Misc
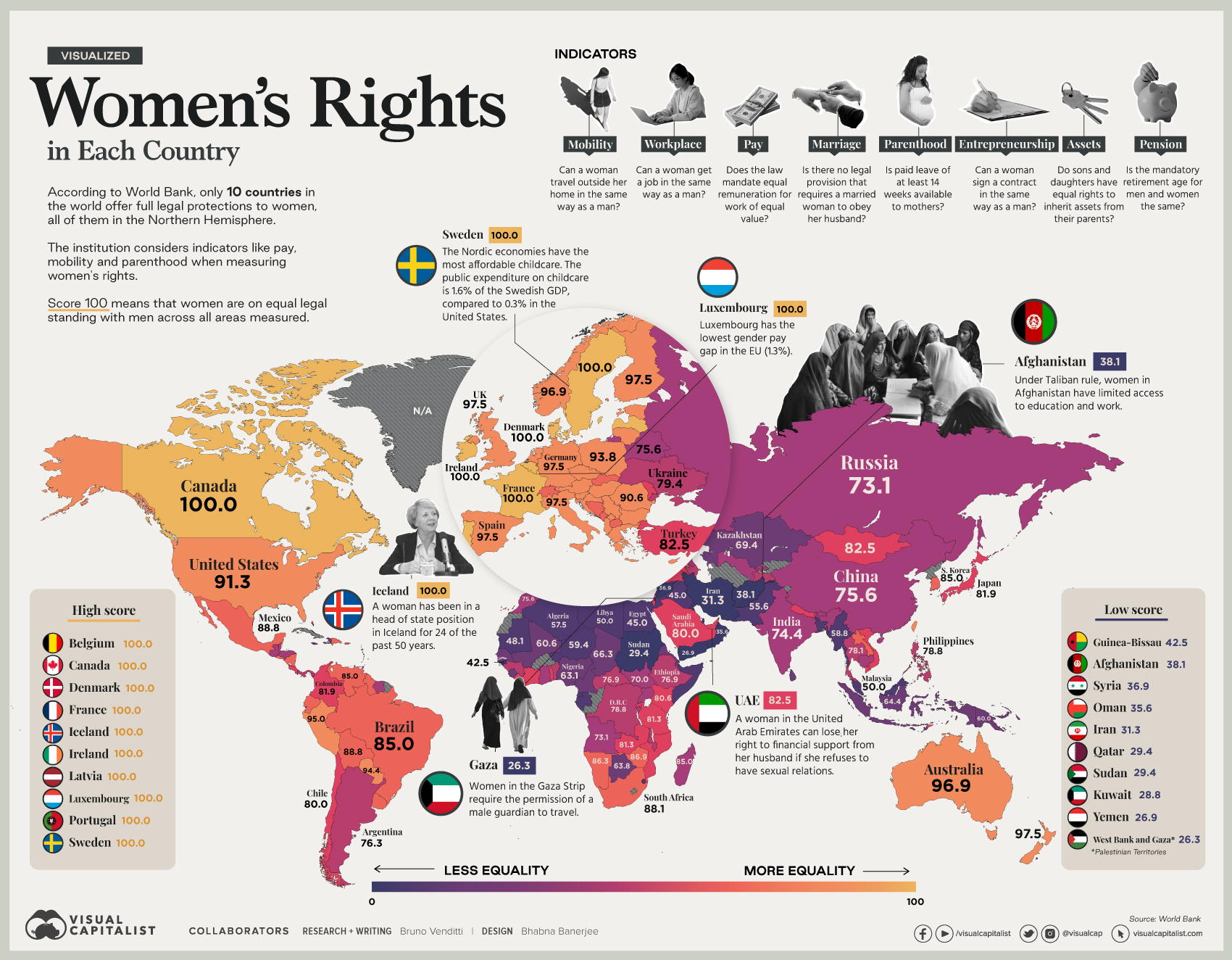
Visualizing Women’s Economic Rights Around the World
Visualizing Women’s Economic Rights in Each Country
In recent years, many economies have made women’s rights a priority by eliminating job restrictions, working to reduce the gender wage gap, or changing legislation related to marriage and parenthood.
Still, many laws continue to inhibit women’s ability to enter the workforce or start a business—and even to travel outside their homes in the same way as men. In fact, on average globally, women have just three-quarters of the economic rights of men.
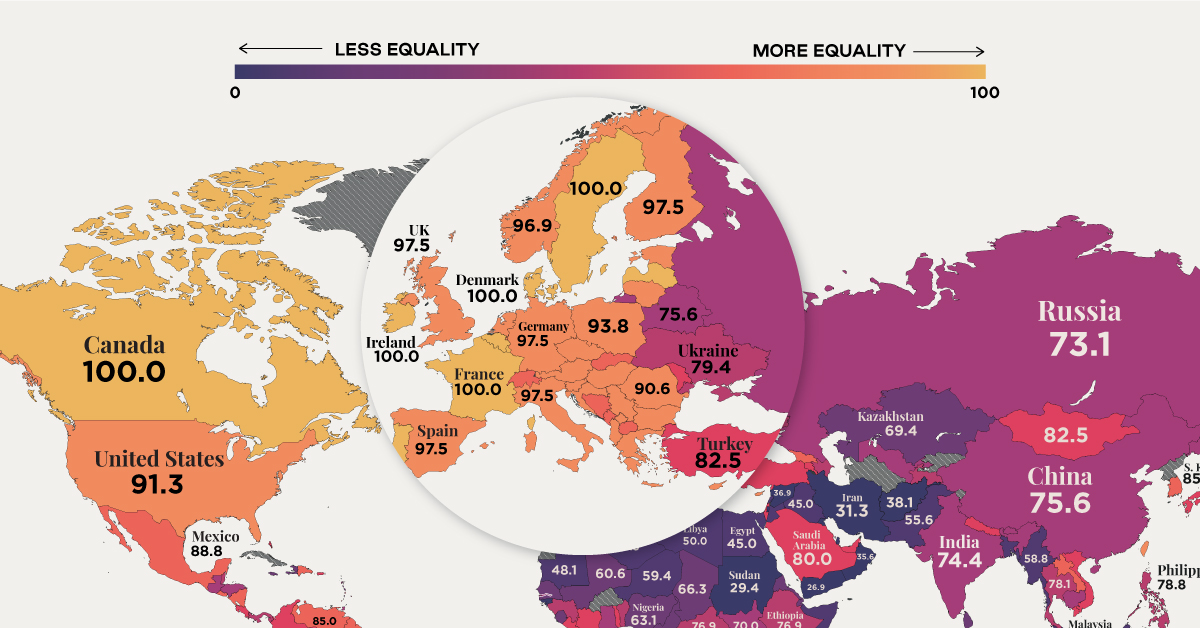
This map uses data from the Women, Business and Law 2021 report by the World Bank, to visualize women’s economic rights around the world.
Legal Protections
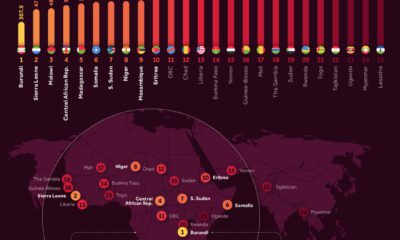
According to the World Bank, only 10 countries offer full legal protections to women, and all of them are in the Northern Hemisphere.
In ranking countries, the institution considers indicators like equal remuneration, legal rights, and mobility. A score of 100 means that women are on equal legal standing with men across all areas measured.
| Rank | Country/Territory | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Belgium | 100.0 |
| 1 | Canada | 100.0 |
| 1 | Denmark | 100.0 |
| 1 | France | 100.0 |
| 1 | Iceland | 100.0 |
| 1 | Ireland | 100.0 |
| 1 | Latvia | 100.0 |
| 1 | Luxembourg | 100.0 |
| 1 | Portugal | 100.0 |
| 1 | Sweden | 100.0 |
| 2 | Estonia | 97.5 |
| 2 | Finland | 97.5 |
| 2 | Germany | 97.5 |
| 2 | Greece | 97.5 |
| 2 | Italy | 97.5 |
| 2 | Netherlands | 97.5 |
| 2 | New Zealand | 97.5 |
| 2 | Spain | 97.5 |
| 2 | United Kingdom | 97.5 |
| 3 | Australia | 96.9 |
| 3 | Austria | 96.9 |
| 3 | Hungary | 96.9 |
| 3 | Norway | 96.9 |
| 3 | Slovenia | 96.9 |
| 4 | Peru | 95.0 |
| 5 | Paraguay | 94.4 |
| 6 | Croatia | 93.8 |
| 6 | Czech Republic | 93.8 |
| 6 | Lithuania | 93.8 |
| 6 | Poland | 93.8 |
| 6 | Serbia | 93.8 |
| 7 | Kosovo | 91.9 |
| 7 | Mauritius | 91.9 |
| 8 | Albania | 91.3 |
| 8 | Cyprus | 91.3 |
| 8 | Taiwan, China | 91.3 |
| 8 | United States | 91.3 |
| 9 | Bulgaria | 90.6 |
| 9 | Romania | 90.6 |
| 10 | Ecuador | 89.4 |
| 10 | Hong Kong, China | 89.4 |
| 11 | Bolivia | 88.8 |
| 11 | El Salvador | 88.8 |
| 11 | Malta | 88.8 |
| 11 | Mexico | 88.8 |
| 11 | Uruguay | 88.8 |
| 12 | Lao PDR | 88.1 |
| 12 | Montenegro | 88.1 |
| 12 | South Africa | 88.1 |
| 13 | Guyana | 86.9 |
| 13 | Zimbabwe | 86.9 |
| 14 | Cabo Verde | 86.3 |
| 14 | Dominican Republic | 86.3 |
| 14 | Namibia | 86.3 |
| 14 | Nicaragua | 86.3 |
| 14 | São Tomé and Príncipe | 86.3 |
| 15 | Georgia | 85.6 |
| 15 | Switzerland | 85.6 |
| 16 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 85.0 |
| 16 | Brazil | 85.0 |
| 16 | Korea, Rep. | 85.0 |
| 16 | North Macedonia | 85.0 |
| 16 | Slovak Republic | 85.0 |
| 16 | Venezuela | 85.0 |
| 17 | Moldova | 84.4 |
| 17 | Togo | 84.4 |
| 18 | Liberia | 83.8 |
| 18 | Puerto Rico (US) | 83.8 |
| 18 | St. Lucia | 83.8 |
| 19 | Costa Rica | 83.1 |
| 19 | Côte d'Ivoire | 83.1 |
| 19 | Timor-Leste | 83.1 |
| 20 | Armenia | 82.5 |
| 20 | Fiji | 82.5 |
| 20 | Mongolia | 82.5 |
| 20 | Mozambique | 82.5 |
| 20 | Singapore | 82.5 |
| 20 | Turkey | 82.5 |
| 20 | United Arab Emirates | 82.5 |
| 21 | Colombia | 81.9 |
| 21 | Japan | 81.9 |
| 21 | Vietnam | 81.9 |
| 22 | Bahamas | 81.3 |
| 22 | Tanzania | 81.3 |
| 22 | Zambia | 81.3 |
| 23 | Grenada | 80.6 |
| 23 | Israel | 80.6 |
| 23 | Kenya | 80.6 |
| 23 | Nepal | 80.6 |
| 23 | Rwanda | 80.6 |
| 24 | Chile | 80.0 |
| 24 | Samoa | 80.0 |
| 24 | San Marino | 80.0 |
| 24 | Saudi Arabia | 80.0 |
| 25 | Belize | 79.4 |
| 25 | Burkina Faso | 79.4 |
| 25 | Panama | 79.4 |
| 25 | Ukraine | 79.4 |
| 26 | Azerbaijan | 78.8 |
| 26 | Congo, Dem. Rep. | 78.8 |
| 26 | Kiribati | 78.8 |
| 26 | Philippines | 78.8 |
| 26 | Tajikistan | 78.8 |
| 27 | Lesotho | 78.1 |
| 27 | Thailand | 78.1 |
| 28 | Benin | 77.5 |
| 28 | Malawi | 77.5 |
| 29 | Barbados | 76.9 |
| 29 | Central African Republic | 76.9 |
| 29 | Ethiopia | 76.9 |
| 29 | Kyrgyz Republic | 76.9 |
| 30 | Argentina | 76.3 |
| 30 | Guinea | 76.3 |
| 30 | Seychelles | 76.3 |
| 31 | Belarus | 75.6 |
| 31 | China | 75.6 |
| 31 | Morocco | 75.6 |
| 32 | Cambodia | 75.0 |
| 32 | Ghana | 75.0 |
| 32 | Honduras | 75.0 |
| 32 | Trinidad and Tobago | 75.0 |
| 33 | Gambia | 74.4 |
| 33 | India | 74.4 |
| 33 | Madagascar | 74.4 |
| 34 | Maldives | 73.8 |
| 34 | Suriname | 73.8 |
| 35 | Angola | 73.1 |
| 35 | Burundi | 73.1 |
| 35 | Russia | 73.1 |
| 35 | Uganda | 73.1 |
| 36 | Bhutan | 71.9 |
| 37 | St. Kitts and Nevis | 71.3 |
| 38 | Guatemala | 70.6 |
| 38 | Uzbekistan | 70.6 |
| 39 | South Sudan | 70.0 |
| 40 | Eritrea | 69.4 |
| 40 | Kazakhstan | 69.4 |
| 40 | Sierra Leone | 69.4 |
| 41 | Dijibouti | 68.1 |
| 41 | Jamaica | 68.1 |
| 41 | Marshall Islands | 68.1 |
| 41 | St. Vicent and the Grenadines | 68.1 |
| 42 | Tunisia | 67.5 |
| 43 | Senegal | 66.9 |
| 44 | Antigua and Barbuda | 66.3 |
| 44 | Chad | 66.3 |
| 45 | Sri Lanka | 65.6 |
| 46 | Comoros | 65.0 |
| 47 | Indonesia | 64.4 |
| 48 | Botswana | 63.8 |
| 48 | Haiti | 63.8 |
| 48 | Micronesia | 63.8 |
| 49 | Nigeria | 63.1 |
| 50 | Dominica | 62.5 |
| 51 | Mali | 60.6 |
| 52 | Cameroon | 60.0 |
| 52 | Papua New Guinea | 60.0 |
| 53 | Niger | 59.4 |
| 54 | Myanmar | 58.8 |
| 54 | Palau | 58.8 |
| 54 | Tonga | 58.8 |
| 55 | Vanuatu | 58.1 |
| 56 | Algeria | 57.5 |
| 56 | Gabon | 57.5 |
| 57 | Solomon Islands | 56.9 |
| 58 | Bahrain | 55.6 |
| 58 | Pakistan | 55.6 |
| 59 | Brunei Darussalam | 53.1 |
| 60 | Lebanon | 52.5 |
| 61 | Equatorial Guinea | 51.9 |
| 62 | Libya | 50.0 |
| 62 | Malaysia | 50.0 |
| 63 | Bangladesh | 49.4 |
| 63 | Congo, Rep. | 49.4 |
| 64 | Mauritania | 48.1 |
| 65 | Jordan | 46.9 |
| 65 | Somalia | 46.9 |
| 66 | Eswatini | 46.3 |
| 67 | Egypt | 45.0 |
| 67 | Iraq | 45.0 |
| 68 | Guinea-Bissau | 42.5 |
| 69 | Afghanistan | 38.1 |
| 70 | Syria | 36.9 |
| 71 | Oman | 35.6 |
| 72 | Iran | 31.3 |
| 73 | Qatar | 29.4 |
| 73 | Sudan | 29.4 |
| 74 | Kuwait | 28.8 |
| 75 | Yemen | 26.9 |
| 76 | West Bank and Gaza | 26.3 |
According to the report, there are 20 economies in the world where women still have half or fewer of the legal economic rights of men.
Under Taliban rule, for example, women in Afghanistan have limited access to education and work. In the Gaza Strip, women must have the permission of a male guardian to travel.
Yet, some differences are also seen in developed countries.
In the U.S, women still earn an average of about 82 cents for each dollar earned by men, and the gap across many countries in Europe is similar. Meanwhile, women are represented in just 23% of seats in national parliaments globally, and make up just 13% of agricultural landholders.
The Shadow Pandemic
COVID-19 has exacerbated existing inequalities that disadvantage girls and women, including barriers to attend school and maintain jobs, according to the United Nations.
In fact, new research shows that the sectors that have been most affected by the pandemic so far are those with high levels of women workers, including the restaurant and hospitality business, as well as the travel sector.
While leaders debate recovery in a post-pandemic world, rights equality remains a central topic for social and economic development.
VC+
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our VC+ Special Dispatch is available exclusively to VC+ members. All you need to do is log into the VC+ Archive.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to access the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members get to see.
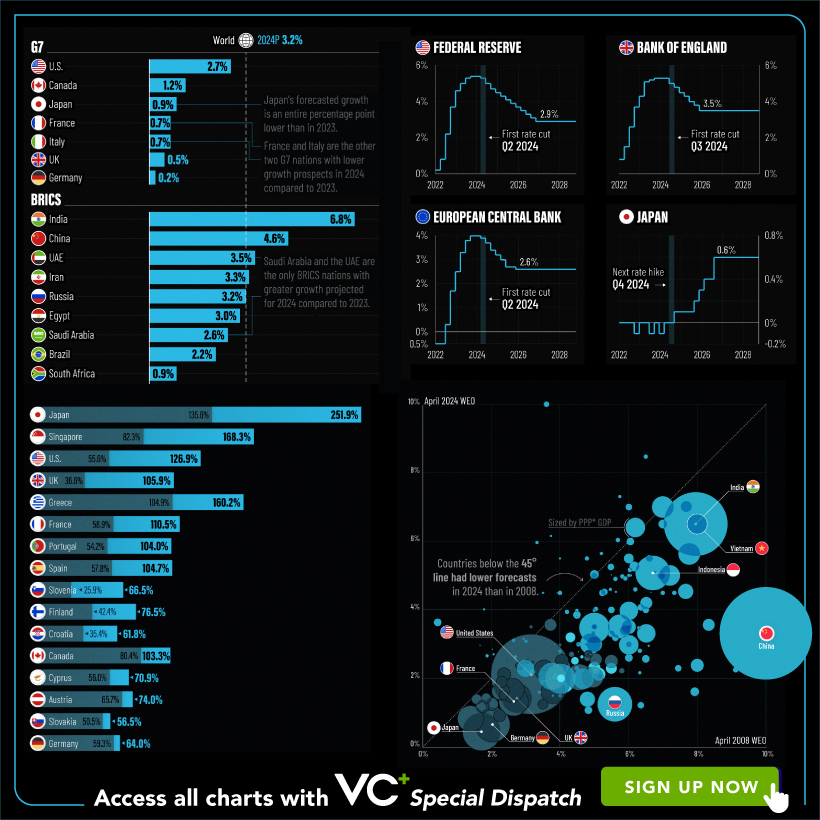
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members can access the full Special Dispatch by logging into the VC+ Archive, where you can also check out previous releases.
Make sure you join VC+ now to see exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries