Technology
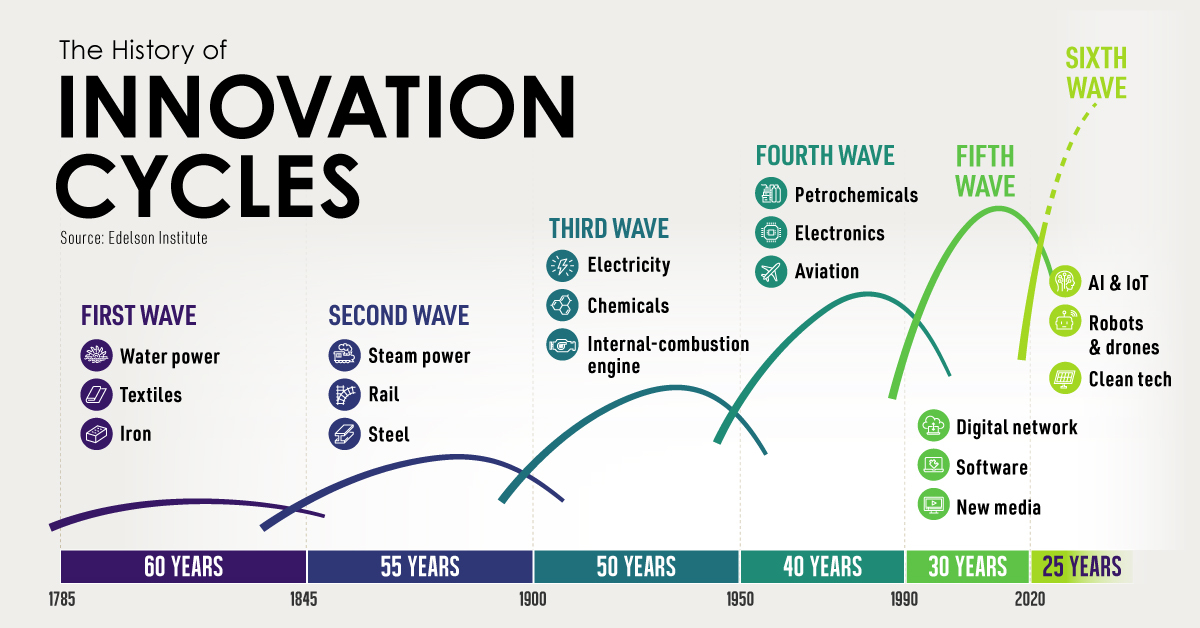
Long Waves: The History of Innovation Cycles
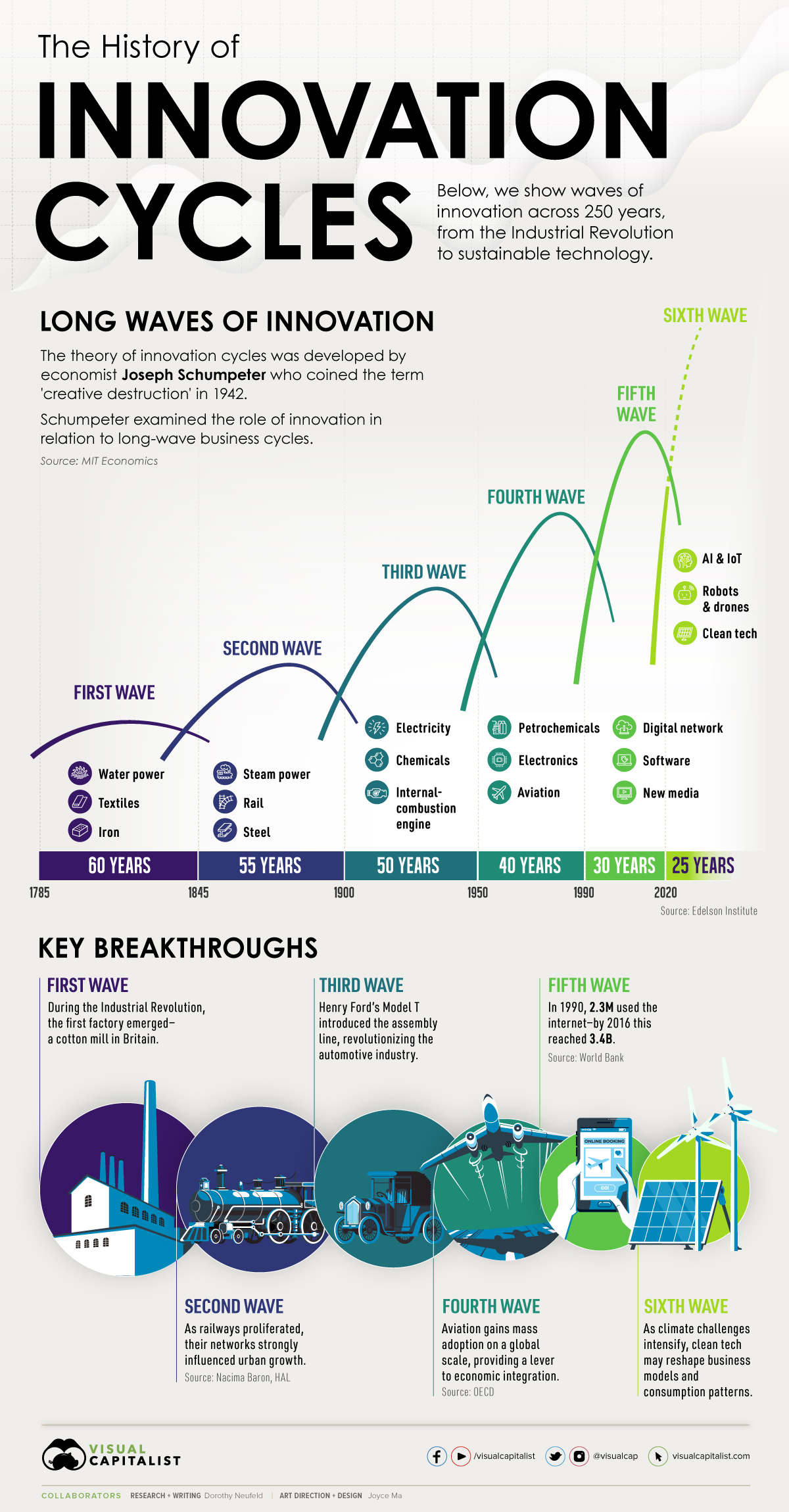
Long Waves: How Innovation Cycles Influence Growth
Creative destruction plays a key role in entrepreneurship and economic development.
Coined by economist Joseph Schumpeter in 1942, the theory of “creative destruction” suggests that business cycles operate under long waves of innovation. Specifically, as markets are disrupted, key clusters of industries have outsized effects on the economy.
Take the railway industry, for example. At the turn of the 19th century, railways completely reshaped urban demographics and trade. Similarly, the internet disrupted entire industries—from media to retail.
The above infographic shows how innovation cycles have impacted economies since 1785, and what’s next for the future.
Innovation Cycles: The Six Waves
From the first wave of textiles and water power in the industrial revolution, to the internet in the 1990s, here are the six waves of innovation and their key breakthroughs.
| First Wave | Second Wave | Third Wave | Fourth Wave | Fifth Wave | Sixth Wave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Power Textiles Iron | Steam Rail Steel | Electricity Chemicals Internal-Combustion Engine | Petrochemicals Electronics Aviation | Digital Network Software New Media | Digitization (AI, IoT, AV, Robots & Drones) Clean Tech |
| 60 years | 55 years | 50 years | 40 years | 30 years | 25 years |
Source: Edelsen Institute, Detlef Reis
During the first wave of the Industrial Revolution, water power was instrumental in manufacturing paper, textiles, and iron goods. Unlike the mills of the past, full-sized dams fed turbines through complex belt systems. Advances in textiles brought the first factory, and cities expanded around them.
With the second wave, between about 1845 and 1900, came significant rail, steam, and steel advancements. The rail industry alone affected countless industries, from iron and oil to steel and copper. In turn, great railway monopolies were formed.
The emergence of electricity powering light and telephone communication through the third wave dominated the first half of the 1900s. Henry Ford introduced the Model T, and the assembly line transformed the auto industry. Automobiles became closely linked with the expansion of the American metropolis. Later, in the fourth wave, aviation revolutionized travel.
After the internet emerged by the early 1990s, barriers to information were upended. New media changed political discourse, news cycles, and communication in the fifth wave. The internet ushered in a new frontier of globalization, a borderless landscape of digital information flows.
Market Power
To the economist Schumpeter, technological innovations boosted economic growth and improved living standards.
However, these disruptors can also have a tendency to lead to monopolies. Especially during a cycle’s upswing, the strongest players realize wide margins, establish moats, and fend off rivals. Typically, these cycles begin when the innovations become of general use.
Of course, this can be seen today—never has the world been so closely connected. Information is more centralized than it has ever been, with Big Tech dominating global search traffic, social networks, and advertising.
Like the Big Tech behemoths of today, the rail industry had the power to control prices and push out competitors during the 19th century. At the peak, listed shares of rail companies on the New York Stock Exchange made up 60% of total stock market capitalization.
Waves of Change
As cycle longevity continues to shorten, the fifth wave may have a few years left under its belt.
The sixth wave, marked by artificial intelligence and digitization across information of things (IoT), robotics, and drones, will likely paint an entirely new picture. Namely, the automation of systems, predictive analytics, and data processing could make an impact. In turn, physical goods and services will likely be digitized. The time to complete tasks could shift from hours to even seconds.
At the same time, clean tech could come to the forefront. At the heart of each technological innovation is solving complex problems, and climate concerns are becoming increasingly pressing. Lower costs in solar PV and wind are also predicating efficiency advantages.
Technology
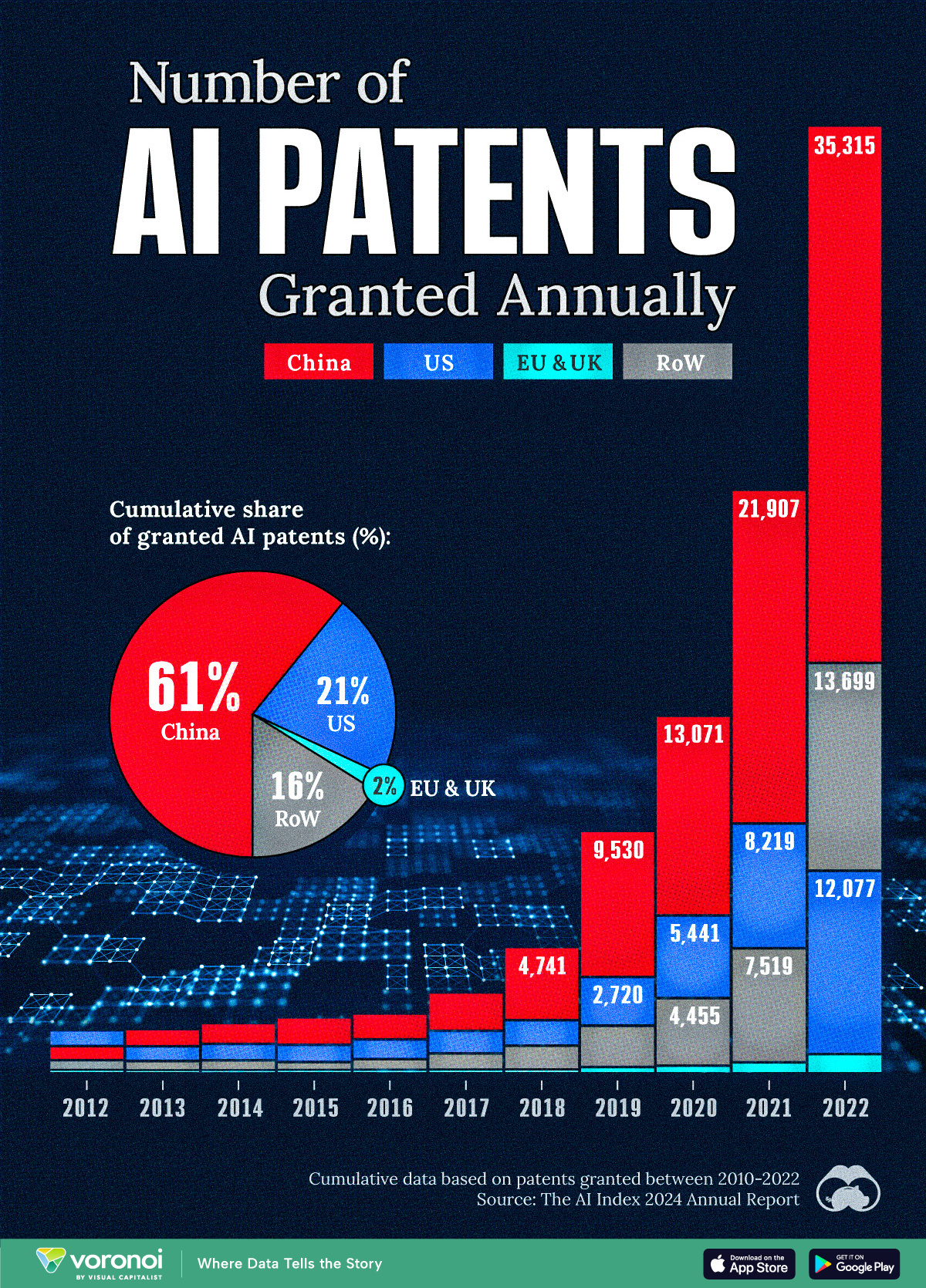
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
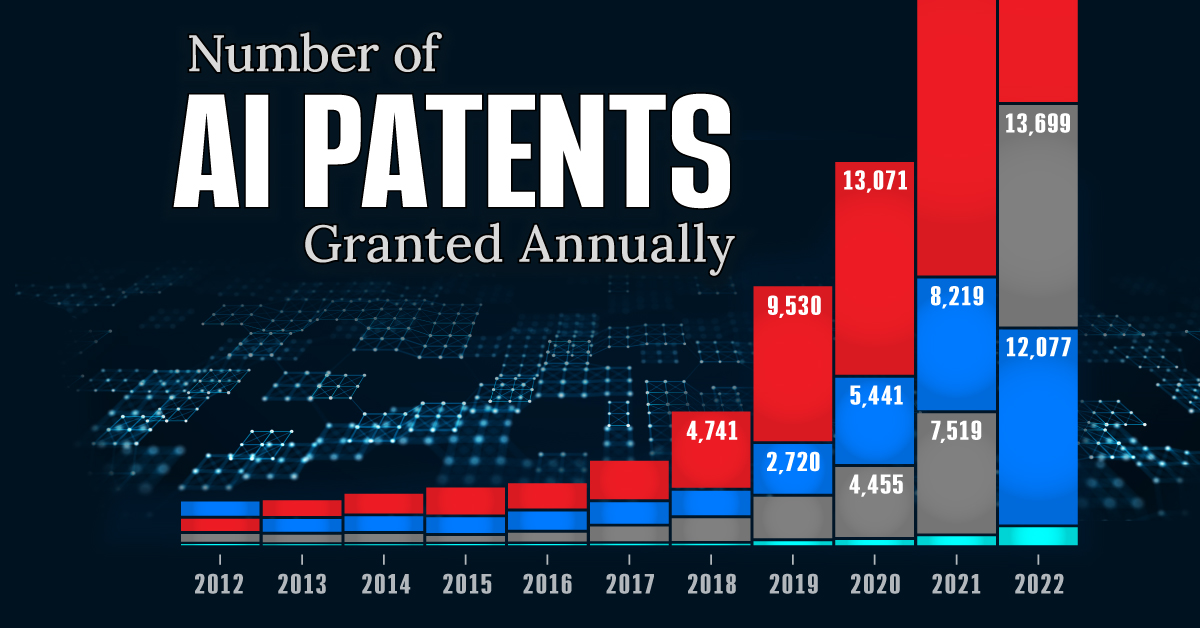
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries