Technology
Map: The World’s Network of Submarine Cables
View the full version of this graphic.
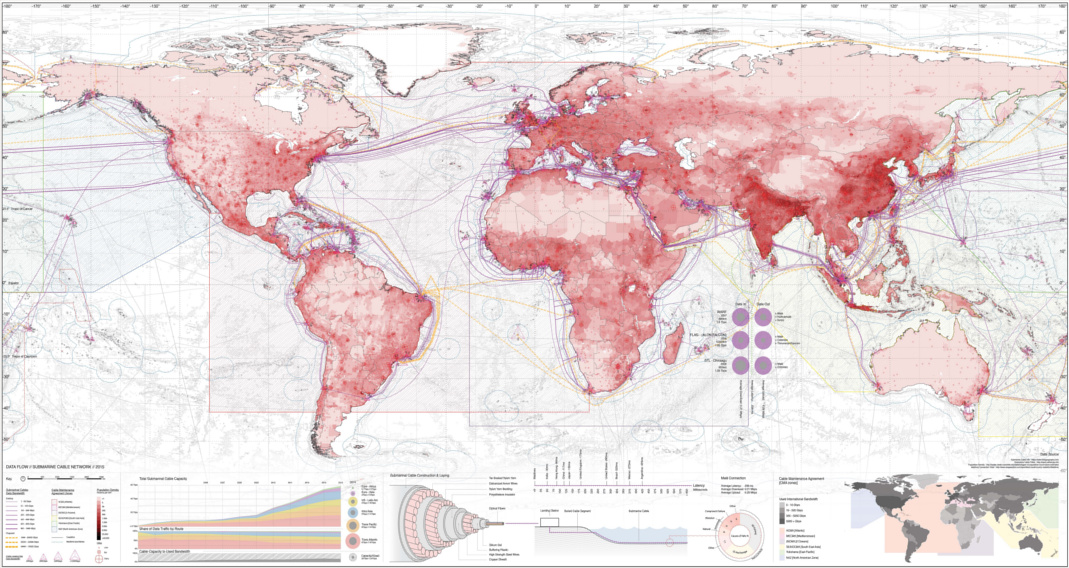
Map: The World’s Network of Submarine Cables
View the above visualization at full resolution for the best experience.
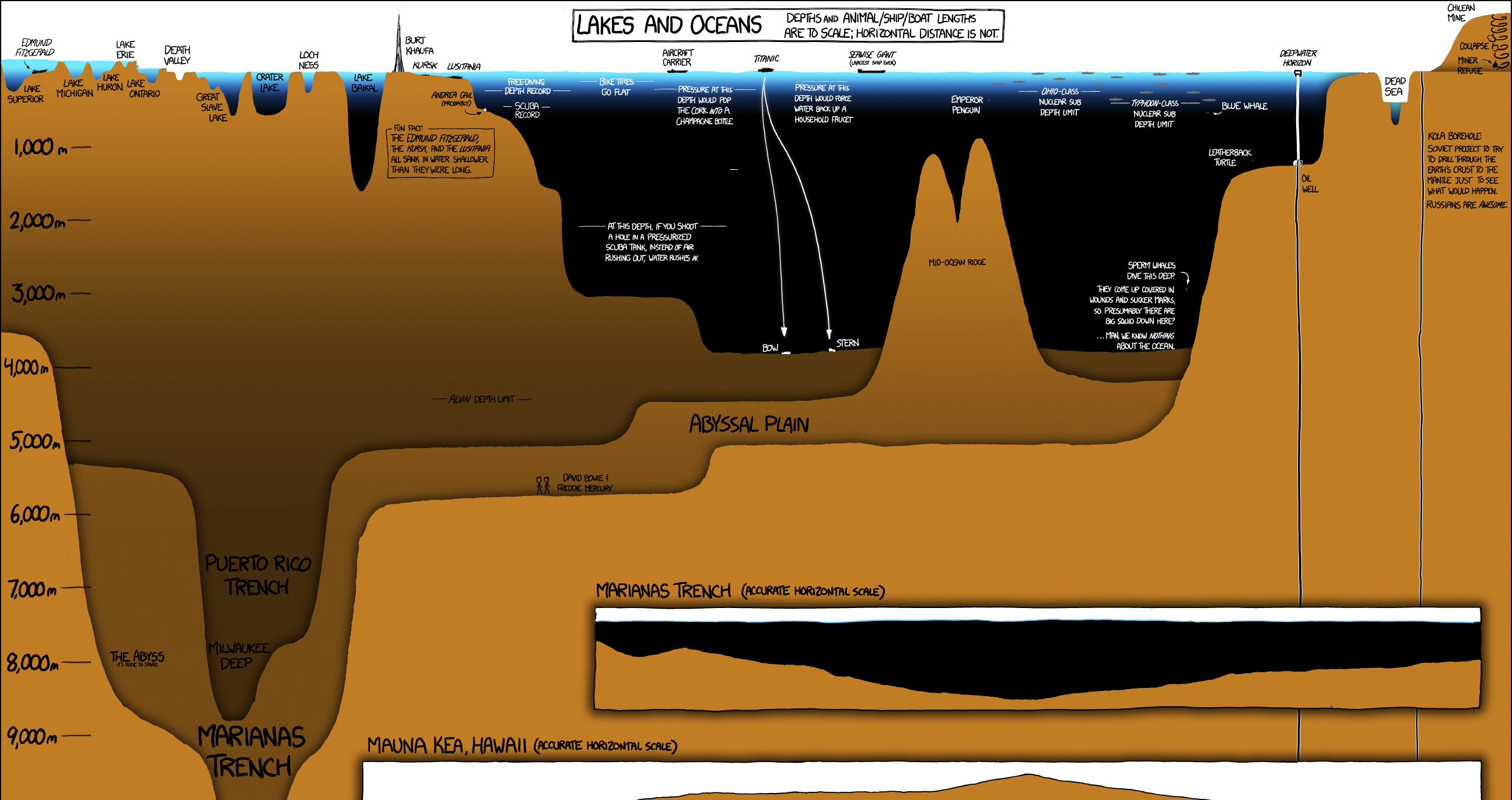
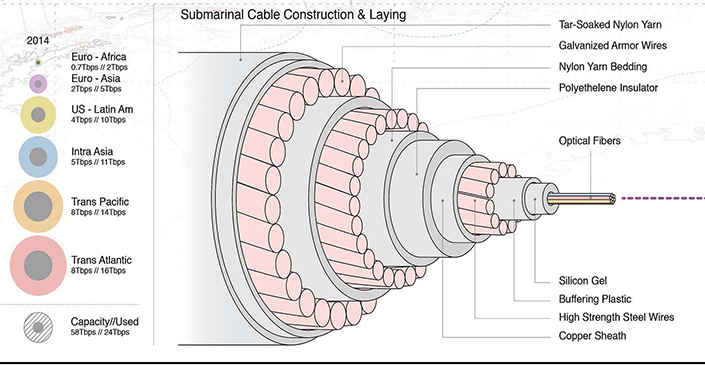
Submarine cables are decidedly uncool. But while they lack the flashiness of satellites, it’s actually the world’s vast network of fiber optic cables that does most of the heavy lifting in keeping our information flowing from place to place.
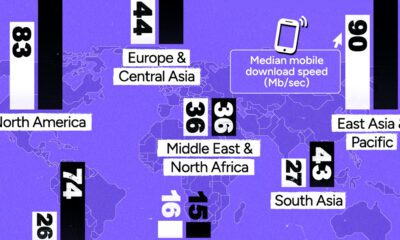
The map above, by Ben Pollock, is a comprehensive look at the world’s cable network, as well as some of the impressive information on bandwidth and maintenance jurisdictions.
The History of Submarine Cables
The first transcontinental cable – laid in 1858 – ran from Ireland to Newfoundland, and made telegraph communication possible between England and Canada.
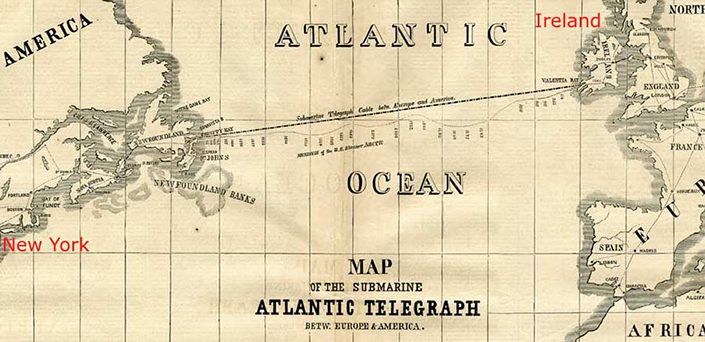
Though communication was expensive and limited to only a few words per hour at best, the speed of communication was unparalleled at the time.
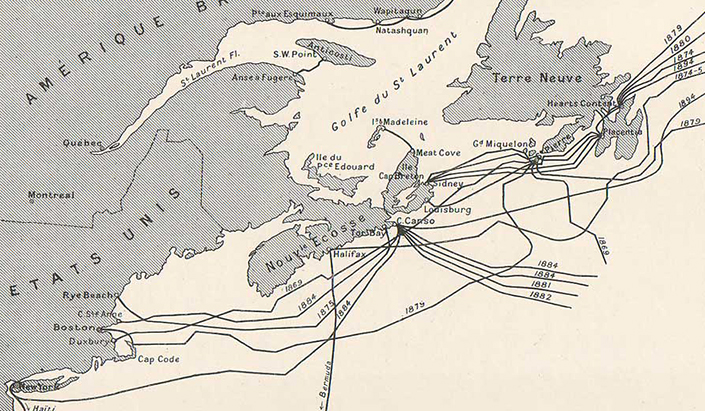
“Instant” communication was a huge commercial hit, and it prompted a cable laying boom. By the year 1900, there were already over 130,000 miles (200,000 km) of cable running along the ocean floor!
Beyond the Telegram
The first transatlantic telephone cables went into service in 1956, and 32 years later, the first fiber optic cable connected Europe and America.
Fiber optic technology made transmitting massive quantities of information fast and cost-effective. The level of speed has only increased with time – and now cables can transmit 160 terabits per second.
(One common misconception is that most of our information is transmitted through satellites, but fiber optic cables actually form the backbone of the internet, transmitting about 99% of all data.)
Today, there are over 420 submarine cables in service, stretching over 700,000 miles (1.1 million km) around the world. The network is clustered around information economy hotspots like Singapore and New York, but cables connect to just about anywhere.
Remote Pacific islands, and even obscure ocean towns in the Arctic Circle have such connections.
Who’s Footing the Bill?
Traditionally, private companies or consortiums formed by telecom carriers owned cables, but that model is changing. Content providers such as Google and Microsoft are increasingly major investors in new cable. Cloud computing is the big demand driver of this new private cable boom.
As more millions more people around the world adopt cloud computing, we’ll be certain to see even more cables criss-crossing the world’s oceans in the near future.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

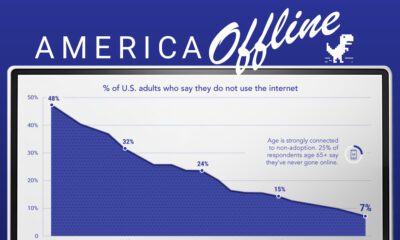
 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
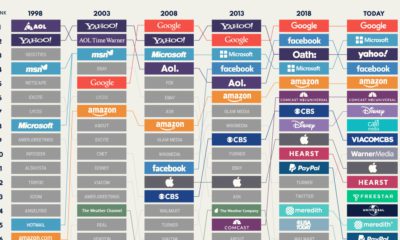
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001