Maps
Visualizing the Uranium Mining Industry in 3 Charts
When uranium was discovered in 1789 by Martin Heinrich Klaproth, it’s likely the German chemist didn’t know how important the element would become to human life.
Used minimally in glazing and ceramics, uranium was originally mined as a byproduct of producing radium until the late 1930s. However, the discovery of nuclear fission, and the potential promise of nuclear power, changed everything.
What’s the current state of the uranium mining industry? This series of charts from Truman Du highlights production and the use of uranium using 2021 data from the World Nuclear Association (WNA) and Our World in Data.
Who are the Biggest Uranium Miners in the World?
Most of the world’s biggest uranium suppliers are based in countries with the largest uranium deposits, like Australia, Kazakhstan, and Canada.
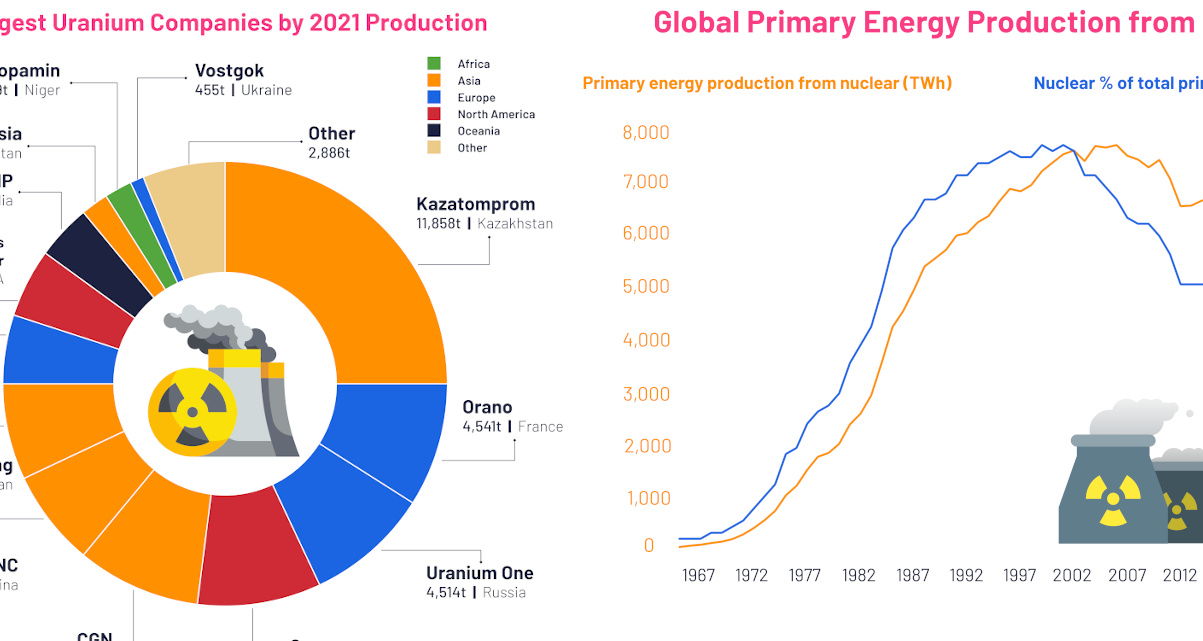
The largest of these companies is Kazatomprom, a Kazakhstani state-owned company that produced 25% of the world’s new uranium supply in 2021.
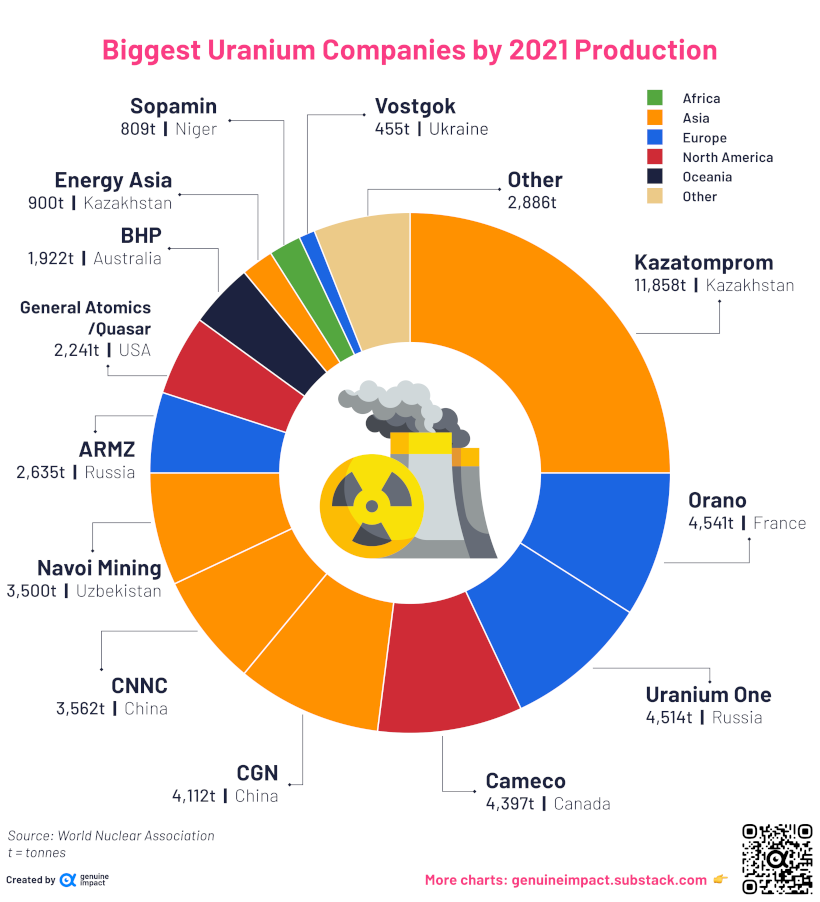
As seen in the above chart, 94% of the roughly 48,000 tonnes of uranium mined globally in 2021 came from just 13 companies.
| Rank | Company | 2021 Uranium Production (tonnes) | Percent of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇰🇿 Kazatomprom | 11,858 | 25% |
| 2 | 🇫🇷 Orano | 4,541 | 9% |
| 3 | 🇷🇺 Uranium One | 4,514 | 9% |
| 4 | 🇨🇦 Cameco | 4,397 | 9% |
| 5 | 🇨🇳 CGN | 4,112 | 9% |
| 6 | 🇺🇿 Navoi Mining | 3,500 | 7% |
| 7 | 🇨🇳 CNNC | 3,562 | 7% |
| 8 | 🇷🇺 ARMZ | 2,635 | 5% |
| 9 | 🇦🇺 General Atomics/Quasar | 2,241 | 5% |
| 10 | 🇦🇺 BHP | 1,922 | 4% |
| 11 | 🇬🇧 Energy Asia | 900 | 2% |
| 12 | 🇳🇪 Sopamin | 809 | 2% |
| 13 | 🇺🇦 VostGok | 455 | 1% |
| 14 | Other | 2,886 | 6% |
| Total | 48,332 | 100% |
France’s Orano, another state-owned company, was the world’s second largest producer of uranium at 4,541 tonnes.
Companies rounding out the top five all had similar uranium production numbers to Orano, each contributing around 9% of the global total. Those include Uranium One from Russia, Cameco from Canada, and CGN in China.
Where are the Largest Uranium Mines Found?
The majority of uranium deposits around the world are found in 16 countries with Australia, Kazakhstan, and Canada accounting for for nearly 40% of recoverable uranium reserves.
But having large reserves doesn’t necessarily translate to uranium production numbers. For example, though Australia has the biggest single deposit of uranium (Olympic Dam) and the largest reserves overall, the country ranks fourth in uranium supplied, coming in at 9%.
Here are the top 10 uranium mines in the world, accounting for 53% of the world’s supply.
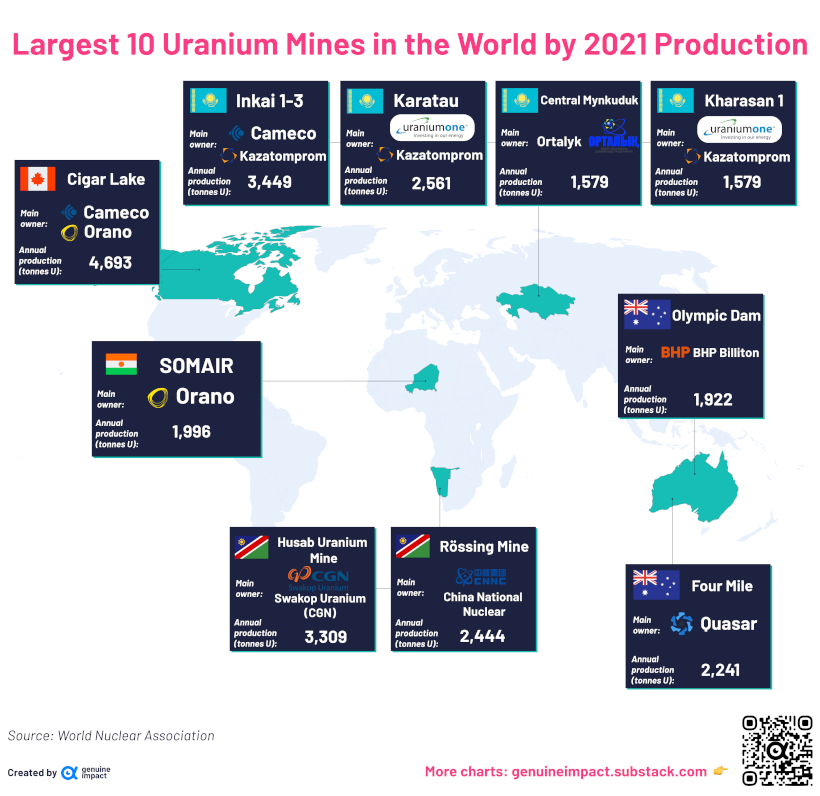
Of the largest mines in the world, four are found in Kazakhstan. Altogether, uranium mined in Kazakhstan accounted for 45% of the world’s uranium supply in 2021.
| Uranium Mine | Country | Main Owner | 2021 Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cigar Lake | 🇨🇦 Canada | Cameco/Orano | 4,693t |
| Inkai 1-3 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Kazaktomprom/Cameco | 3,449t |
| Husab | 🇳🇦 Namibia | Swakop Uranium (CGN) | 3,309t |
| Karatau (Budenovskoye 2) | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Uranium One/Kazatomprom | 2,561t |
| Rössing | 🇳🇦 Namibia | CNNC | 2,444t |
| Four Mile | 🇦🇺 Australia | Quasar | 2,241t |
| SOMAIR | 🇳🇪 Niger | Orano | 1,996t |
| Olympic Dam | 🇦🇺 Australia | BHP Billiton | 1,922t |
| Central Mynkuduk | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Ortalyk | 1,579t |
| Kharasan 1 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Kazatomprom/Uranium One | 1,579t |
Namibia, which has two of the five largest uranium mines in operation, is the second largest supplier of uranium by country, at 12%, followed by Canada at 10%.
Interestingly, the owners of these mines are not necessarily local. For example, France’s Orano operates mines in Canada and Niger. Russia’s Uranium One operates mines in Kazakhstan, the U.S., and Tanzania. China’s CGN owns mines in Namibia.
And despite the African continent holding a sizable amount of uranium reserves, no African company placed in the top 10 biggest companies by production. Sopamin from Niger was the highest ranked at #12 with 809 tonnes mined.
Uranium Mining and Nuclear Energy
Uranium mining has changed drastically since the first few nuclear power plants came online in the 1950s.
For 30 years, uranium production grew steadily due to both increasing demand for nuclear energy and expanding nuclear arsenals, eventually peaking at 69,692 tonnes mined in 1980 at the height of the Cold War.
Nuclear energy production (measured in terawatt-hours) also rose consistently until the 21st century, peaking in 2001 when it contributed nearly 7% to the world’s energy supply. But in the years following, it started to drop and flatline.
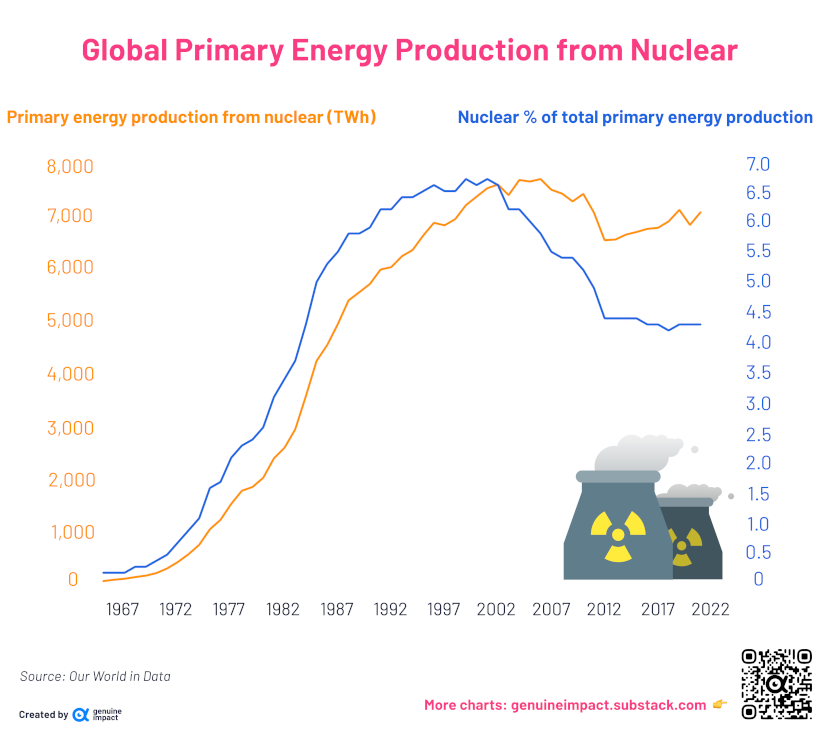
By 2021, nuclear energy had fallen to 4.3% of global energy production. Several nuclear accidents—Chernobyl, Three Mile Island, and Fukushima—contributed to turning sentiment against nuclear energy.
| Year | Nuclear Energy Production | % of Total Energy |
|---|---|---|
| 1965 | 72 TWh | 0.2% |
| 1966 | 98 TWh | 0.2% |
| 1967 | 116 TWh | 0.2% |
| 1968 | 148 TWh | 0.3% |
| 1969 | 175 TWh | 0.3% |
| 1970 | 224 TWh | 0.4% |
| 1971 | 311 TWh | 0.5% |
| 1972 | 432 TWh | 0.7% |
| 1973 | 579 TWh | 0.9% |
| 1974 | 756 TWh | 1.1% |
| 1975 | 1,049 TWh | 1.6% |
| 1976 | 1,228 TWh | 1.7% |
| 1977 | 1,528 TWh | 2.1% |
| 1978 | 1,776 TWh | 2.3% |
| 1979 | 1,847 TWh | 2.4% |
| 1980 | 2,020 TWh | 2.6% |
| 1981 | 2,386 TWh | 3.1% |
| 1982 | 2,588 TWh | 3.4% |
| 1983 | 2,933 TWh | 3.7% |
| 1984 | 3,560 TWh | 4.3% |
| 1985 | 4,225 TWh | 5% |
| 1986 | 4,525 TWh | 5.3% |
| 1987 | 4,922 TWh | 5.5% |
| 1988 | 5,366 TWh | 5.8% |
| 1989 | 5,519 TWh | 5.8% |
| 1990 | 5,676 TWh | 5.9% |
| 1991 | 5,948 TWh | 6.2% |
| 1992 | 5,993 TWh | 6.2% |
| 1993 | 6,199 TWh | 6.4% |
| 1994 | 6,316 TWh | 6.4% |
| 1995 | 6,590 TWh | 6.5% |
| 1996 | 6,829 TWh | 6.6% |
| 1997 | 6,782 TWh | 6.5% |
| 1998 | 6,899 TWh | 6.5% |
| 1999 | 7,162 TWh | 6.7% |
| 2000 | 7,323 TWh | 6.6% |
| 2001 | 7,481 TWh | 6.7% |
| 2002 | 7,552 TWh | 6.6% |
| 2003 | 7,351 TWh | 6.2% |
| 2004 | 7,636 TWh | 6.2% |
| 2005 | 7,608 TWh | 6% |
| 2006 | 7,654 TWh | 5.8% |
| 2007 | 7,452 TWh | 5.5% |
| 2008 | 7,382 TWh | 5.4% |
| 2009 | 7,233 TWh | 5.4% |
| 2010 | 7,374 TWh | 5.2% |
| 2011 | 7,022 TWh | 4.9% |
| 2012 | 6,501 TWh | 4.4% |
| 2013 | 6,513 TWh | 4.4% |
| 2014 | 6,607 TWh | 4.4% |
| 2015 | 6,656 TWh | 4.4% |
| 2016 | 6,715 TWh | 4.3% |
| 2017 | 6,735 TWh | 4.3% |
| 2018 | 6,856 TWh | 4.2% |
| 2019 | 7,073 TWh | 4.3% |
| 2020 | 6,789 TWh | 4.3% |
| 2021 | 7,031 TWh | 4.3% |
More recently, a return to nuclear energy has gained some support as countries push for transitions to cleaner energy, since nuclear power generates no direct carbon emissions.
What’s Next for Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear remains one of the least harmful sources of energy, and some countries are pursuing advancements in nuclear tech to fight climate change.
Small, modular nuclear reactors are one of the current proposed solutions to both bring down costs and reduce construction time of nuclear power plants. The benefits include smaller capital investments and location flexibility by trading off energy generation capacity.
With countries having to deal with aging nuclear reactors and climate change at the same time, replacements need to be considered. Will they come in the form of new nuclear power and uranium mining, or alternative sources of energy?

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Maps
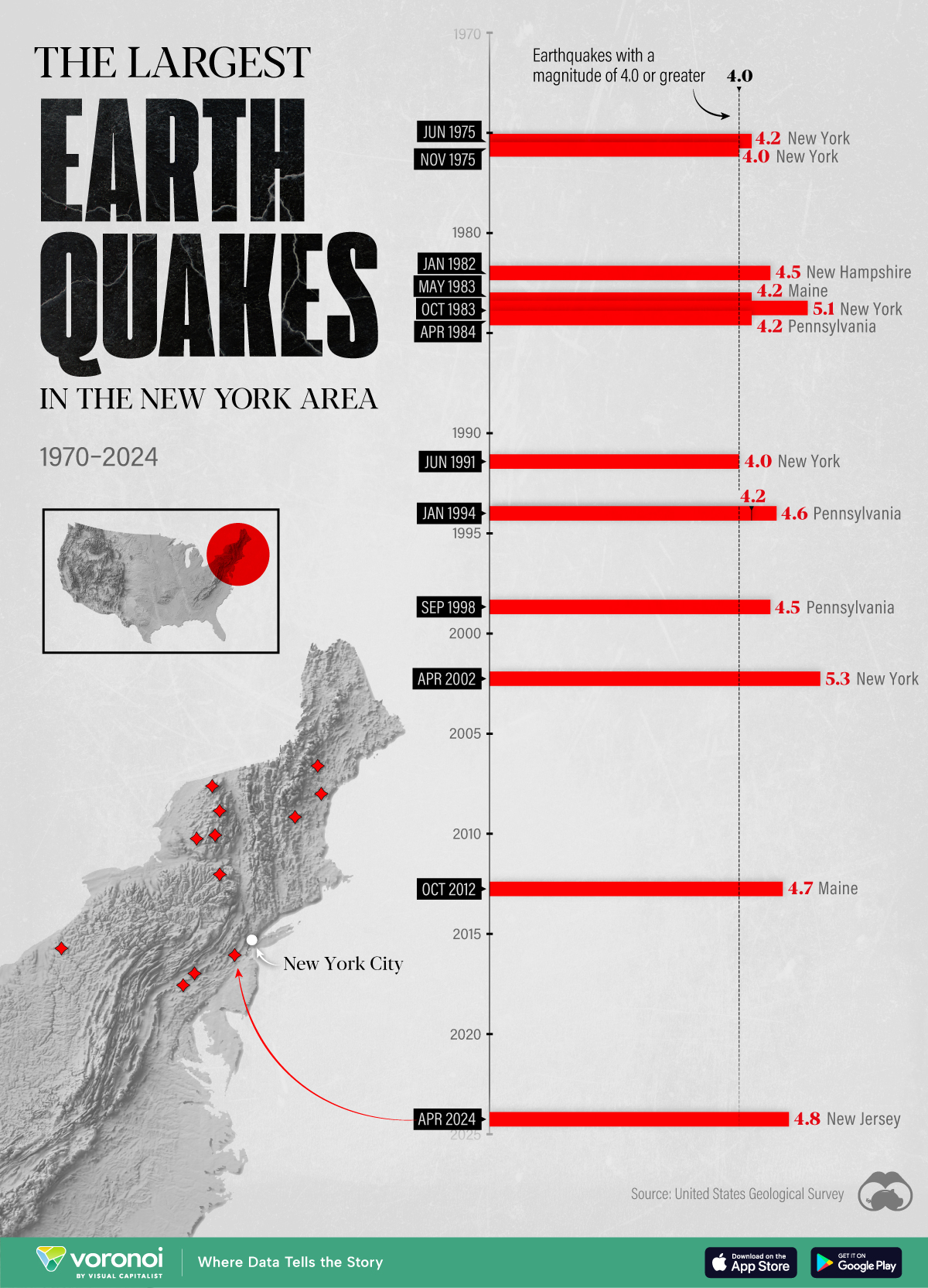
The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
The earthquake that shook buildings across New York in April 2024 was the third-largest quake in the Northeast U.S. over the past 50 years.

The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The 4.8 magnitude earthquake that shook buildings across New York on Friday, April 5th, 2024 was the third-largest quake in the U.S. Northeast area over the past 50 years.
In this map, we illustrate earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.0 or greater recorded in the Northeastern U.S. since 1970, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Shallow Quakes and Older Buildings
The earthquake that struck the U.S. Northeast in April 2024 was felt by millions of people from Washington, D.C., to north of Boston. It even caused a full ground stop at Newark Airport.
The quake, occurring just 5 km beneath the Earth’s surface, was considered shallow, which is what contributed to more intense shaking at the surface.
According to the USGS, rocks in the eastern U.S. are significantly older, denser, and harder than those on the western side, compressed by time. This makes them more efficient conduits for seismic energy. Additionally, buildings in the Northeast tend to be older and may not adhere to the latest earthquake codes.
Despite disrupting work and school life, the earthquake was considered minor, according to the Michigan Technological University magnitude scale:
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 or less | Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph. | Millions |
| 2.5 to 5.4 | Often felt, but only causes minor damage. | 500,000 |
| 5.5 to 6.0 | Slight damage to buildings and other structures. | 350 |
| 6.1 to 6.9 | May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas. | 100 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
The largest earthquake felt in the area over the past 50 years was a 5.3 magnitude quake that occurred in Au Sable Forks, New York, in 2002. It damaged houses and cracked roads in a remote corner of the Adirondack Mountains, but caused no injuries.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 20, 2002 | 5.3 | Au Sable Forks | New York |
| October 7, 1983 | 5.1 | Newcomb | New York |
| April 5, 2024 | 4.8 | Whitehouse Station | New Jersey |
| October 16, 2012 | 4.7 | Hollis Center | Maine |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.6 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| January 19, 1982 | 4.5 | Sanbornton | New Hampshire |
| September 25, 1998 | 4.5 | Adamsville | Pennsylvania |
| June 9, 1975 | 4.2 | Altona | New York |
| May 29, 1983 | 4.2 | Peru | Maine |
| April 23, 1984 | 4.2 | Conestoga | Pennsylvania |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.2 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| November 3, 1975 | 4 | Long Lake | New York |
| June 17, 1991 | 4 | Worcester | New York |
The largest earthquake in U.S. history, however, was the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska, measuring 9.2 magnitude and killing 131 people.
-
 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)