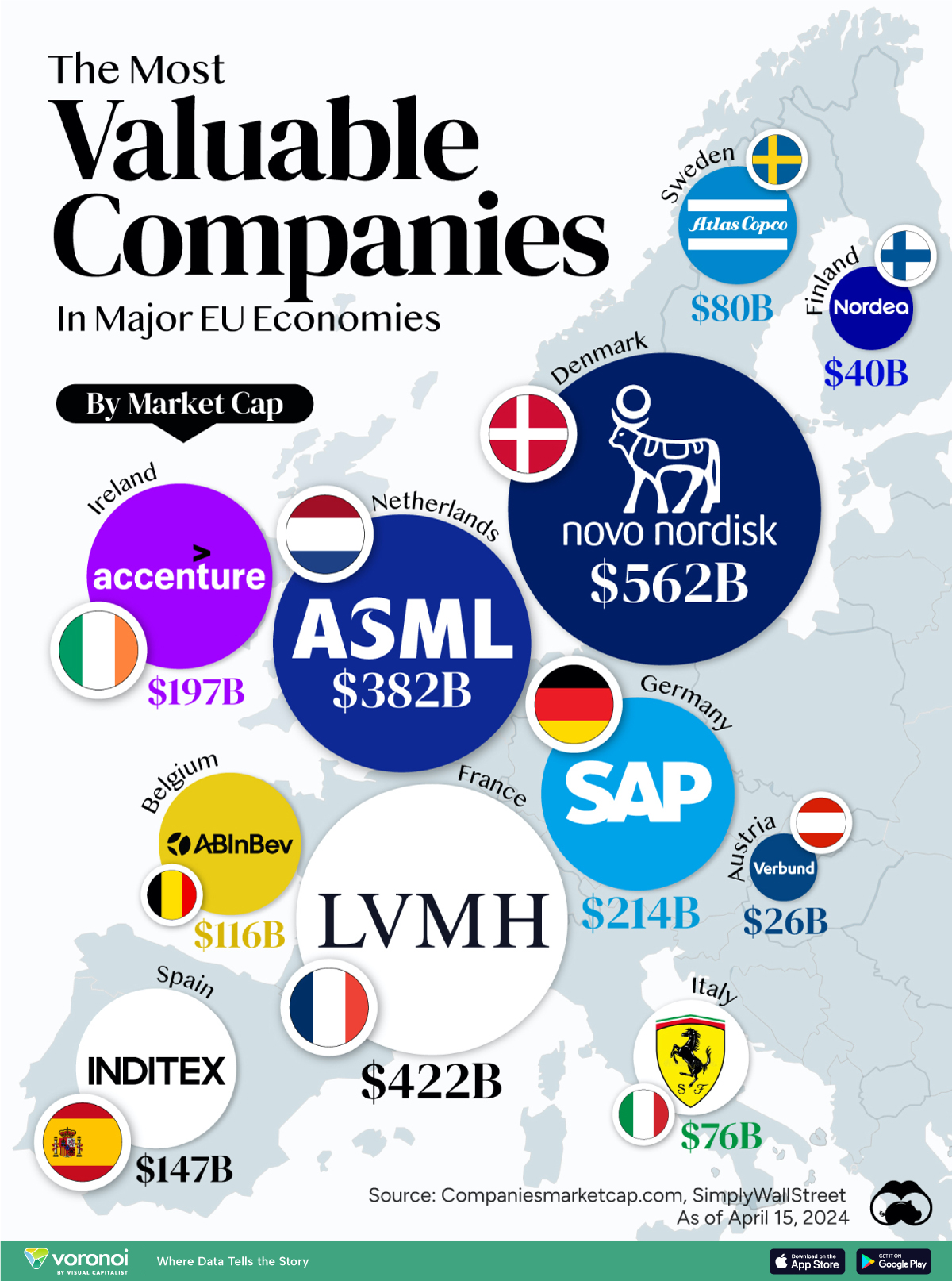
The Most Valuable Companies in Major EU Economies
From semiconductor equipment manufacturers to supercar makers, the EU’s most valuable companies run the gamut of industries.

Most Valuable Companies in the EU, by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
In this graphic, we mapped out the most valuable corporations in 11 major EU economies, based on their market capitalizations as of April 15th, 2024. All figures are in USD, and were sourced from Companiesmarketcap.com.
Novo Nordisk is currently worth more than $550 billion, making it Europe’s most valuable company by a wide margin. The pharmaceutical giant specializes in diabetes and weight-loss drugs. Demand for two of them, Ozempic and Wegovy, has surged due to their weight-loss capabilities, even causing nationwide shortages in the United States.
The following table includes an expanded list of the most valuable publicly-traded company in larger EU economies. Many of these were not included in the graphic due to space limitations.
| Country | Company | Sector | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | 💊 Novo Nordisk | Pharmaceuticals | $562B |
| 🇫🇷 France | 👜 LVMH | Luxury Goods | $422B |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 🔧 ASML | Semiconductor Equipment | $382B |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 💼 SAP | Enterprise Software | $214B |
| 🇮🇪 Ireland | 🖥️ Accenture | IT Services | $197B |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 👗 Inditex | Retail | $147B |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 🍻 Anheuser-Busch InBev | Beverages | $116B |
| 🇸🇪 Sweden | 🛠️ Atlas Copco | Industrial Equipment | $80B |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 🏎️ Ferrari | Automotive | $76B |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 🏦 Nordea Bank | Banking | $40B |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 🔌 Verbund AG | Energy | $26B |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 🏗️ Tenaris | Oil & Gas Equipment | $22B |
| 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 💡 CEZ Group | Energy | $20B |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | ⛽ PKN Orlen | Energy | $20B |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 🔌 EDP Group | Energy | $16B |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 🏦 Eurobank | Banking | $7B |
| 🇭🇺 Hungary | ⛽ MOL Group | Energy | $7B |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 🏦 Zagrebacka Banka | Banking | $6B |
| 🇷🇴 Romania | ⛽ Romgaz | Energy | $4B |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 💊 Krka | Pharmaceuticals | $4B |
Note: Figures are rounded and last updated on April 15th, 2024. Countries with top publicly-traded companies worth under $4 billion are excluded.
Luxury supergiant LVMH—which owns brands like Tiffany, Christian Dior, and TAG Heuer to name a few—is Europe’s second largest company by market cap, at $420 billion.
Rounding out the top three is ASML, which produces equipment crucial to chip manufacturers, worth $380 billion.
When looking at the region, there is a vast disparity between EU member states and their most valuable companies.
For example, as mentioned earlier, Denmark’s Novo Nordisk and France’s LVMH are worth between $400-550 billion each. Meanwhile, some countries don’t even have a single publicly-listed company that is worth over $1 billion.
In fact, only 12 EU countries (less than half of the union) are home to the top 100 most valuable companies within the bloc. An additional four countries are represented if you look at the list of the top 200 companies.
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
-

 Uranium2 weeks ago
Uranium2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Debt2 weeks ago
Debt2 weeks agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands1 week ago
Brands1 week agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023