Markets
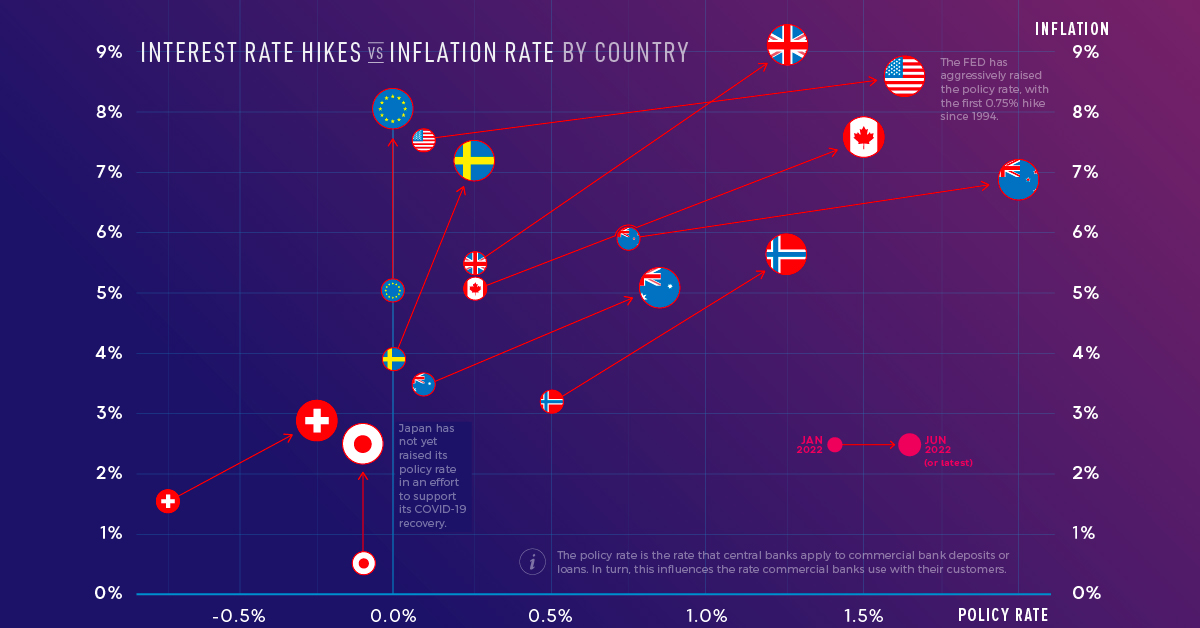
Interest Rate Hikes vs. Inflation Rate, by Country
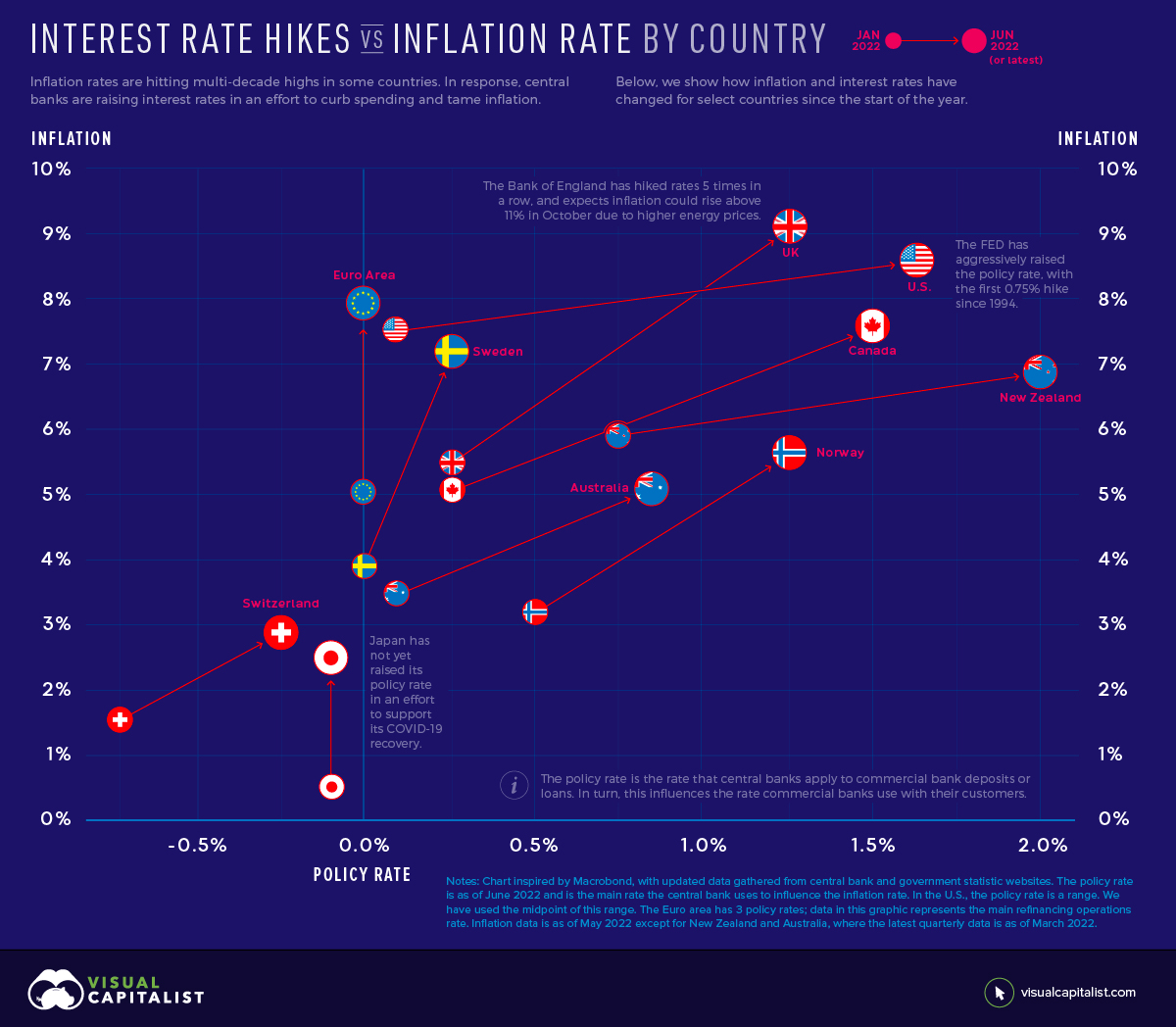
Interest Rate Hikes vs. Inflation Rate, by Country
Imagine today’s high inflation like a car speeding down a hill. In order to slow it down, you need to hit the brakes. In this case, the “brakes” are interest rate hikes intended to slow spending. However, some central banks are hitting the brakes faster than others.
This graphic uses data from central banks and government websites to show how policy interest rates and inflation rates have changed since the start of the year. It was inspired by a chart created by Macrobond.
How Do Interest Rate Hikes Combat Inflation?
To understand how interest rates influence inflation, we need to understand how inflation works. Inflation is the result of too much money chasing too few goods. Over the last several months, this has occurred amid a surge in demand and supply chain disruptions worsened by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
In an effort to combat inflation, central banks will raise their policy rate. This is the rate they charge commercial banks for loans or pay commercial banks for deposits. Commercial banks pass on a portion of these higher rates to their customers, which reduces the purchasing power of businesses and consumers. For example, it becomes more expensive to borrow money for a house or car.
Ultimately, interest rate hikes act to slow spending and encourage saving. This motivates companies to increase prices at a slower rate, or lower prices, to stimulate demand.
Rising Interest Rates and Inflation
With inflation rates hitting multi-decade highs in some countries, many central banks have announced interest rate hikes. Below, we show how the inflation rate and policy interest rate have changed for select countries and regions since January 2022. The jurisdictions are ordered from highest to lowest current inflation rate.
| Jurisdiction | Jan 2022 Inflation | May 2022 Inflation | Jan 2022 Policy Rate | Jun 2022 Policy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK | 5.50% | 9.10% | 0.25% | 1.25% |
| U.S. | 7.50% | 8.60% | 0.00%-0.25% | 1.50%-1.75% |
| Euro Area | 5.10% | 8.10% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Canada | 5.10% | 7.70% | 0.25% | 1.50% |
| Sweden | 3.90% | 7.20% | 0.00% | 0.25% |
| New Zealand | 5.90% | 6.90% | 0.75% | 2.00% |
| Norway | 3.20% | 5.70% | 0.50% | 1.25% |
| Australia | 3.50% | 5.10% | 0.10% | 0.85% |
| Switzerland | 1.60% | 2.90% | -0.75% | -0.25% |
| Japan | 0.50% | 2.50% | -0.10% | -0.10% |
The Euro area has 3 policy rates; the data above represents the main refinancing operations rate. Inflation data is as of May 2022 except for New Zealand and Australia, where the latest quarterly data is as of March 2022.
The U.S. Federal Reserve has been the most aggressive with its interest rate hikes. It has raised its policy rate by 1.5% since January, with half of that increase occurring at the June 2022 meeting. Jerome Powell, the Federal Reserve chair, said the committee would like to “do a little more front-end loading” to bring policy rates to normal levels. The action comes as the U.S. faces its highest inflation rate in 40 years.
On the other hand, the European Union is experiencing inflation of 8.1% but has not yet raised its policy rate. The European Central Bank has, however, provided clear forward guidance. It intends to raise rates by 0.25% in July, by a possibly larger increment in September, and with gradual but sustained increases thereafter. Clear forward guidance is intended to help people make spending and investment decisions, and avoid surprises that could disrupt markets.
Pacing Interest Rate Hikes
Raising interest rates is a fine balancing act. If central banks raise rates too quickly, it’s like slamming the brakes on that car speeding downhill: the economy could come to a standstill. This occurred in the U.S. in the 1980’s when the Federal Reserve, led by Chair Paul Volcker, raised the policy rate to 20%. The economy went into a recession, though the aggressive monetary policy did eventually tame double digit inflation.
However, if rates are raised too slowly, inflation could gather enough momentum that it becomes difficult to stop. The longer high price increases linger, the more future inflation expectations build. This can result in people buying more in anticipation of prices rising further, perpetuating high demand.
“There’s always a risk of going too far or not going far enough, and it’s going to be a very difficult judgment to make.” — Jerome Powell, U.S. Federal Reserve Chair
It’s worth noting that while central banks can influence demand through policy rates, this is only one side of the equation. Inflation is also being caused by supply chain issues, a problem that is more or less outside of the control of central banks.
Markets
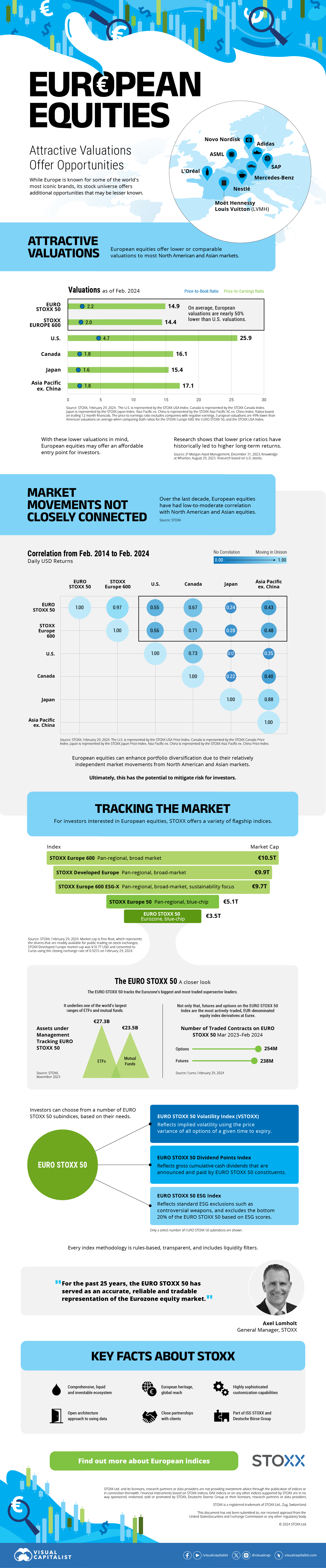
The European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
On average, the European stock market has valuations that are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations. But how can you access the market?
European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
Europe is known for some established brands, from L’Oréal to Louis Vuitton. However, the European stock market offers additional opportunities that may be lesser known.
The above infographic, sponsored by STOXX, outlines why investors may want to consider European stocks.
Attractive Valuations
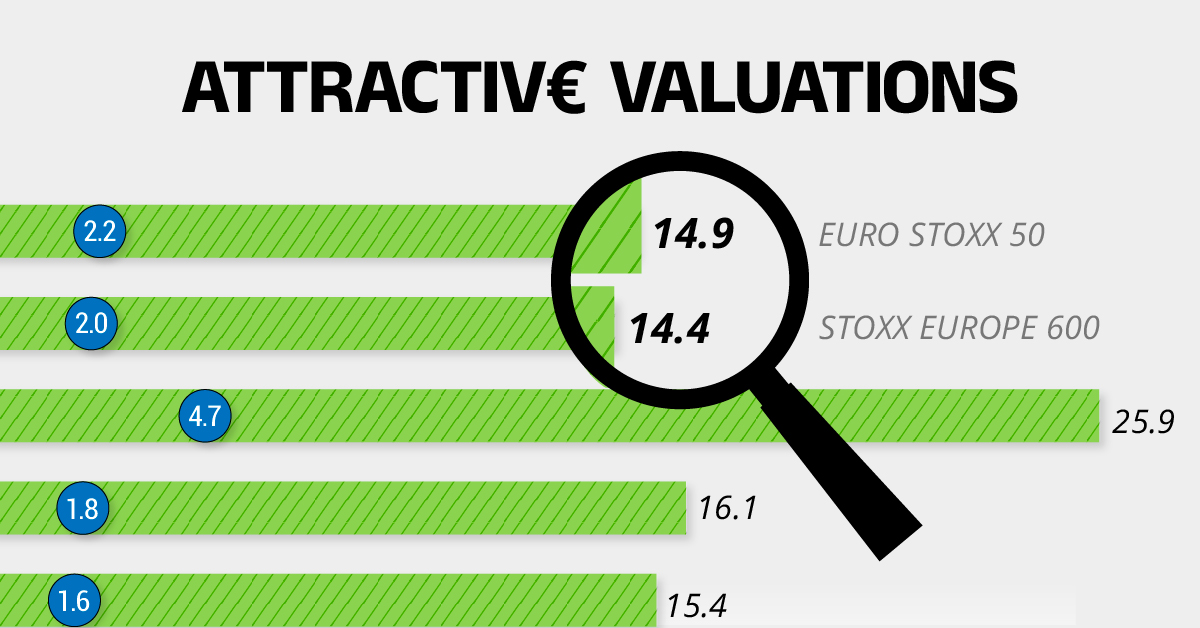
Compared to most North American and Asian markets, European stocks offer lower or comparable valuations.
| Index | Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Price-to-Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 14.9 | 2.2 |
| STOXX Europe 600 | 14.4 | 2 |
| U.S. | 25.9 | 4.7 |
| Canada | 16.1 | 1.8 |
| Japan | 15.4 | 1.6 |
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 17.1 | 1.8 |
Data as of February 29, 2024. See graphic for full index names. Ratios based on trailing 12 month financials. The price to earnings ratio excludes companies with negative earnings.
On average, European valuations are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations, potentially offering an affordable entry point for investors.
Research also shows that lower price ratios have historically led to higher long-term returns.
Market Movements Not Closely Connected
Over the last decade, the European stock market had low-to-moderate correlation with North American and Asian equities.
The below chart shows correlations from February 2014 to February 2024. A value closer to zero indicates low correlation, while a value of one would indicate that two regions are moving in perfect unison.
| EURO STOXX 50 | STOXX EUROPE 600 | U.S. | Canada | Japan | Asia Pacific ex. China |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| STOXX EUROPE 600 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.48 | |
| U.S. | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| Canada | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.40 | |||
| Japan | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 1.00 |
Data is based on daily USD returns.
European equities had relatively independent market movements from North American and Asian markets. One contributing factor could be the differing sector weights in each market. For instance, technology makes up a quarter of the U.S. market, but health care and industrials dominate the broader European market.
Ultimately, European equities can enhance portfolio diversification and have the potential to mitigate risk for investors.
Tracking the Market
For investors interested in European equities, STOXX offers a variety of flagship indices:
| Index | Description | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| STOXX Europe 600 | Pan-regional, broad market | €10.5T |
| STOXX Developed Europe | Pan-regional, broad-market | €9.9T |
| STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X | Pan-regional, broad market, sustainability focus | €9.7T |
| STOXX Europe 50 | Pan-regional, blue-chip | €5.1T |
| EURO STOXX 50 | Eurozone, blue-chip | €3.5T |
Data is as of February 29, 2024. Market cap is free float, which represents the shares that are readily available for public trading on stock exchanges.
The EURO STOXX 50 tracks the Eurozone’s biggest and most traded companies. It also underlies one of the world’s largest ranges of ETFs and mutual funds. As of November 2023, there were €27.3 billion in ETFs and €23.5B in mutual fund assets under management tracking the index.
“For the past 25 years, the EURO STOXX 50 has served as an accurate, reliable and tradable representation of the Eurozone equity market.”
— Axel Lomholt, General Manager at STOXX
Partnering with STOXX to Track the European Stock Market
Are you interested in European equities? STOXX can be a valuable partner:
- Comprehensive, liquid and investable ecosystem
- European heritage, global reach
- Highly sophisticated customization capabilities
- Open architecture approach to using data
- Close partnerships with clients
- Part of ISS STOXX and Deutsche Börse Group
With a full suite of indices, STOXX can help you benchmark against the European stock market.

Learn how STOXX’s European indices offer liquid and effective market access.

-

 Economy3 days ago
Economy3 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees