Technology
5G Revolution: Unlocking the Digital Age
5G Revolution: Unlocking the Digital Age
Imagine if you were to jump straight from using a typewriter one day, to typing on a laptop the next. The speed and ease at which it would improve your tasks is undeniable.
With 5G, we’re on the cusp of a similar transition in the global communications system. Total connectivity could soon be at our fingertips.
Today’s infographic breaks down the potential that 5G promises, and the immense opportunities stemming from its implications for smart tech and the Internet of Things (IoT).
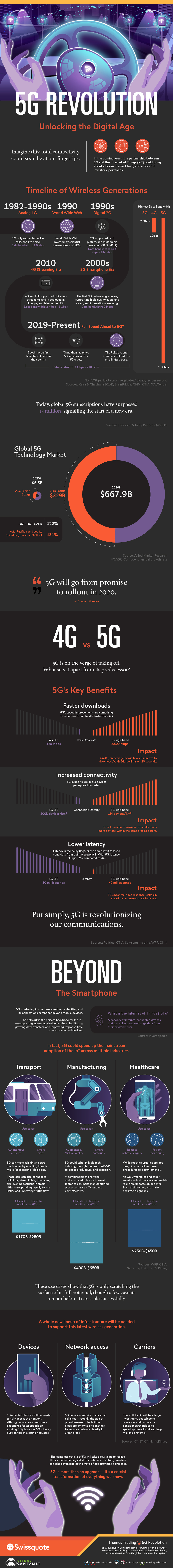
A Timeline of Wireless Generations
The world’s appetite for wireless speed has been insatiable. We’ve powered through five generations of wireless connectivity in just 40 years.
- 1982-1990s: Analog 1G
1G only supported voice calls, and little else.
Data bandwidth: 1.9 kbps - 1990s: Digital 2G
2G supported text, picture, and multimedia messaging (SMS, MMS).
Data bandwidth: 14.4 kbps – 384 kbps - 2000s: 3G Smartphone Era
The first 3G networks go online, supporting high-quality audio and video, and international roaming.
Data bandwidth: 2 Mbps - 2010: 4G Streaming Era
4G and LTE supported HD video streaming, and is deployed in Europe, and later in the U.S.
Data bandwidth: 2 Mbps – 1 Gbps - 2019-Present: Full Speed Ahead to 5G?
South Korea first launches 5G across the country, followed by 50 cities in China. The U.S., UK, and Germany also roll out 5G on a limited basis.
Data bandwidth: 1 Gbps – >10 Gbps
*k/M/Gbps: kilobytes/ megabytes/ gigabytes per second.
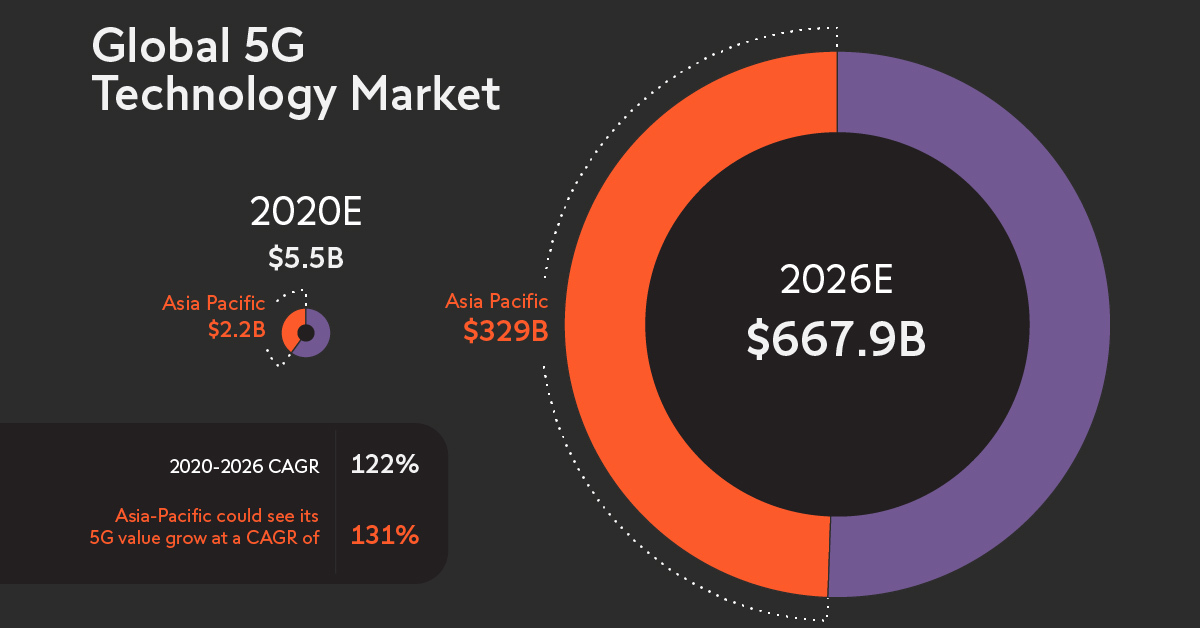
The global 5G market is projected to reach $668 billion at a 122% compound annual growth rate (2020-2026), with nearly half this growth coming from Asia-Pacific.
4G versus 5G: What’s the Difference?
5G is on the verge of taking off. What sets it apart from its predecessor?
For starters, 5G’s speed improvements are something to behold—it is up to 20x faster than 4G. On 4G, an average movie takes 6 minutes to download. With 5G, it will take less than 20 seconds.
| 4G | 5G | |
|---|---|---|
| Faster downloads Peak data date | 125 megabytes/second | 2,500 Mbs |
| Increased connectivity Devices supported per km² | 100,000 devices/km² | 1,000,000 devices/km² |
| Lower Latency Delay/ lag time | 50 milliseconds | <2 ms |
In other benefits, 5G supports 10x more devices per square kilometer. As a result, 5G will be able to seamlessly handle many more devices, within the same area as before. This is pivotal for its use in the imminent Internet of Things (IoT).
Finally, latency is the delay (lag), or the time that it takes to send data from point A to point B. With 5G, latency plunges 25x compared to 4G. This results in almost instantaneous data transfers.
5G will go from promise to roll-out in 2020.
Beyond the Smartphone
5G is one of the most anticipated technologies of our time, and with good reason. In the coming years, the partnership between 5G and the IoT could bring about a boom in smart tech, and this effect could trickle into growth for the economy and investor portfolios.
The 5G network is the perfect backbone for the IoT—supporting increasing device numbers, facilitating growing data transfers, and improving response time among connected devices.
According to McKinsey, 5G will likely speed up the mainstream adoption of the IoT across multiple industries:
1. Transport
5G enables self-driving cars to make “split second” decisions, making them safer. These cars can also connect to buildings, street lights, other cars, and even pedestrians in smart cities—responding rapidly to any issues and improving traffic flow.
These two use cases are estimated to bring a $170-$280 billion global GDP boost to the mobility sector by 2030.
2. Manufacturing
5G could usher in high-tech industry, using AR/VR to boost productivity and precision. Analytics and advanced robotics in smart factories can streamline manufacturing processes, leading to efficiency gains and cost savings. Altogether, the impact could be a $400-$650 billion GDP boost to the industry by 2030.
3. Healthcare
While robotic surgeries are not new, 5G could allow these procedures to occur remotely.
Wearables and other smart medical devices provide real-time updates on patients, and make accurate diagnoses. These two applications will contribute an additional $250-$450 billion in GDP to the healthcare space by 2030.
A New Wireless Era
5G is only scratching the surface of its full potential, though a few caveats remain before it can scale successfully. A whole new lineup of infrastructure will be needed to support this latest wireless generation, including enabled devices, network density and access, and getting telecoms operators and carriers on board.
The complete uptake of 5G will take a few years to realize. But as the technological shift continues to unfold, investors can take advantage of the wave of opportunities it presents.
5G is more than an upgrade—it’s a crucial transformation of major segments of the economy.
Brands
How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.

How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
One would be hard-pressed to find a company that has never changed its logo. Granted, some brands—like Rolex, IBM, and Coca-Cola—tend to just have more minimalistic updates. But other companies undergo an entire identity change, thus necessitating a full overhaul.
In this graphic, we visualized the evolution of prominent tech companies’ logos over time. All of these brands ranked highly in a Q1 2024 YouGov study of America’s most famous tech brands. The logo changes are sourced from 1000logos.net.
How Many Times Has Google Changed Its Logo?
Google and Facebook share a 98% fame rating according to YouGov. But while Facebook’s rise was captured in The Social Network (2010), Google’s history tends to be a little less lionized in popular culture.
For example, Google was initially called “Backrub” because it analyzed “back links” to understand how important a website was. Since its founding, Google has undergone eight logo changes, finally settling on its current one in 2015.
| Company | Number of Logo Changes |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| HP | 8 |
| Amazon | 6 |
| Microsoft | 6 |
| Samsung | 6 |
| Apple | 5* |
Note: *Includes color changes. Source: 1000Logos.net
Another fun origin story is Microsoft, which started off as Traf-O-Data, a traffic counter reading company that generated reports for traffic engineers. By 1975, the company was renamed. But it wasn’t until 2012 that Microsoft put the iconic Windows logo—still the most popular desktop operating system—alongside its name.
And then there’s Samsung, which started as a grocery trading store in 1938. Its pivot to electronics started in the 1970s with black and white television sets. For 55 years, the company kept some form of stars from its first logo, until 1993, when the iconic encircled blue Samsung logo debuted.
Finally, Apple’s first logo in 1976 featured Isaac Newton reading under a tree—moments before an apple fell on his head. Two years later, the iconic bitten apple logo would be designed at Steve Jobs’ behest, and it would take another two decades for it to go monochrome.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue