Technology
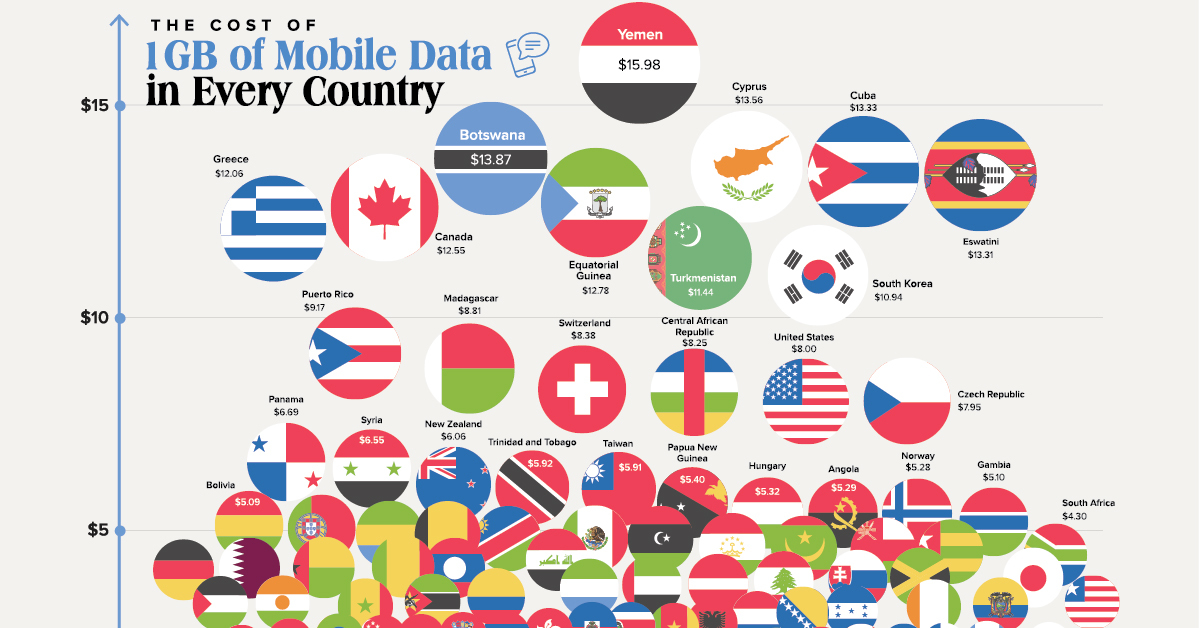
What Does 1GB of Mobile Data Cost in Every Country?
What Does 1GB of Mobile Data Cost in Every Country?
Billions of people around the world rely on their mobile phones every day.
Even in a saturated market, mobile networks have continued to expand their reach. In the last five years alone, almost one billion additional people have gained access to mobile data services.
Despite the growing prevalence of these networks worldwide, the cost of gaining access can vary greatly from country to country—particularly when it comes to the price of mobile data.
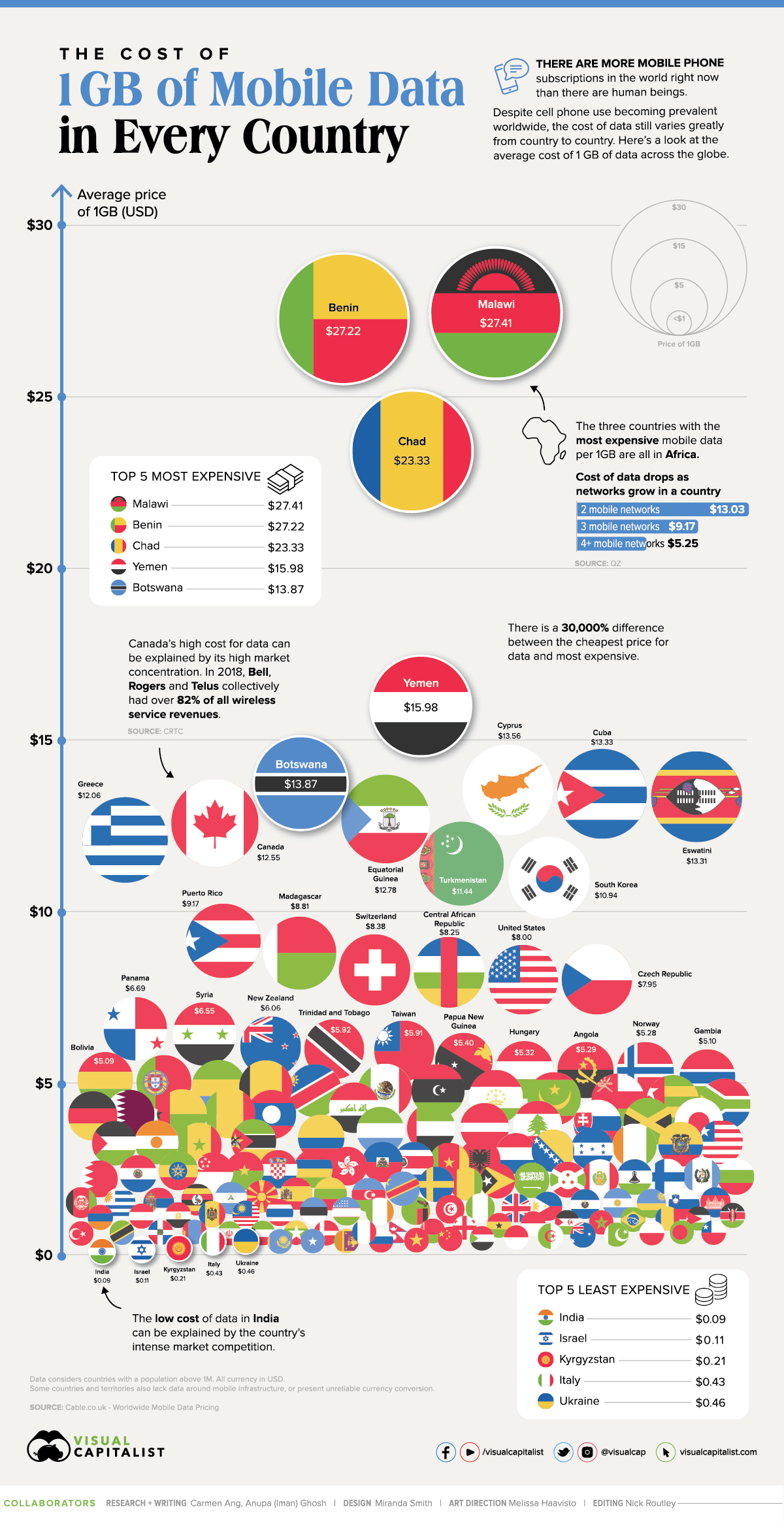
Today’s chart uses figures from Cable.co.uk to showcase the average cost of one gigabyte (GB) of mobile data in 155 different countries and jurisdictions. Despite the vast global reach of the mobile economy, it’s clear it still has a long way to go to reach true accessibility.
Discrepancies in Mobile Data Costs
Researchers have identified several key elements that help explain the cost variation for mobile data between countries:
- Existing infrastructure (or lack thereof): This might seem counterintuitive, but most mobile networks rely on a fixed-line connection. As a result, countries with existing infrastructure are able to offer mobile plans with more data, at a cheaper price. This is the case for India and Italy. Countries with minimal or no infrastructure rely on more costly connection alternatives like satellites, and the cost typically gets passed down to the consumer.
- Reliance on mobile data: When mobile data is the primary source of internet in a particular region, adoption can become nearly universal. This high demand typically leads to an increase in competing providers, which in turn lowers the cost. Kyrgyzstan is a good example of this.
- Low data consumption: Countries with poor infrastructure tend to use less data. With mobile plans that offer smaller data limits, the overall average cost per GB tends to skew higher. Countries like Malawi and Benin are examples of this phenomenon.
- Average income of consumer: Relatively wealthy nations tend to charge more for mobile services since the population can generally afford to pay more, and the cost of operating a network is higher. This is apparent in countries like Canada or Germany.
The Cheapest Countries for 1 GB of Data
Even among the cheapest countries for mobile data, the cost variation is significant. Here’s a look at the top five cheapest countries for 1 GB of data:
| Overall Rank | Country | Average price of 1GB (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇮🇳 India | 9¢ |
| 2 | 🇮🇱 Israel | 11¢ |
| 3 | 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | 21¢ |
| 4 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 43¢ |
| 5 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 46¢ |
India ranks the cheapest at $0.09 per GB, a 65% decrease in price compared to the country’s average cost in 2019.
Why is data so cheap in India? A significant factor is the country’s intense market competition, driven by Reliance Jio—a telecom company owned by Reliance Industries, one of the largest conglomerates in India. Reliance Jio launched in 2016, offering customers free trial periods and plans for less than a $1 a month. This forced other providers to drop their pricing, driving down the overall cost of data in the region.
Because these prices are likely unsustainable for the long term, India’s cheaper-than-usual prices may soon come to an end.
Another country worth highlighting is Kyrgyzstan, which ranks as the third cheapest at $0.21 per GB, ahead of Italy and Ukraine. This ranking is surprising, given the country’s minimal fixed-line infrastructure and large rural population. Researchers suspect the low cost is a result of Kyrgyzstan’s heavy reliance on mobile data as the population’s primary source of internet.
The Most Expensive Countries for 1 GB of Data
On the other end of the spectrum, here are the top five most expensive countries for one gigabyte of mobile data:
| Overall Rank | Country | Average price of 1GB (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 155 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | $27.41 |
| 154 | 🇧🇯 Benin | $27.22 |
| 153 | 🇹🇩 Chad | $23.33 |
| 152 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | $15.98 |
| 151 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | $13.87 |
A striking trend worth noting is that four out of five of the most expensive countries for mobile data are in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).
A significant factor behind the high cost of data in SSA is its lack of infrastructure. With overburdened networks, the data bundles offered in the region are generally smaller. This drives up the average cost per GB when compared to countries with unlimited packages.
Another element that contributes to SSA’s high costs is its lack of market competition. In countries with multiple competing networks, such as Nigeria, the cost of data skews lower.
The Full Breakdown
The below table has a full list of all 155 countries and jurisdictions included in the data set. It helps demonstrate the stark contrast in the cost of mobile data between the most expensive and cheapest countries globally.
| Rank | Country | Average price of 1GB (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | India | 9¢ |
| 2 | Israel | 11¢ |
| 3 | Kyrgyzstan | 21¢ |
| 4 | Italy | 43¢ |
| 5 | Ukraine | 46¢ |
| 6 | Kazakhstan | 46¢ |
| 7 | Somalia | 50¢ |
| 8 | Sri Lanka | 51¢ |
| 9 | Russian Federation | 52¢ |
| 10 | Vietnam | 57¢ |
| 11 | China | 61¢ |
| 12 | Sudan | 63¢ |
| 13 | Indonesia | 64¢ |
| 14 | Algeria | 65¢ |
| 15 | Australia | 68¢ |
| 16 | Pakistan | 69¢ |
| 17 | Poland | 70¢ |
| 18 | Bangladesh | 70¢ |
| 19 | Chile | 71¢ |
| 20 | Turkey | 72¢ |
| 21 | Tanzania | 73¢ |
| 22 | Dominican Republic | 74¢ |
| 23 | Mongolia | 74¢ |
| 24 | Iran | 75¢ |
| 25 | Kuwait | 77¢ |
| 26 | Myanmar | 78¢ |
| 27 | Denmark | 80¢ |
| 28 | France | 81¢ |
| 29 | Nepal | 86¢ |
| 30 | Belarus | 89¢ |
| 31 | Georgia | 93¢ |
| 32 | Ghana | 94¢ |
| 33 | Monaco | 98¢ |
| 34 | Western Sahara | 99¢ |
| 35 | Morocco | 99¢ |
| 36 | Brazil | $1.01 |
| 37 | Romania | $1.03 |
| 38 | Jordan | $1.03 |
| 39 | Kenya | $1.05 |
| 40 | Armenia | $1.05 |
| 41 | Austria | $1.08 |
| 42 | Egypt | $1.09 |
| 43 | Moldova | $1.12 |
| 44 | Malaysia | $1.12 |
| 45 | Thailand | $1.23 |
| 46 | Estonia | $1.27 |
| 47 | Uzbekistan | $1.34 |
| 48 | Ireland | $1.36 |
| 49 | Zambia | $1.36 |
| 50 | Tunisia | $1.37 |
| 51 | Nigeria | $1.39 |
| 52 | United Kingdom | $1.39 |
| 53 | Philippines | $1.42 |
| 54 | El Salvador | $1.45 |
| 55 | Argentina | $1.45 |
| 56 | Rwanda | $1.48 |
| 57 | Slovenia | $1.48 |
| 58 | Cambodia | $1.50 |
| 59 | Afghanistan | $1.55 |
| 60 | Uruguay | $1.58 |
| 61 | Serbia | $1.60 |
| 62 | Uganda | $1.62 |
| 63 | Nicaragua | $1.71 |
| 64 | Macedonia | $1.75 |
| 65 | Spain | $1.81 |
| 66 | Lithuania | $1.85 |
| 67 | Azerbaijan | $1.86 |
| 68 | Congo | $1.94 |
| 69 | Sweden | $2.07 |
| 70 | Guinea | $2.08 |
| 71 | Timor-Leste | $2.08 |
| 72 | Saudi Arabia | $2.12 |
| 73 | Burundi | $2.12 |
| 74 | Peru | $2.13 |
| 75 | Lesotho | $2.13 |
| 76 | Finland | $2.14 |
| 77 | Guatemala | $2.17 |
| 78 | Bulgaria | $2.22 |
| 79 | Bahrain | $2.27 |
| 80 | Paraguay | $2.30 |
| 81 | Ethiopia | $2.44 |
| 82 | Singapore | $2.47 |
| 83 | Burkina Faso | $2.47 |
| 84 | Croatia | $2.48 |
| 85 | Mauritius | $2.48 |
| 86 | Hong Kong | $2.55 |
| 87 | Haiti | $2.74 |
| 88 | Costa Rica | $2.74 |
| 89 | Cameroon | $2.75 |
| 90 | Albania | $2.83 |
| 91 | Netherlands | $2.98 |
| 92 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | $3.04 |
| 93 | Honduras | $3.12 |
| 94 | Côte d'Ivoire | $3.20 |
| 95 | Ecuador | $3.24 |
| 96 | Liberia | $3.25 |
| 97 | Palestine | $3.26 |
| 98 | Niger | $3.30 |
| 99 | Senegal | $3.30 |
| 100 | Mozambique | $3.33 |
| 101 | Colombia | $3.46 |
| 102 | Sierra Leone | $3.69 |
| 103 | United Arab Emirates | $3.78 |
| 104 | Latvia | $3.79 |
| 105 | Lebanon | $3.82 |
| 106 | Slovakia | $3.84 |
| 107 | Jamaica | $3.88 |
| 108 | Japan | $3.91 |
| 109 | Germany | $4.06 |
| 110 | Qatar | $4.12 |
| 111 | Guinea-Bissau | $4.12 |
| 112 | Mali | $4.12 |
| 113 | Lao PDR | $4.16 |
| 114 | Iraq | $4.20 |
| 115 | South Africa | $4.30 |
| 116 | Togo | $4.50 |
| 117 | Oman | $4.58 |
| 118 | Mauritania | $4.63 |
| 119 | Tajikistan | $4.65 |
| 120 | Libya | $4.73 |
| 121 | Mexico | $4.77 |
| 122 | Namibia | $4.78 |
| 123 | Belgium | $4.88 |
| 124 | Gabon | $4.89 |
| 125 | Portugal | $4.97 |
| 126 | Bolivia | $5.09 |
| 127 | Gambia | $5.10 |
| 128 | Norway | $5.28 |
| 129 | Angola | $5.29 |
| 130 | Hungary | $5.32 |
| 131 | Papua New Guinea | $5.40 |
| 132 | Taiwan | $5.91 |
| 133 | Trinidad and Tobago | $5.92 |
| 134 | New Zealand | $6.06 |
| 135 | Syria | $6.55 |
| 136 | Panama | $6.69 |
| 137 | Czech Republic | $7.95 |
| 138 | United States | $8.00 |
| 139 | Central African Republic | $8.25 |
| 140 | Switzerland | $8.38 |
| 141 | Madagascar | $8.81 |
| 142 | Puerto Rico | $9.17 |
| 143 | South Korea | $10.94 |
| 144 | Turkmenistan | $11.44 |
| 145 | Greece | $12.06 |
| 146 | Canada | $12.55 |
| 147 | Equatorial Guinea | $12.78 |
| 148 | Eswatini | $13.31 |
| 149 | Cuba | $13.33 |
| 150 | Cyprus | $13.56 |
| 151 | Botswana | $13.87 |
| 152 | Yemen | $15.98 |
| 153 | Chad | $23.33 |
| 154 | Benin | $27.22 |
| 155 | Malawi | $27.41 |
Interestingly, the highest average cost is 30,000% more than the cheapest average price.
The Technology Gap
Will we reach a point of equal accessibility across the globe, or will the technology gap between countries continue to widen?
With 5G networks on the rise, just seven countries are expected to make up the majority of 5G related investments. Time will tell what this means for adoption worldwide.
Editor’s Note: The methodology used by Cable.co.uk represents a region’s national average, based on both pre-paid and post-paid plans. While the data correctly represents each region’s average cost on 1 GB based on the chosen methodology, Cable.co.uk acknowledges that it may not reflect the way most people in a country consume data.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001