Datastream
Electric Vehicle Prices Fall as Battery Technology Improves
The Briefing
- Declining electric vehicle (EV) battery costs are driving production costs down
- At the battery pack price point of $100/kWh, electric vehicles will become as cheap to make as gas-powered cars
Electric Vehicle Prices Fall as EV Battery Tech Improves
Electric vehicles (EVs) only accounted for around 3.2% of global car sales in 2020—a figure that’s set to grow in the coming decade, largely due to falling EV battery costs.
With rising production and technological improvements, batteries are becoming cheaper to produce, making EVs increasingly competitive with gas-powered cars.
Wright’s Law is Right So Far
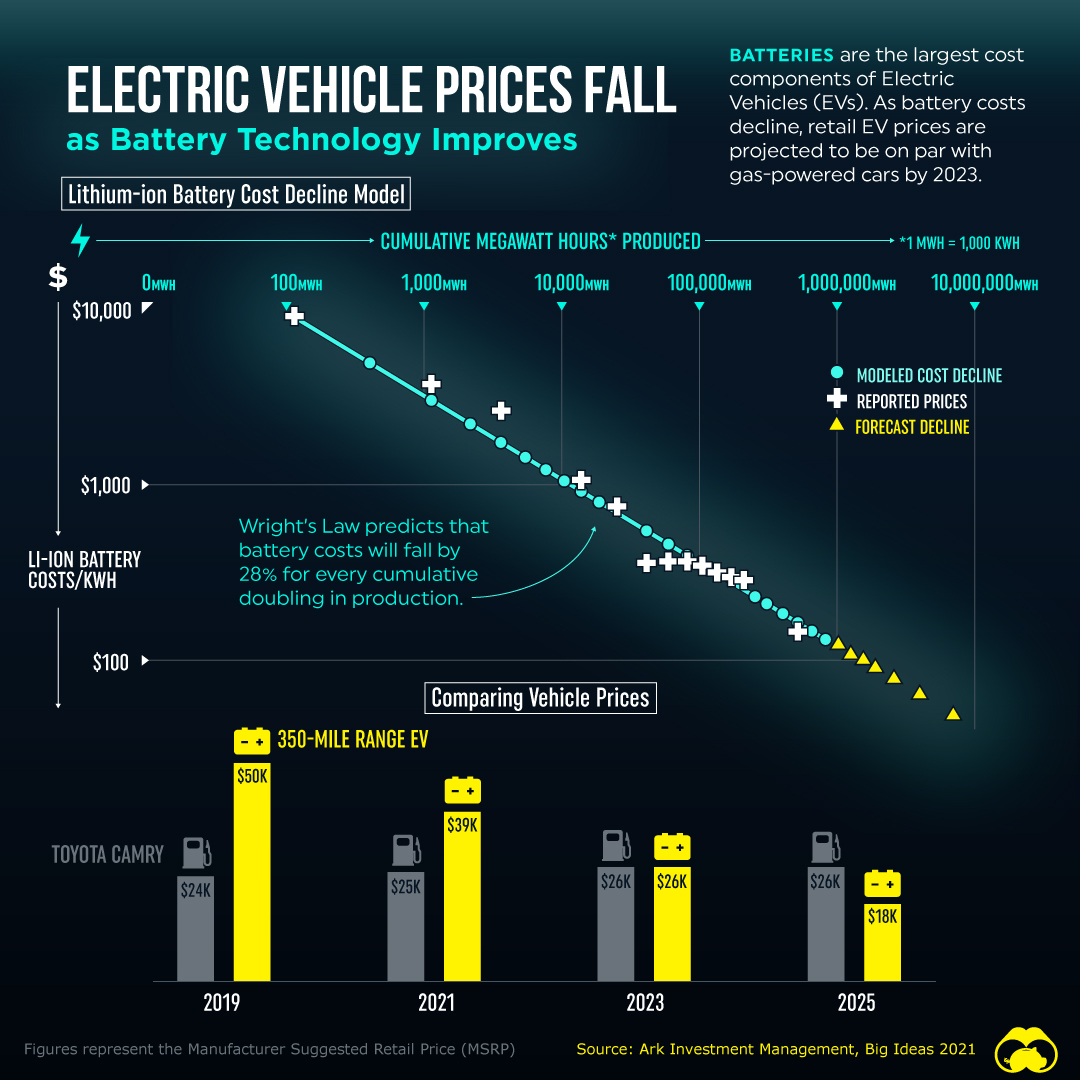
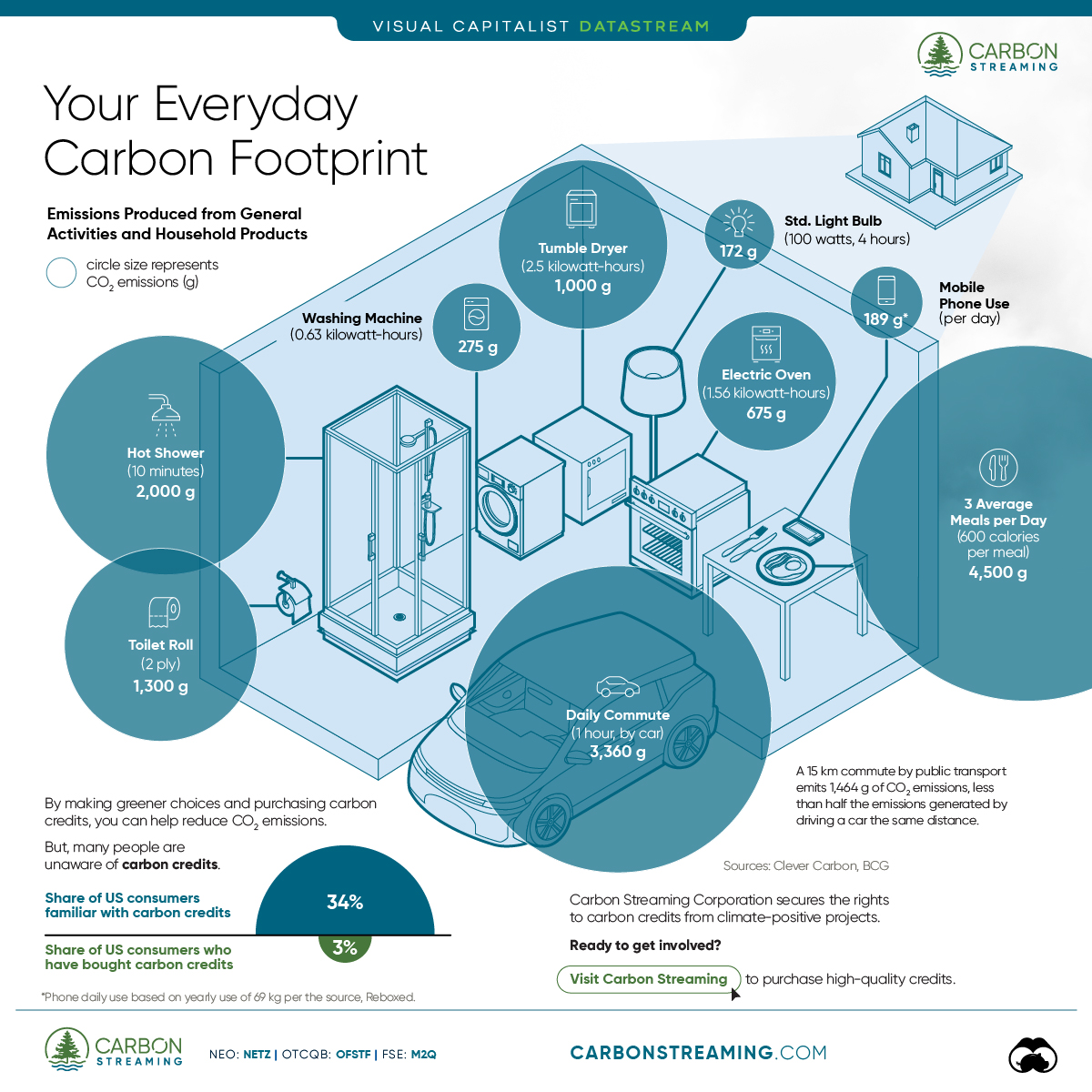
According to Wright’s Law, also known as the learning curve effect, lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery cell costs fall by 28% for every cumulative doubling of units produced.
Wright’s Law has accurately predicted the decline in battery costs and so far, reported battery prices have been in line with modeled forecasts. The battery pack is the most expensive part of an electric vehicle. Consequently, the sticker prices of EVs fall with declining battery costs.
By 2023, the cost of Li-ion batteries is expected to fall to around $100/kWh—the price point at which EVs are as cheap to make as gas-powered cars.
| Year | Price of Toyota Camry ⛽️ | Price of a 350-mile Range EV 🔋 |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | $24,000 | $50,000 |
| 2021 | $25,000 | $39,000 |
| 2023 | $26,000 | $26,000 |
| 2025 | $26,000 | $18,000 |
Figures represent the Manufacturer Suggested Retail Price (MSRP)
EVs are already cheaper to own and operate than comparable gas-powered cars due to savings from gas, maintenance, and resale value. Therefore, a reduction in retail electric vehicle prices may enable them to compete more directly with gas-powered cars.
According to ARK Invest, the manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP) of a 350-mile range EV will be on par with that of a like-for-like Toyota Camry in 2023. Furthermore, the price of a 350-mile range EV is projected to drop by 53% between 2021-2025—making it $8,000 cheaper than the Camry.
The Electric Catch Up
Electric vehicles are a key piece of the puzzle in the transition to clean energy. Hence, growing consumer awareness around climate change is a catalyst for the EV space.
However, as EV production increases, so does the need for various critical minerals, charging infrastructure, and more. Price is just one of the hurdles that EV manufacturers need to overcome on the road to mainstream EV adoption.
Where does this data come from?
Datastream
Can You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?
Discover how the average person’s carbon footprint impacts the environment and learn how carbon credits can offset your carbon footprint.
The Briefing
- A person’s carbon footprint is substantial, with activities such as food consumption creating as much as 4,500 g of CO₂ emissions daily.
- By purchasing carbon credits from Carbon Streaming Corporation, you can offset your own emissions and fund positive climate action.
Your Everyday Carbon Footprint
While many large businesses and countries have committed to net-zero goals, it is essential to acknowledge that your everyday activities also contribute to global emissions.
In this graphic, sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation, we will explore how the choices we make and the products we use have a profound impact on our carbon footprint.
Carbon Emissions by Activity
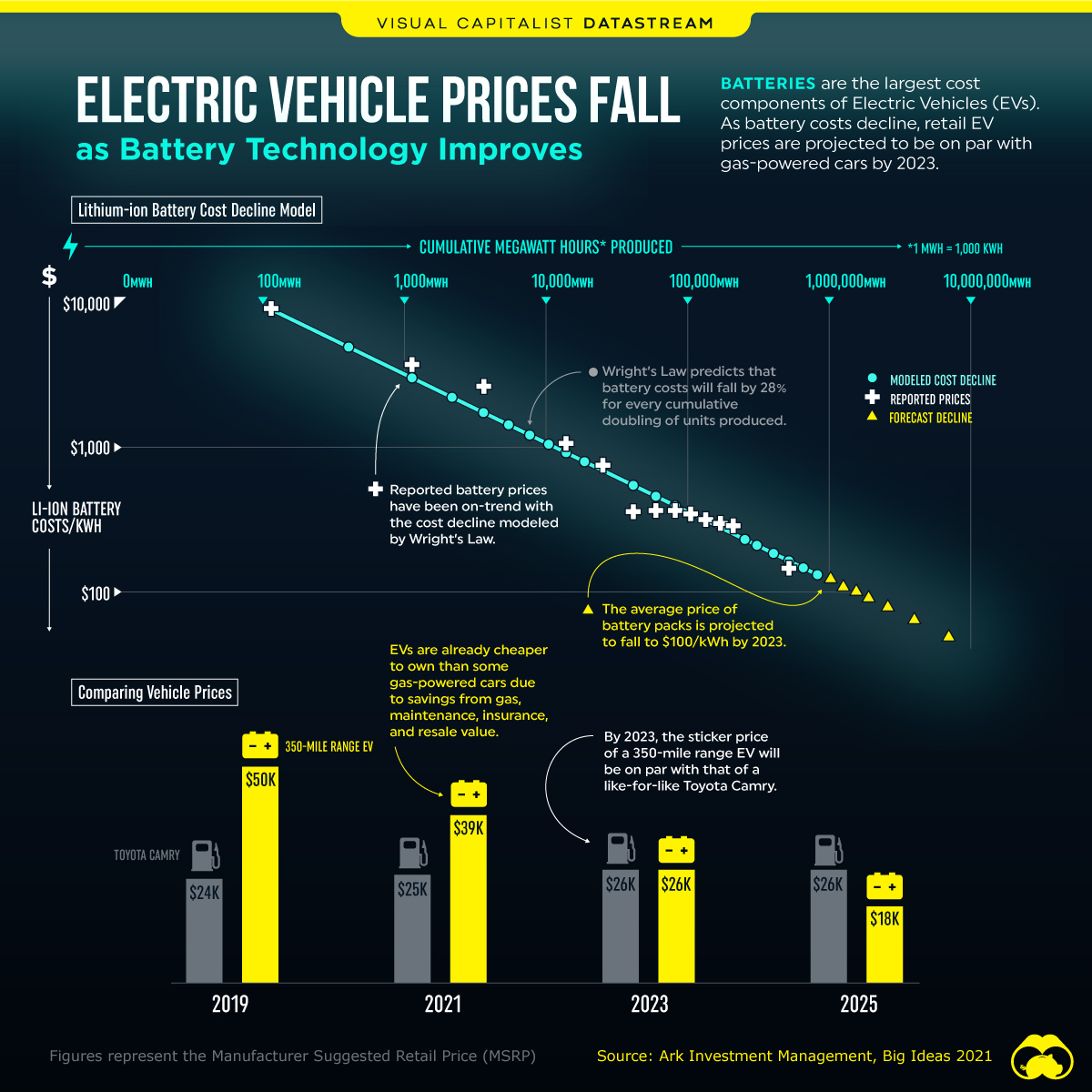
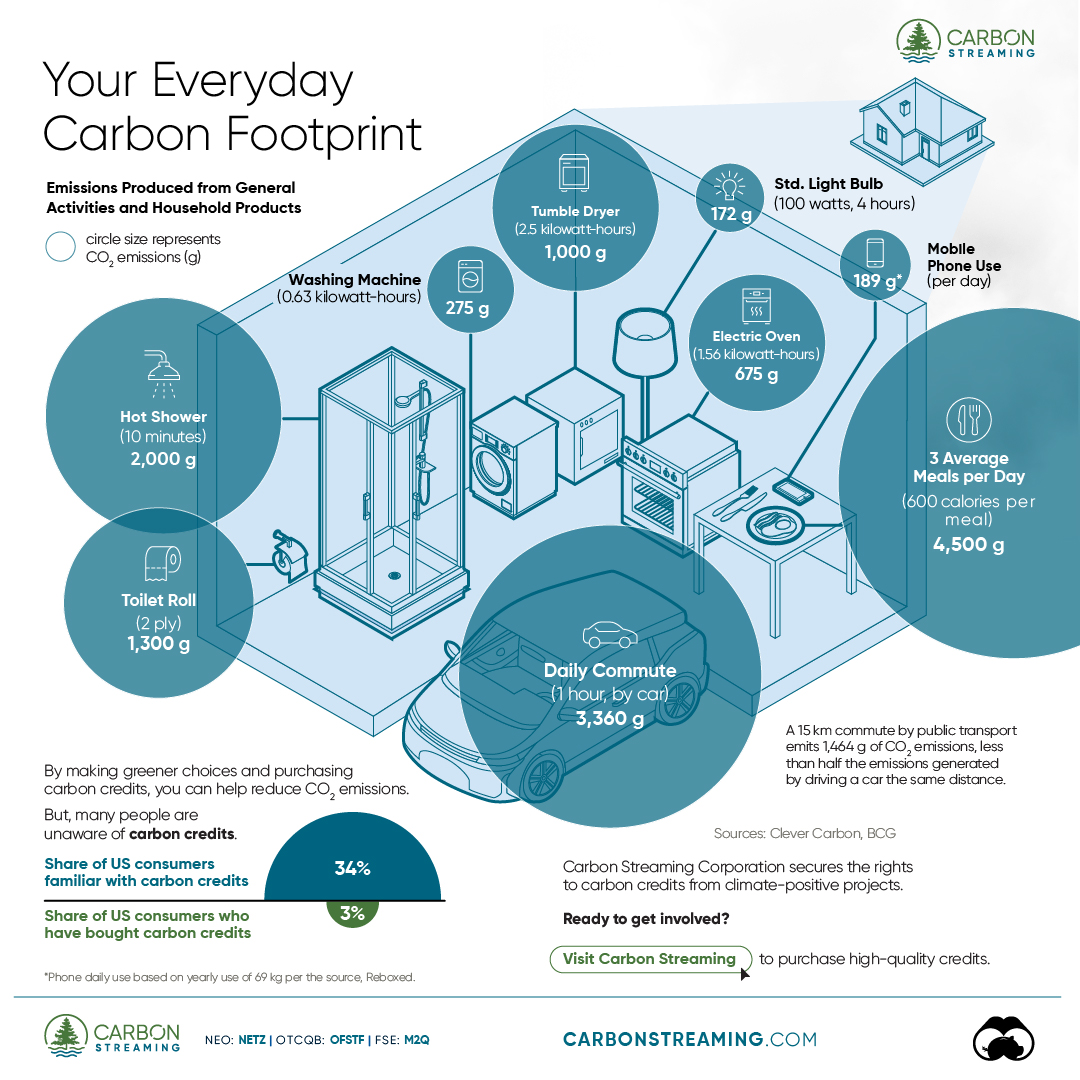
Here are some of the daily activities and products of the average person and their carbon footprint, according to Clever Carbon.
| Household Activities & Products | CO2 Emissions (g) |
|---|---|
| 💡 Standard Light Bulb (100 watts, four hours) | 172 g |
| 📱 Mobile Phone Use (195 minutes per day)* | 189 g |
| 👕 Washing Machine (0.63 kWh) | 275 g |
| 🔥 Electric Oven (1.56 kWh) | 675 g |
| ♨️ Tumble Dryer (2.5 kWh) | 1,000 g |
| 🧻 Toilet Roll (2 ply) | 1,300 g |
| 🚿 Hot Shower (10 mins) | 2,000 g |
| 🚙 Daily Commute (one hour, by car) | 3,360 g |
| 🍽️ Average Daily Food Consumption (three meals of 600 calories) | 4,500 g |
| *Phone use based on yearly use of 69kg per the source, Reboxed | |
Your choice of transportation plays a crucial role in determining your carbon footprint. For instance, a 15 km daily commute to work on public transport generates an average of 1,464 g of CO₂ emissions. Compared to 3,360 g—twice the volume for a journey the same length by car.
By opting for more sustainable modes of transport, such as cycling, walking, or public transportation, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
Addressing Your Carbon Footprint
One way to compensate for your emissions is by purchasing high-quality carbon credits.
Carbon credits are used to help fund projects that avoid, reduce or remove CO₂ emissions. This includes nature-based solutions such as reforestation and improved forest management, or technology-based solutions such as the production of biochar and carbon capture and storage (CCS).
While carbon credits offer a potential solution for individuals to help reduce global emissions, public awareness remains a significant challenge. A BCG-Patch survey revealed that only 34% of U.S. consumers are familiar with carbon credits, and only 3% have purchased them in the past.
About Carbon Streaming
By financing the creation or expansion of carbon projects, Carbon Streaming Corporation secures the rights to future carbon credits generated by these sustainable projects. You can then purchase these carbon credits to help fund climate solutions around the world and compensate for your own emissions.
Ready to get involved?
>> Learn more about purchasing carbon credits at Carbon Streaming
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries