Money
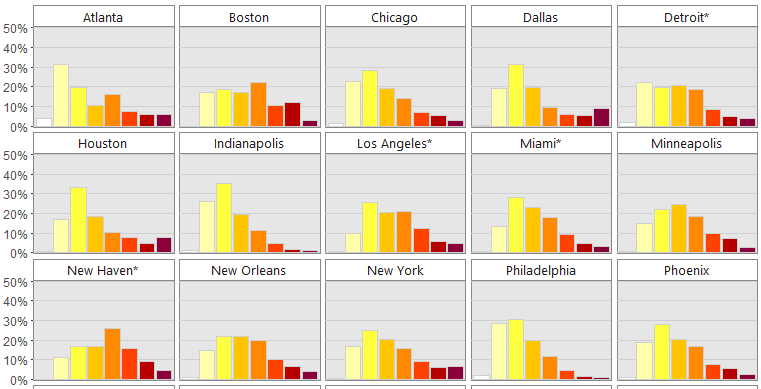
Animation: The Collapse of the Middle Class in 20 Major U.S. Cities
When future historians look back at the beginning of the 21st century, they’ll note that we grappled with many big issues.
They’ll write about the battle between nationalism and globalism, soaring global debt, a dysfunctional healthcare system, societal concerns around automation and AI, and pushback on immigration. They will also note the growing number of populist leaders in Western democracies, ranging from Marine Le Pen to Donald Trump.
However, these historians will not view these ideas and events in isolation. Instead, they will link them all, at least partially, to an overarching trend that is intimately connected to today’s biggest problems: the “hollowing out” of the middle class.
Visualizing the Collapse of the Middle Class
The fact is many people have less money in their pockets – and understandably, this has motivated people to take action against the status quo.
And while the collapse of the middle class and income inequality are issues that receive a fair share of discussion, we thought that this particular animation from Metrocosm helped to put things in perspective.
The following animation shows the change in income distribution in 20 major U.S. cities between 1970 and 2015:
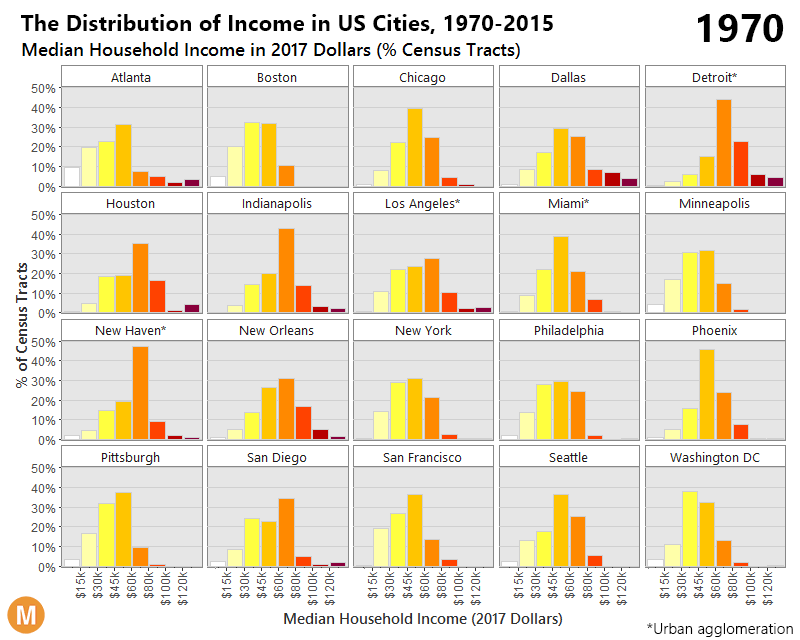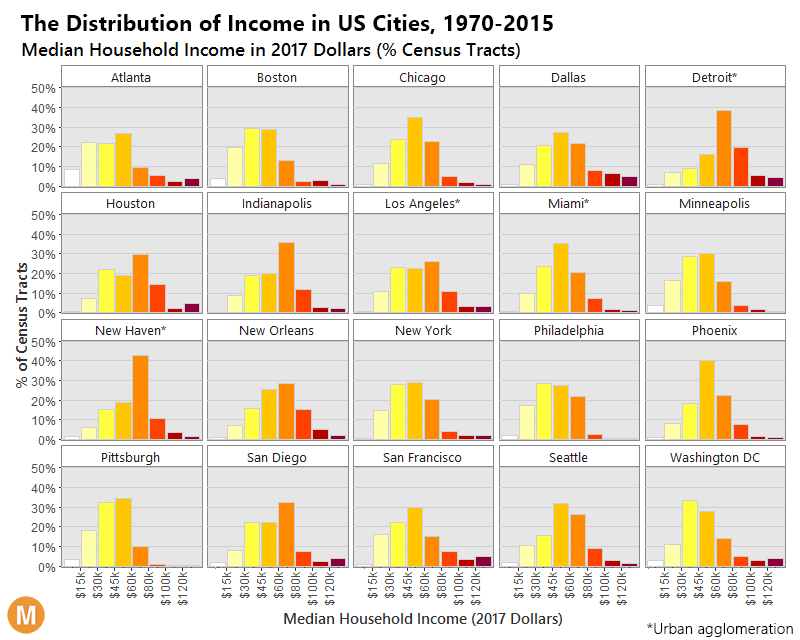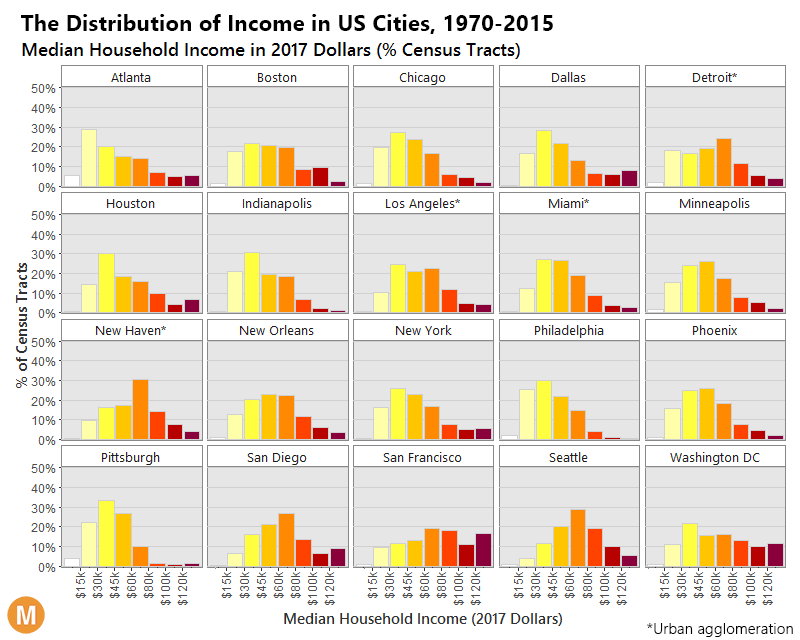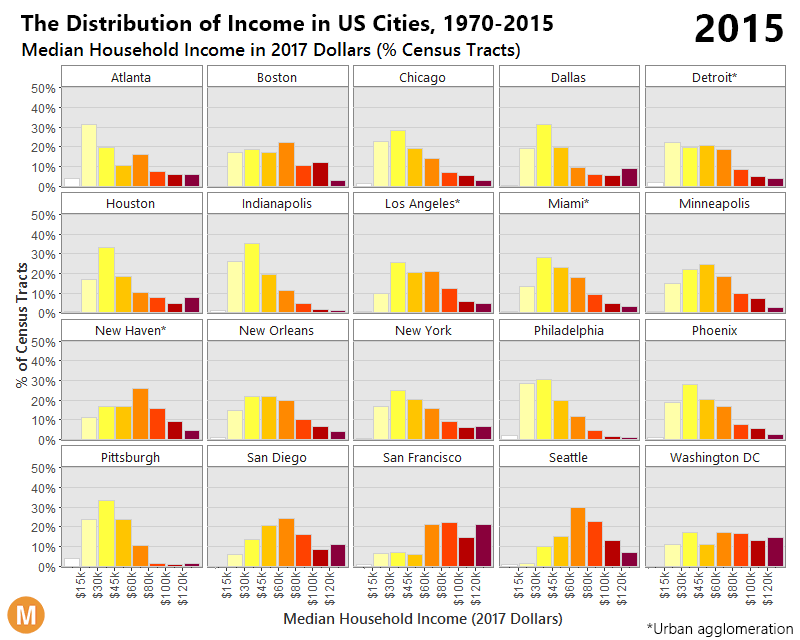
The differences between 1970 and 2015 are intense. At first, each distribution is more bell-shaped, with the majority of people in a middle income bracket – and by 2015, those people are “pushed” out towards the extremes as they either get richer or poorer.
A Broader Look at Income Inequality
This phenomenon is not limited to major cities, either.
Here’s another look at the change in income distribution using smaller brackets and the whole U.S. adult population:
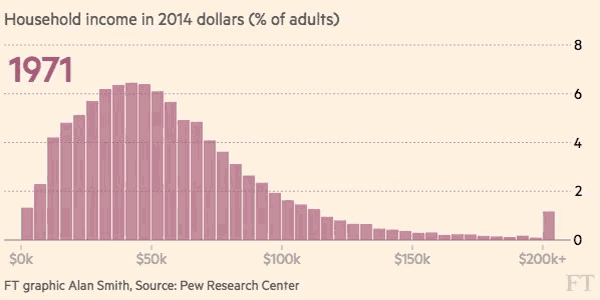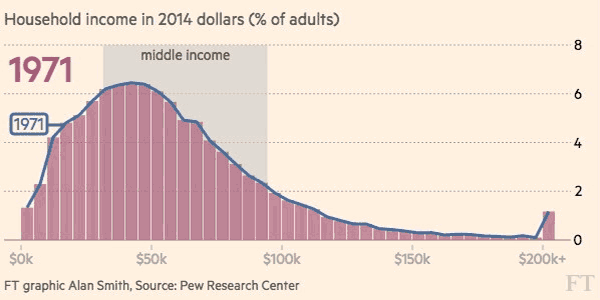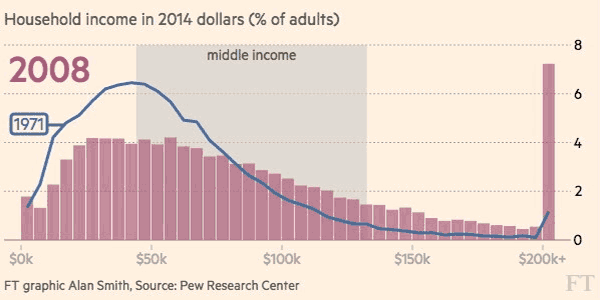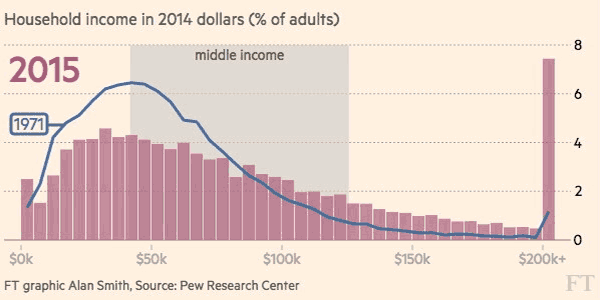
Courtesy of: FT (h/t Metrocosm)
It’s a multi-faceted challenge, because while a significant portion of middle class households are being shifted into lower income territory, there are also many households that are doing the opposite. According to Pew Research, the percentage of households in the upper income bracket has grown from 14% to 21% between 1971 and 2015.
The end result? With people being pushed to both ends of the spectrum, the middle class has decreased considerably in size. In 1971, the middle class made up 61% of the adult population, and by 2014 it accounted for less than 50%.
As this “core” of society shrinks, it aggravates the aforementioned problems. People and governments borrow more money to make up for a lack of middle class wealth, while backlashes against globalism, free trade, and open borders are fueled. The populists who can “fix” the broken system are elected, and so on.
Money
Charted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
Just two countries account for half of the top 20 cities with the most billionaires. And the majority of the other half are found in Asia.
Charted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Some cities seem to attract the rich. Take New York City for example, which has 340,000 high-net-worth residents with investable assets of more than $1 million.
But there’s a vast difference between being a millionaire and a billionaire. So where do the richest of them all live?
Using data from the Hurun Global Rich List 2024, we rank the top 20 cities with the highest number of billionaires in 2024.
A caveat to these rich lists: sources often vary on figures and exact rankings. For example, in last year’s reports, Forbes had New York as the city with the most billionaires, while the Hurun Global Rich List placed Beijing at the top spot.
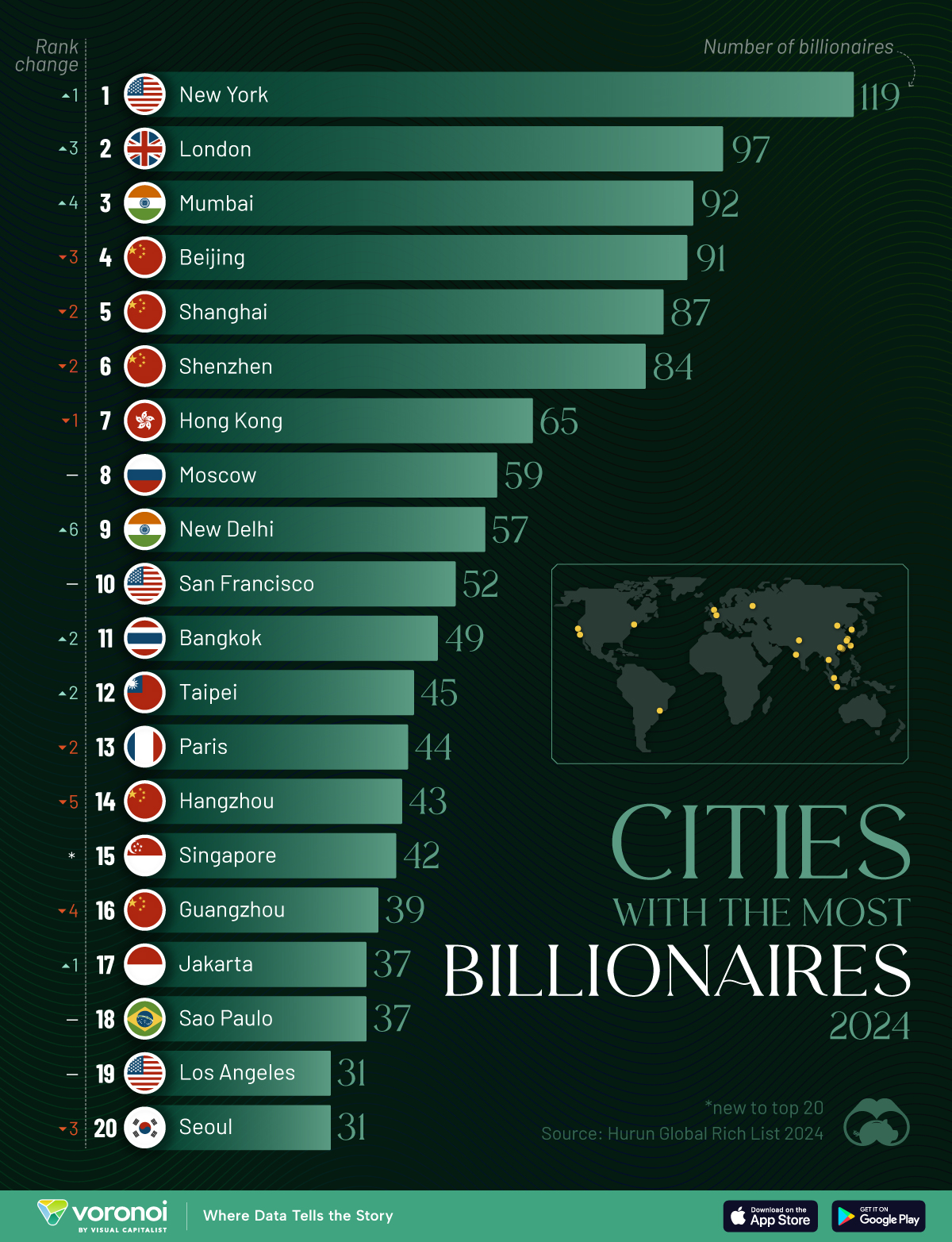
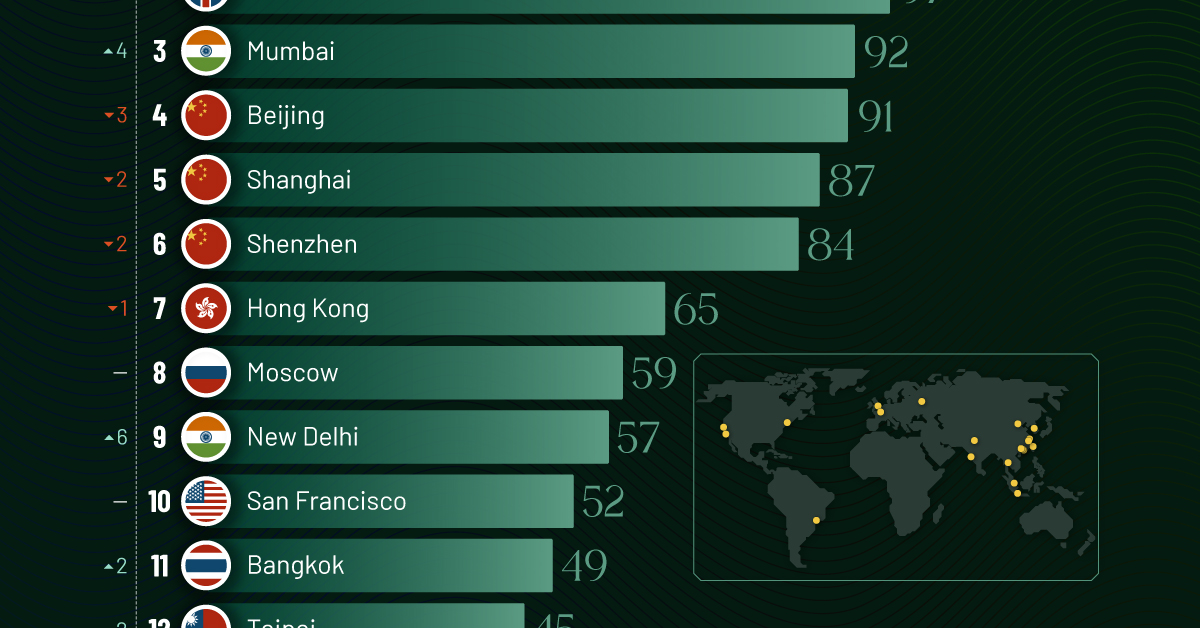
Ranked: Top 20 Cities with the Most Billionaires in 2024
The Chinese economy’s doldrums over the course of the past year have affected its ultra-wealthy residents in key cities.
Beijing, the city with the most billionaires in 2023, has not only ceded its spot to New York, but has dropped to #4, overtaken by London and Mumbai.
| Rank | City | Billionaires | Rank Change YoY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 New York | 119 | +1 |
| 2 | 🇬🇧 London | 97 | +3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Mumbai | 92 | +4 |
| 4 | 🇨🇳 Beijing | 91 | -3 |
| 5 | 🇨🇳 Shanghai | 87 | -2 |
| 6 | 🇨🇳 Shenzhen | 84 | -2 |
| 7 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | 65 | -1 |
| 8 | 🇷🇺 Moscow | 59 | No Change |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi | 57 | +6 |
| 10 | 🇺🇸 San Francisco | 52 | No Change |
| 11 | 🇹🇭 Bangkok | 49 | +2 |
| 12 | 🇹🇼 Taipei | 45 | +2 |
| 13 | 🇫🇷 Paris | 44 | -2 |
| 14 | 🇨🇳 Hangzhou | 43 | -5 |
| 15 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 42 | New to Top 20 |
| 16 | 🇨🇳 Guangzhou | 39 | -4 |
| 17T | 🇮🇩 Jakarta | 37 | +1 |
| 17T | 🇧🇷 Sao Paulo | 37 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇺🇸 Los Angeles | 31 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇰🇷 Seoul | 31 | -3 |
In fact all Chinese cities on the top 20 list have lost billionaires between 2023–24. Consequently, they’ve all lost ranking spots as well, with Hangzhou seeing the biggest slide (-5) in the top 20.
Where China lost, all other Asian cities—except Seoul—in the top 20 have gained ranks. Indian cities lead the way, with New Delhi (+6) and Mumbai (+3) having climbed the most.
At a country level, China and the U.S combine to make up half of the cities in the top 20. They are also home to about half of the world’s 3,200 billionaire population.
In other news of note: Hurun officially counts Taylor Swift as a billionaire, estimating her net worth at $1.2 billion.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries