Energy
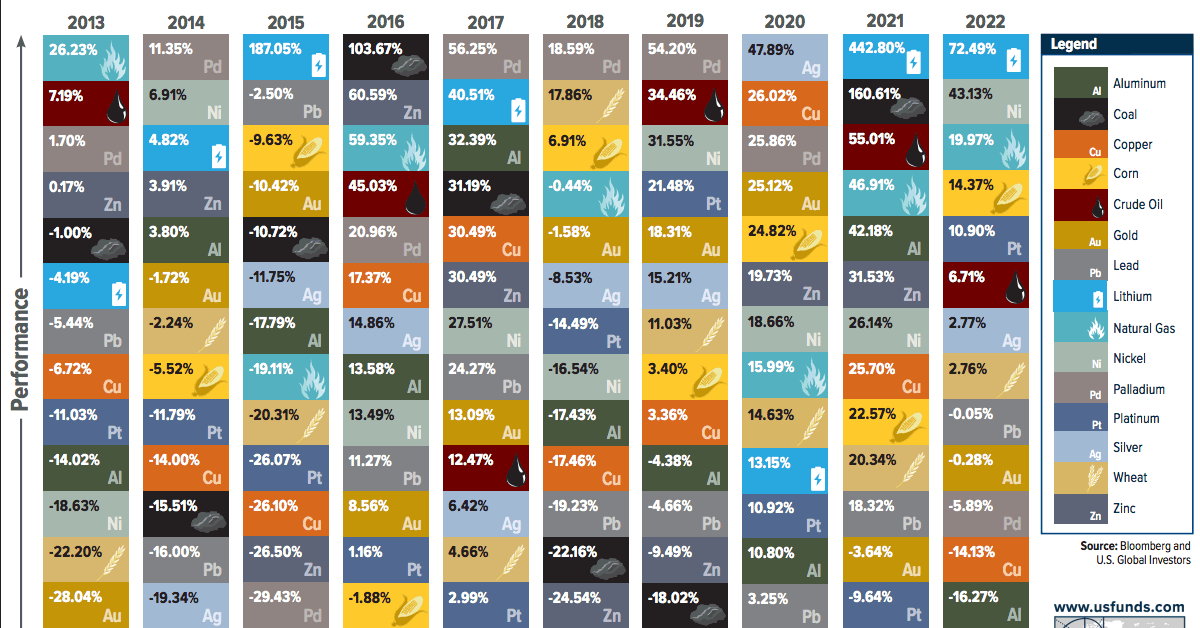
The Periodic Table of Commodity Returns (2013-2022)
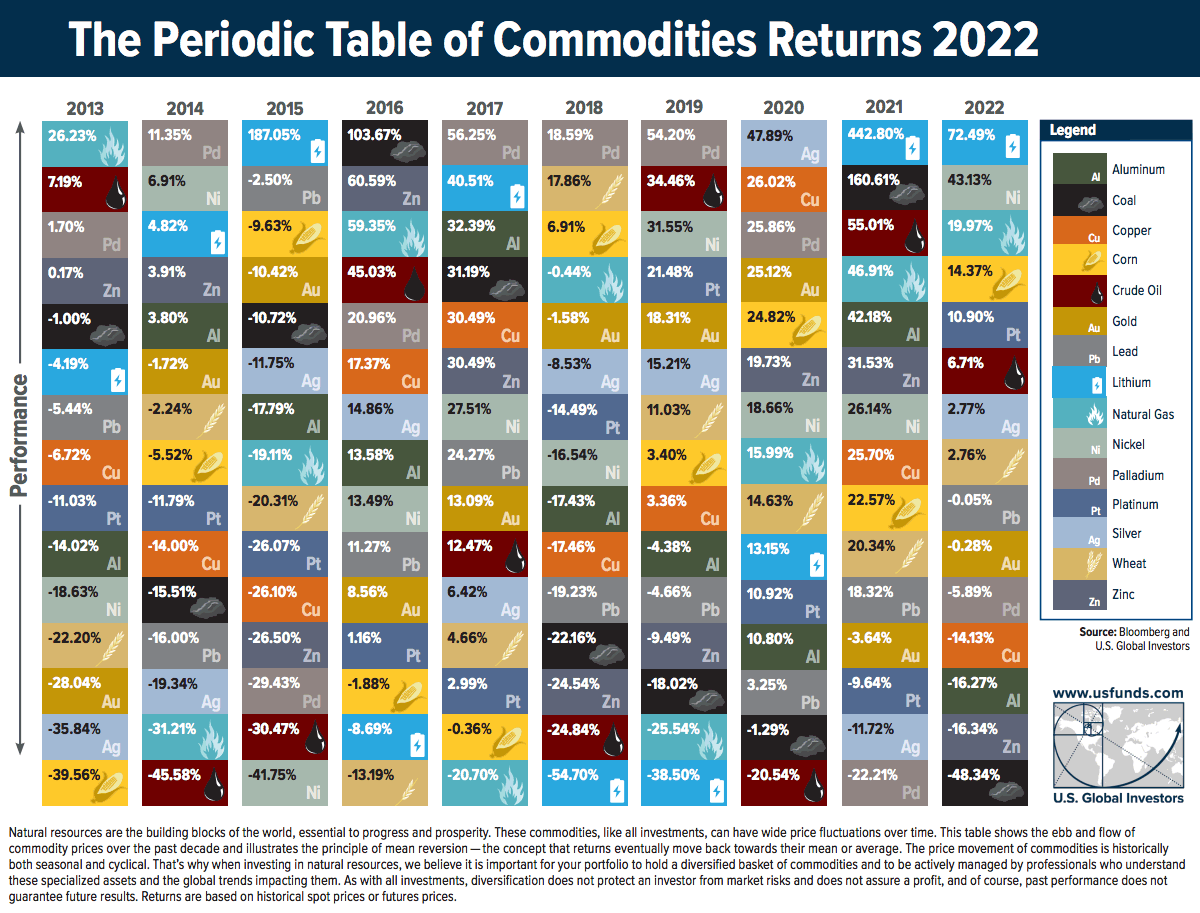
The Periodic Table of Commodity Returns (2013-2022)
Trying to predict which commodities will come out on top in any given year is tricky business—especially during this turbulent period in markets.
By looking back at previous years, investors can gain insights into long-term trends and patterns in commodity prices. To help better understand these trends, U.S. Global Investors releases a visualization called the Periodic Table of Commodity Returns at the outset of each year.
This year’s edition looks back over the past decade of returns between 2013 and 2022, and features an interactive design that allows users to sort returns by various categories including returns, volatility, and other groupings.
Editor’s note: Because of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, regional benchmarks for some commodities (coal, natural gas) had much bigger price divergences than is typical. In this case the graphic focuses in on U.S. regional benchmarks like Powder River Basin coal and Henry Hub natural gas prices. These prices may differ from price action seen around the world.
More Volatility, but Positive Returns
After 2021 saw an impressive surge in commodity prices as the world reopened post-pandemic, 2022 brought another year of positive returns for the asset class that were defined by high levels of volatility.
The broad-based S&P Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI) surged 52.1% in the first five months of 2022, as supply disruptions and fears across grains, metals, and energy fuels were spurred by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
The second half of the year saw prices cool as the U.S. continued to release crude oil from its strategic petroleum reserve while Russia and Ukraine established an agreement to enable grain and agricultural exports, quelling fears of extended supply disruptions.
The result? In the last seven months of the year the S&P GSCI nearly completed a return trip and only ended up rising 8.7% in 2022 overall.
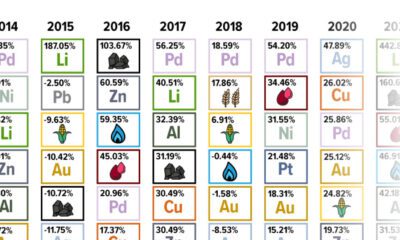
| Commodity | 2022 Returns |
|---|---|
| Lithium | 72.49% |
| Nickel | 43.13% |
| Natural Gas (Henry Hub) | 19.97% |
| Corn | 14.37% |
| Platinum | 10.90% |
| S&P Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI) | 8.71% |
| Crude oil | 6.71% |
| Silver | 2.77% |
| Wheat | 2.76% |
| Lead | -0.05% |
| Gold | -0.28% |
| Palladium | -5.89% |
| Copper | -14.13% |
| Aluminum | -16.27% |
| Zinc | -16.34% |
| Coal (PRB) | -48.34% |
Another key factor that helped keep commodity prices cool in 2022 was China’s extended lockdowns which slowed down the country’s manufacturing and industrial capabilities. This helped reduce the demand of energy fuels in 2022, along with industrial metals like copper, aluminum, and zinc.
Lithium Continues to Top Commodity Returns
A metal that did shine brightly in 2022 was lithium, which has been newly added to the Periodic Table of Commodity Returns.
After topping the table in 2021 with an outsized price increase of 442.8%, lithium kept its top spot in 2022 with a more modest price increase of 72.5%.
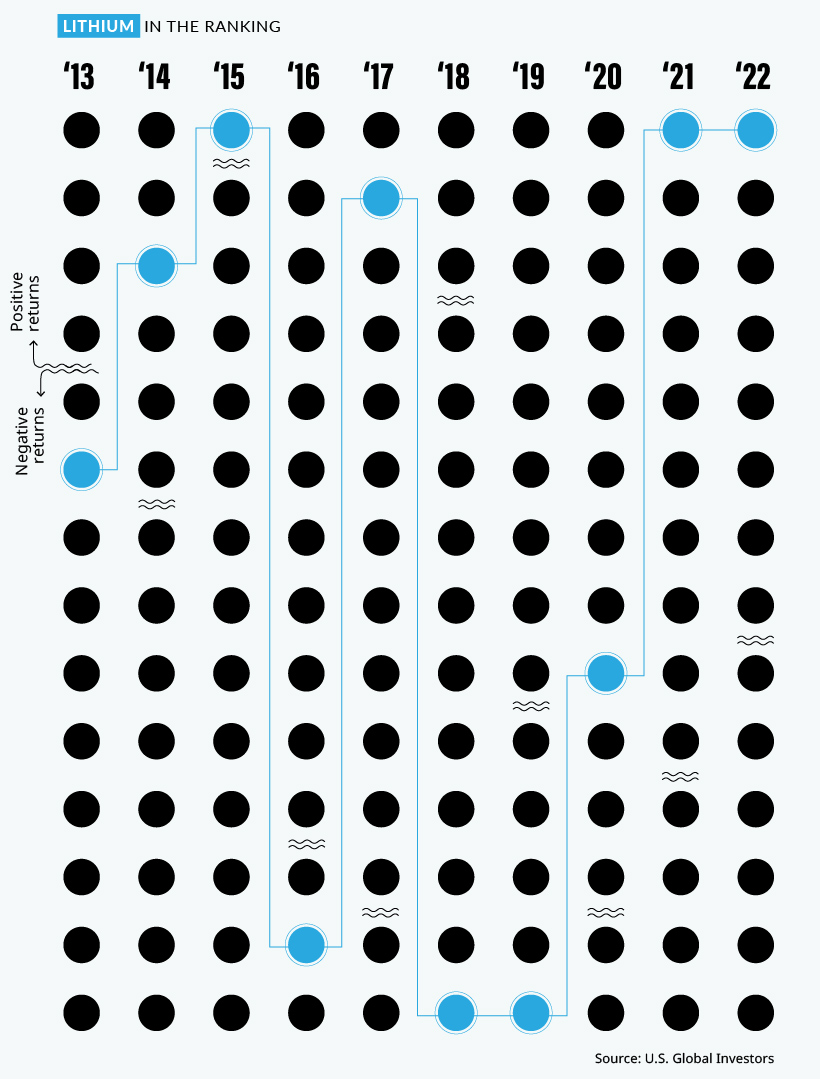
The growing global push towards electric vehicles (EVs) has been a major contributor to the increase in demand for lithium and nickel, which was the second-best performing commodity in 2022 with a price increase of 43.1%. As more countries set targets to phase out gasoline and diesel vehicles, demand for key battery minerals like lithium and nickel is expected to continue to rise.
While the U.S. is working to strengthen its battery metals production and supply chains with $2.8 billion in grants for domestic lithium, graphite, and nickel projects, it will be years before more supply comes online as a result. In the meantime, robust demand for EVs in China has provided a constant need for these battery metals which are currently in short supply.
Energy Price Variance Fueled by Regional Uncertainty
After 2021 saw energy fuels dominate the top spots after lithium, energy fuel prices in 2022 were more volatile with more scattered returns. Natural gas was the only fuel which saw double-digit returns at a 19.9%, with crude oil returning 6.7% and coal at the bottom of the table at -48.3%.
It’s important to keep in mind how geopolitical events and supply disruptions last year affected the regional price differences for energy fuels. While WTI crude oil (North America’s benchmark) increased by 6.7% in 2022, Brent crude oil (Europe’s benchmark) was up 10.4% as Urals crude oil (Russia’s benchmark) fell by more than 26.5%.
| Type of Crude Oil | 2022 Returns | Price in U.S. dollars (Jan 17, 2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Brent Crude Oil (European benchmark) | 10.35% | $86.72 |
| WTI Crude Oil (North American benchmark) | 6.72% | $81.01 |
| Urals Crude Oil (Russian benchmark) | -26.53% | $55.60 |
As a result of the war and ensuing sanctions, the discount of Urals crude oil compared to Brent crude oil went from -$1.72 at the start of 2022 all the way to -$30.71 by the end of the year.
Thermal coal prices faced similar regional divergences, with Powder River Basin (PRB) coal (America’s benchmark for coal) falling by 48.3% this year while Newcastle coal, which is delivered out of the port of Newcastle, Australia primarily to various Asian nations, saw prices skyrocket up by 156.6% in 2022.
After such a wild year with huge variance in commodity prices, we’ll see if 2023 can bring some stability or if high volatility and growing regional price discrepancies will become the norm.
Energy
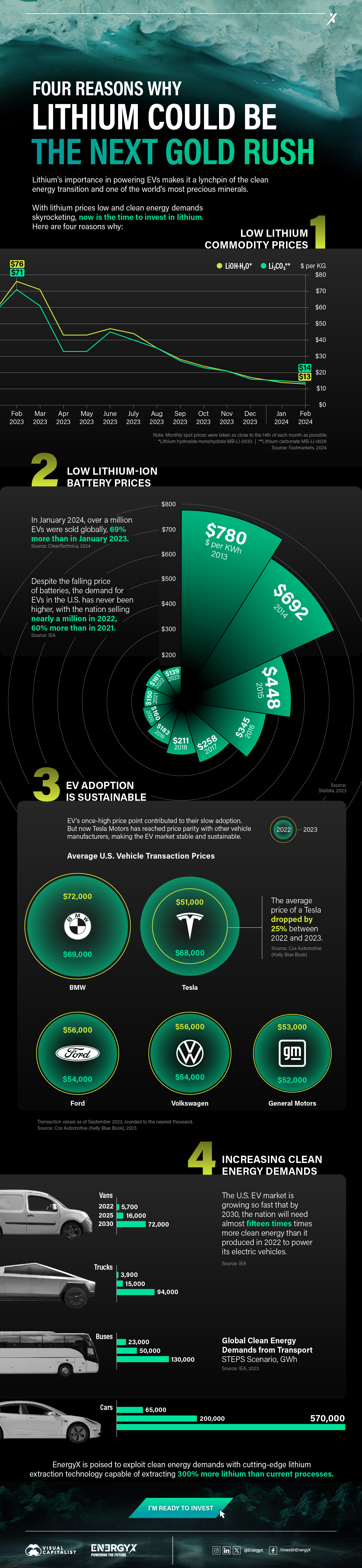
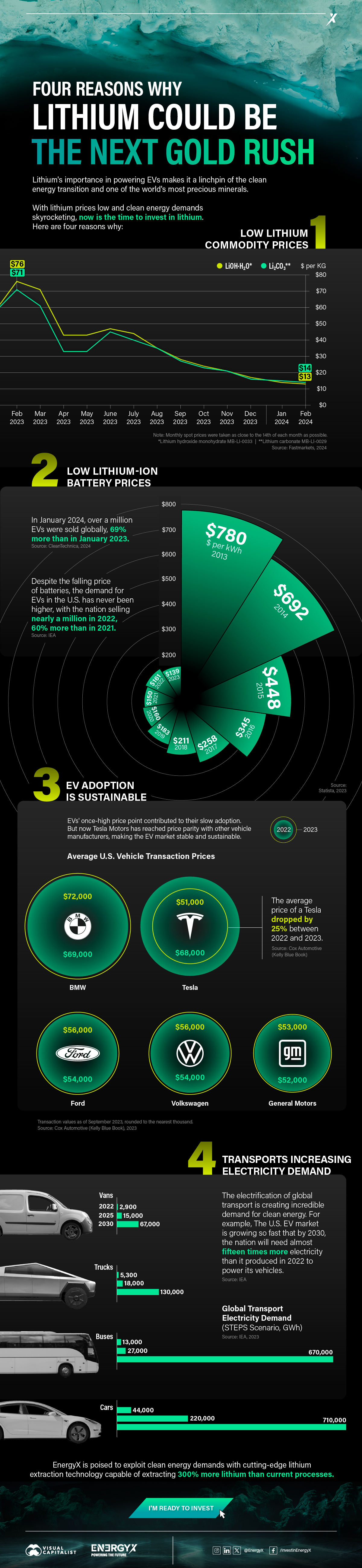
Charted: 4 Reasons Why Lithium Could Be the Next Gold Rush
Visual Capitalist has partnered with EnergyX to show why drops in prices and growing demand may make now the right time to invest in lithium.
4 Reasons Why You Should Invest in Lithium
Lithium’s importance in powering EVs makes it a linchpin of the clean energy transition and one of the world’s most precious minerals.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnered with EnergyX to explore why now may be the time to invest in lithium.
1. Lithium Prices Have Dropped
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating an investment is ensuring that the asset’s value is higher than its price would indicate. Lithium is integral to powering EVs, and, prices have fallen fast over the last year:
| Date | LiOH·H₂O* | Li₂CO₃** |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2023 | $76 | $71 |
| March 2023 | $71 | $61 |
| Apr 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| May 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| June 2023 | $47 | $45 |
| July 2023 | $44 | $40 |
| Aug 2023 | $35 | $35 |
| Sept 2023 | $28 | $27 |
| Oct 2023 | $24 | $23 |
| Nov 2023 | $21 | $21 |
| Dec 2023 | $17 | $16 |
| Jan 2024 | $14 | $15 |
| Feb 2024 | $13 | $14 |
Note: Monthly spot prices were taken as close to the 14th of each month as possible.
*Lithium hydroxide monohydrate MB-LI-0033
**Lithium carbonate MB-LI-0029
2. Lithium-Ion Battery Prices Are Also Falling
The drop in lithium prices is just one reason to invest in the metal. Increasing economies of scale, coupled with low commodity prices, have caused the cost of lithium-ion batteries to drop significantly as well.
In fact, BNEF reports that between 2013 and 2023, the price of a Li-ion battery dropped by 82%.
| Year | Price per KWh |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $139 |
| 2022 | $161 |
| 2021 | $150 |
| 2020 | $160 |
| 2019 | $183 |
| 2018 | $211 |
| 2017 | $258 |
| 2016 | $345 |
| 2015 | $448 |
| 2014 | $692 |
| 2013 | $780 |

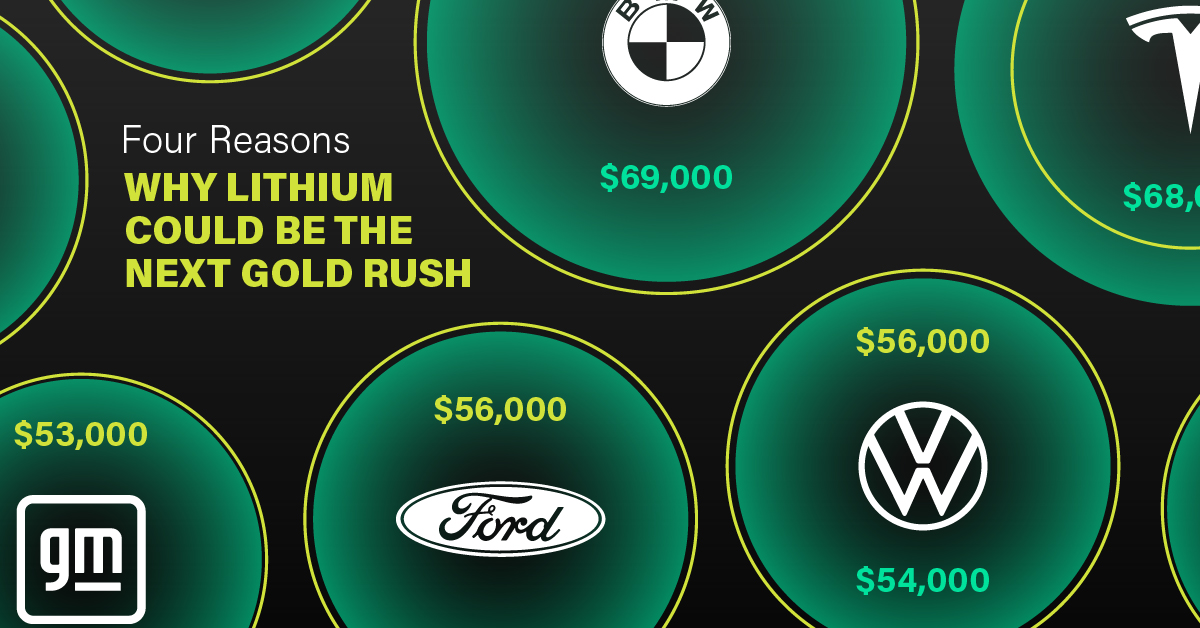
3. EV Adoption is Sustainable
One of the best reasons to invest in lithium is that EVs, one of the main drivers behind the demand for lithium, have reached a price point similar to that of traditional vehicle.
According to the Kelly Blue Book, Tesla’s average transaction price dropped by 25% between 2022 and 2023, bringing it in line with many other major manufacturers and showing that EVs are a realistic transport option from a consumer price perspective.
| Manufacturer | September 2022 | September 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| BMW | $69,000 | $72,000 |
| Ford | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| Volkswagon | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| General Motors | $52,000 | $53,000 |
| Tesla | $68,000 | $51,000 |
4. Electricity Demand in Transport is Growing
As EVs become an accessible transport option, there’s an investment opportunity in lithium. But possibly the best reason to invest in lithium is that the IEA reports global demand for the electricity in transport could grow dramatically by 2030:
| Transport Type | 2022 | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buses 🚌 | 23,000 GWh | 50,000 GWh | 130,000 GWh |
| Cars 🚙 | 65,000 GWh | 200,000 GWh | 570,000 GWh |
| Trucks 🛻 | 4,000 GWh | 15,000 GWh | 94,000 GWh |
| Vans 🚐 | 6,000 GWh | 16,000 GWh | 72,000 GWh |
The Lithium Investment Opportunity
Lithium presents a potentially classic investment opportunity. Lithium and battery prices have dropped significantly, and recently, EVs have reached a price point similar to other vehicles. By 2030, the demand for clean energy, especially in transport, will grow dramatically.
With prices dropping and demand skyrocketing, now is the time to invest in lithium.
EnergyX is poised to exploit lithium demand with cutting-edge lithium extraction technology capable of extracting 300% more lithium than current processes.

-

 Lithium4 days ago
Lithium4 days agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
-

 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.
-

 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoThe World’s Biggest Oil Producers in 2023
Just three countries accounted for 40% of global oil production last year.
-
 Energy1 month ago
Energy1 month agoHow Much Does the U.S. Depend on Russian Uranium?
Currently, Russia is the largest foreign supplier of nuclear power fuel to the U.S.
-
 Uranium2 months ago
Uranium2 months agoCharted: Global Uranium Reserves, by Country
We visualize the distribution of the world’s uranium reserves by country, with 3 countries accounting for more than half of total reserves.
-
 Energy3 months ago
Energy3 months agoVisualizing the Rise of the U.S. as Top Crude Oil Producer
Over the last decade, the United States has established itself as the world’s top producer of crude oil, surpassing Saudi Arabia and Russia.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001