Money
10 Banknotes From Around the World, and Their Security Features
The history of counterfeiting is almost as extensive as the history of money itself.
It’s said that even the first electrum coins in Lydia were regularly faked, and coming across counterfeit coins in Ancient Rome was a daily occurrence. Roman Emperors, like other rulers, also famously did their own counterfeiting, debasing the metal in coins and trying to pass them off as having higher value.
The problem of funny money remained an issue for society even thousands of years later. For example, at the start of the U.S. Civil War in 1861 – when banks still issued their own currencies – it was estimated that half of the banknotes in circulation were forgeries.
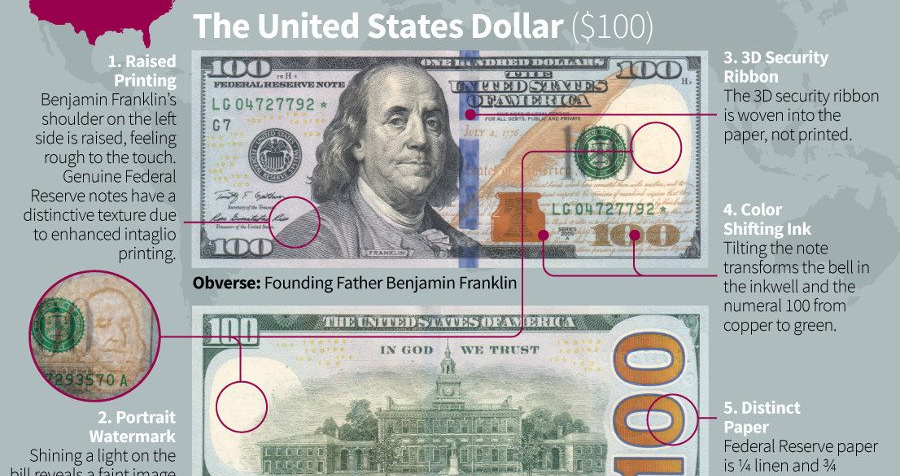
Banknote Security Features
And as we move towards a more digital world, the cat and mouse games between authorities and counterfeiters continues.
Today’s infographic comes to us from TitleMax and it details 10 popular banknotes from around the world, including the anti-counterfeiting measures that have been taken for each note.

Through centuries of collective experience, advances in technology, and many episodes of trial and error, the latest fiat banknotes have impressive security features that blow previous generations out of the water.
Common Security Features Used
Many national mints have adopted similar anti-counterfeiting technologies for their banknotes:
Plastic money: In Canada, authorities were starting to find 470 counterfeits for every one million legitimate banknotes that existed – a rate almost 10x as high as other G20 countries. In light of this problem, the Bank of Canada recently introduced polymer notes that make counterfeiting considerably more difficult.
Polymer banknotes were pioneered in Australia in 1988, and like Canada, many countries have made the switch to polymer including the United Kingdom, Malaysia, Chile, New Zealand, and Mexico.
Holograms: More than 300 denominations in 97 currencies use holograms for protection, making them one of the most common security features globally. They can be incorporated into designs by the way of security threads, stripes, patches and window features.
Watermarks: One of the most common security features, watermarks are created by using different thicknesses of paper in the printing process. When hit with light, an image will be illuminated.
Microtext: Tiny text, which can only be read with a magnifying glass, is a common safety feature on many bills globally.
Color-changing features: Roughly 42% of banknotes issued since 2011 use color-changing features in which parts of the note change color to the viewer depending on the angle.
Security thread: Many notes use this security feature, which consists of a thin ribbon that is threaded through the note’s paper.
Invisible marks: Notes can also incorporate ink or markings that are only visible in fluorescent or infrared light, making them invisible to the naked eye.
Money
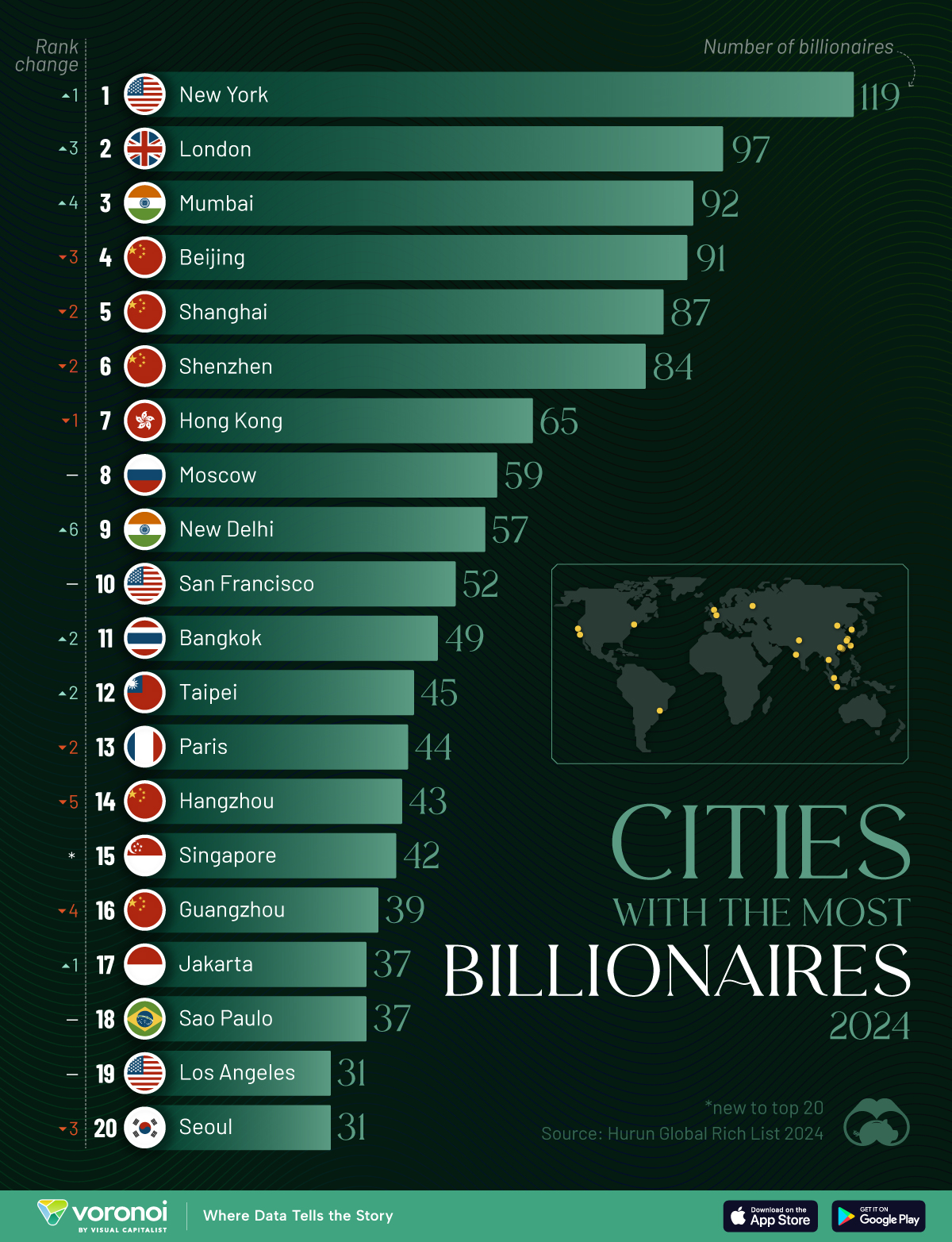
Charted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
Just two countries account for half of the top 20 cities with the most billionaires. And the majority of the other half are found in Asia.
Charted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Some cities seem to attract the rich. Take New York City for example, which has 340,000 high-net-worth residents with investable assets of more than $1 million.
But there’s a vast difference between being a millionaire and a billionaire. So where do the richest of them all live?
Using data from the Hurun Global Rich List 2024, we rank the top 20 cities with the highest number of billionaires in 2024.
A caveat to these rich lists: sources often vary on figures and exact rankings. For example, in last year’s reports, Forbes had New York as the city with the most billionaires, while the Hurun Global Rich List placed Beijing at the top spot.
Ranked: Top 20 Cities with the Most Billionaires in 2024
The Chinese economy’s doldrums over the course of the past year have affected its ultra-wealthy residents in key cities.
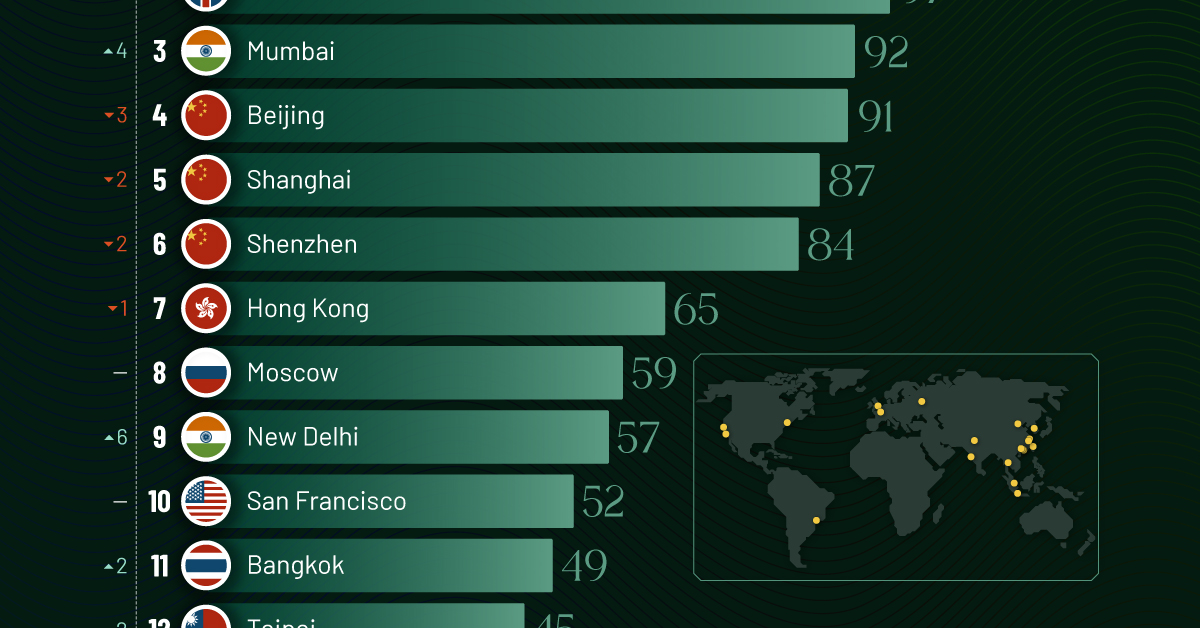
Beijing, the city with the most billionaires in 2023, has not only ceded its spot to New York, but has dropped to #4, overtaken by London and Mumbai.
| Rank | City | Billionaires | Rank Change YoY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 New York | 119 | +1 |
| 2 | 🇬🇧 London | 97 | +3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Mumbai | 92 | +4 |
| 4 | 🇨🇳 Beijing | 91 | -3 |
| 5 | 🇨🇳 Shanghai | 87 | -2 |
| 6 | 🇨🇳 Shenzhen | 84 | -2 |
| 7 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | 65 | -1 |
| 8 | 🇷🇺 Moscow | 59 | No Change |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi | 57 | +6 |
| 10 | 🇺🇸 San Francisco | 52 | No Change |
| 11 | 🇹🇭 Bangkok | 49 | +2 |
| 12 | 🇹🇼 Taipei | 45 | +2 |
| 13 | 🇫🇷 Paris | 44 | -2 |
| 14 | 🇨🇳 Hangzhou | 43 | -5 |
| 15 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 42 | New to Top 20 |
| 16 | 🇨🇳 Guangzhou | 39 | -4 |
| 17T | 🇮🇩 Jakarta | 37 | +1 |
| 17T | 🇧🇷 Sao Paulo | 37 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇺🇸 Los Angeles | 31 | No Change |
| 19T | 🇰🇷 Seoul | 31 | -3 |
In fact all Chinese cities on the top 20 list have lost billionaires between 2023–24. Consequently, they’ve all lost ranking spots as well, with Hangzhou seeing the biggest slide (-5) in the top 20.
Where China lost, all other Asian cities—except Seoul—in the top 20 have gained ranks. Indian cities lead the way, with New Delhi (+6) and Mumbai (+3) having climbed the most.
At a country level, China and the U.S combine to make up half of the cities in the top 20. They are also home to about half of the world’s 3,200 billionaire population.
In other news of note: Hurun officially counts Taylor Swift as a billionaire, estimating her net worth at $1.2 billion.
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023