Datastream
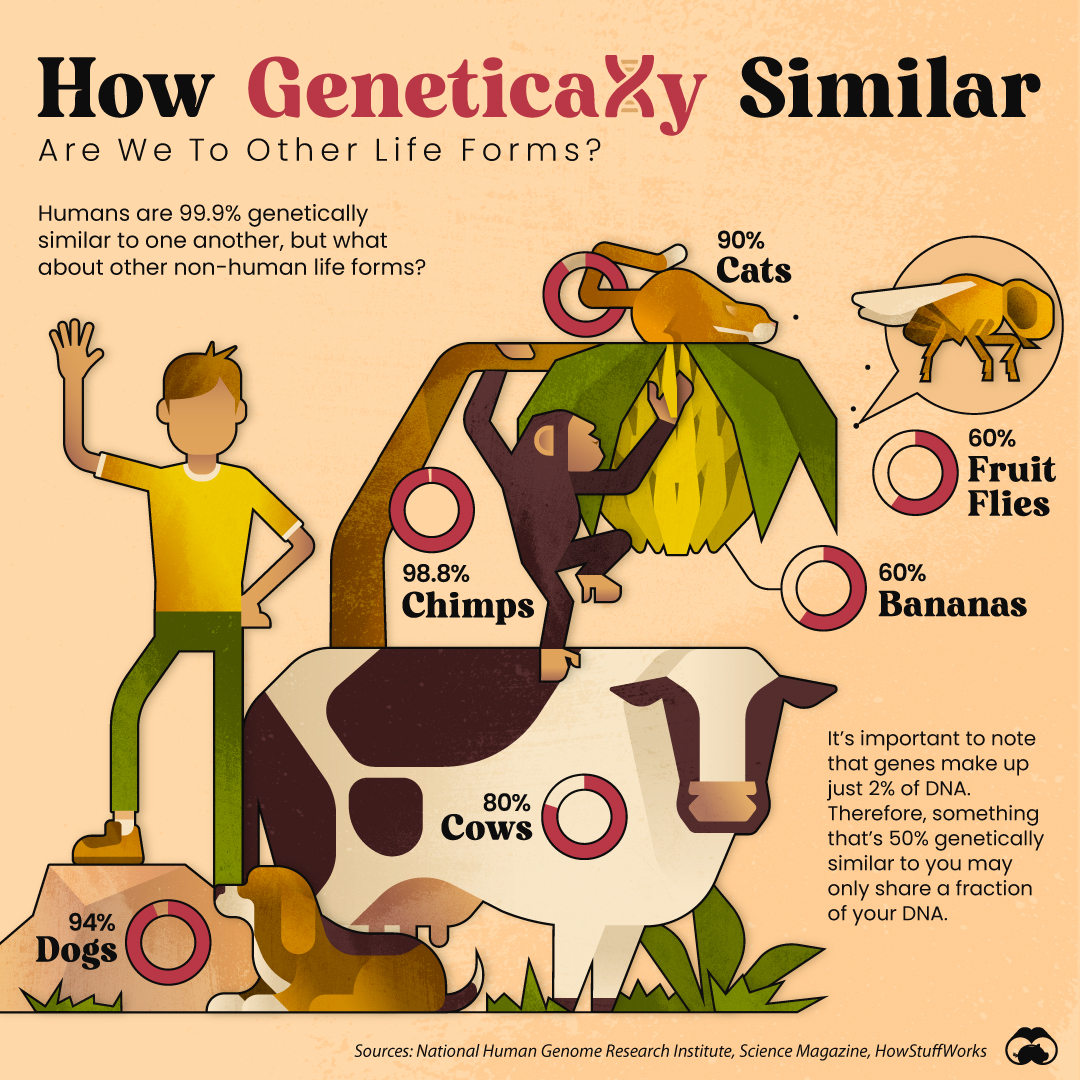
How Genetically Similar Are We To Other Life Forms?
The Briefing
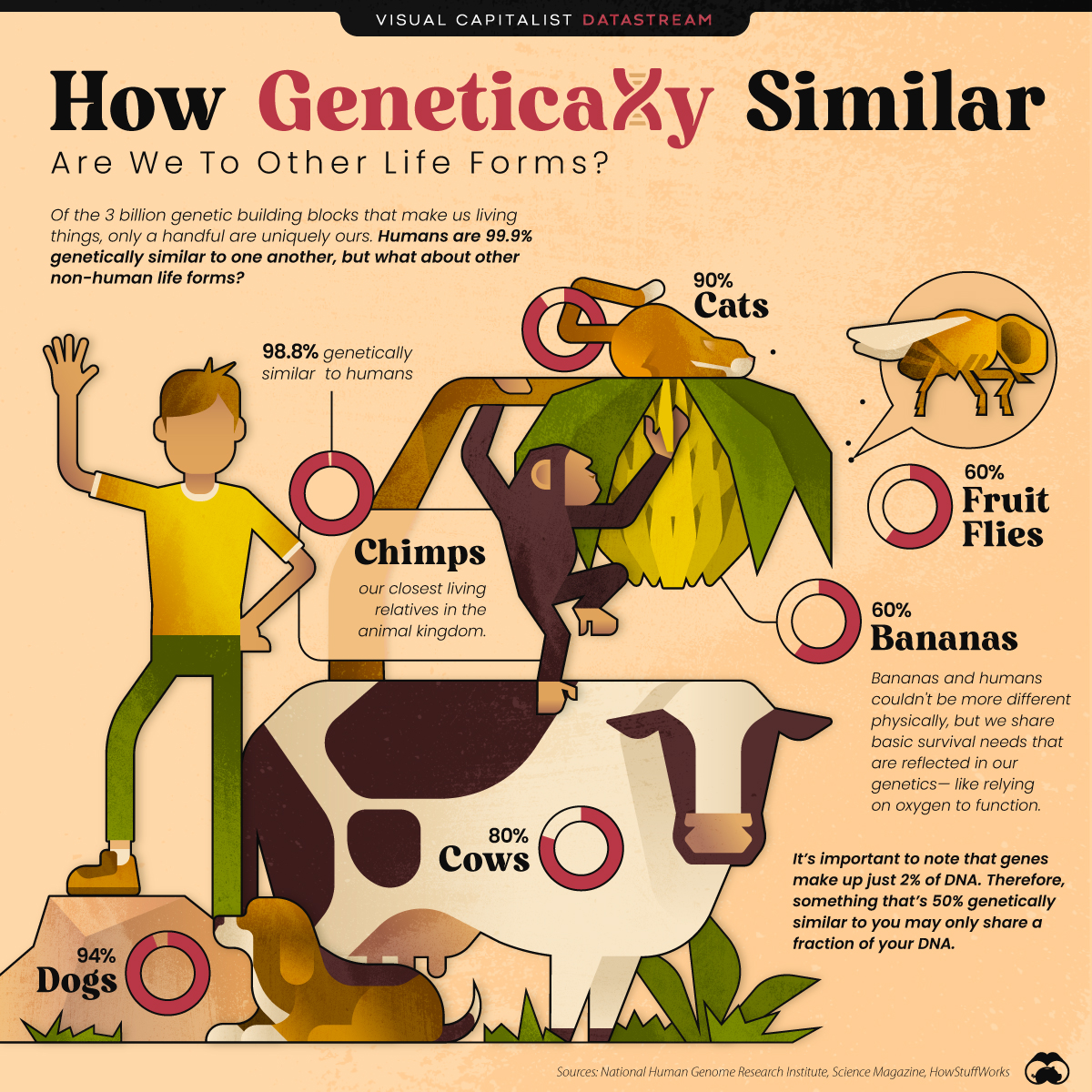
- Chimps are 98.8% genetically similar, making them one of our closest relatives in the animal kingdom
- The genetic similarity between humans and fruit flies is 60%
Comparing Human Genetic Similarity to Other Life Forms
Of the three billion genetic building blocks that make us living things, only a handful are uniquely ours. In fact, despite our differences on the outside, humans are 99.9% genetically similar to one another.
But how alike are we to other, non-human life forms? Turns out, we’re a lot more similar than you might think.
Comparative Genomics 101
First, how do scientists compare the genetic makeup of various life forms?
Comparative genomics is a branch of biology that compares genome sequences across different species to identify their similarities and differences.
This field of research is important because it:
- Helps us better understand evolution, and how living things have adapted over time.
- Builds knowledge around genes and how they influence various systems in our bodies.
- Has wider applications in agriculture, especially in conservation efforts among endangered species.
According to the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), scientists have already sequenced the genomes of more than 250 animal species, as well as 50 bird species.
Human Genetic Makeup vs. Other Life Forms
Perhaps unsurprisingly, chimps are one of our closest genetic relatives in the animal kingdom.
Because of our similarities, chimpanzees have a similar immune system to humans, which means they’re susceptible to viruses such as AIDS and hepatitis.
Though chimps are one of our closest relatives, other species are strongly linked to humans as well—and not necessarily the ones you’d think.
| Category | Genetic Similarity |
|---|---|
| Humans and Humans | 99.9% |
| Humans and Chimps | 98.8% |
| Humans and Dogs | 94% |
| Humans and Cats | 90% |
| Humans and Cows | 80% |
| Humans and Fruit Flies | 60% |
| Humans and Bananas | 60% |
For instance, according to NHGRI, fruit flies are 60% genetically similar to humans.
This may sound confusing at first, since humans and insects couldn’t be more physically different. However, because we share many of the same essential needs to sustain life, such as the need for oxygen, these similarities are reflected in our genetics.
DNA vs Genes
It’s important to note that being genetically similar to something is different than sharing the same DNA. That’s because genes (the part of DNA responsible for making protein) only account for up to 2% of your DNA, while the rest of your genome is made up of what scientists call “non-coding DNA.”
So while a banana is 60% genetically similar to humans, only 1.2% of our DNA is shared.
» Like this? Then check out this article on Earth’s Biomass
Where does this data come from?
Sources: National Human Genome Research Institute, Genome Research, Science Magazine
Details:: This post was inspired by an article published in Business Insider
Datastream
Can You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?
Discover how the average person’s carbon footprint impacts the environment and learn how carbon credits can offset your carbon footprint.
The Briefing
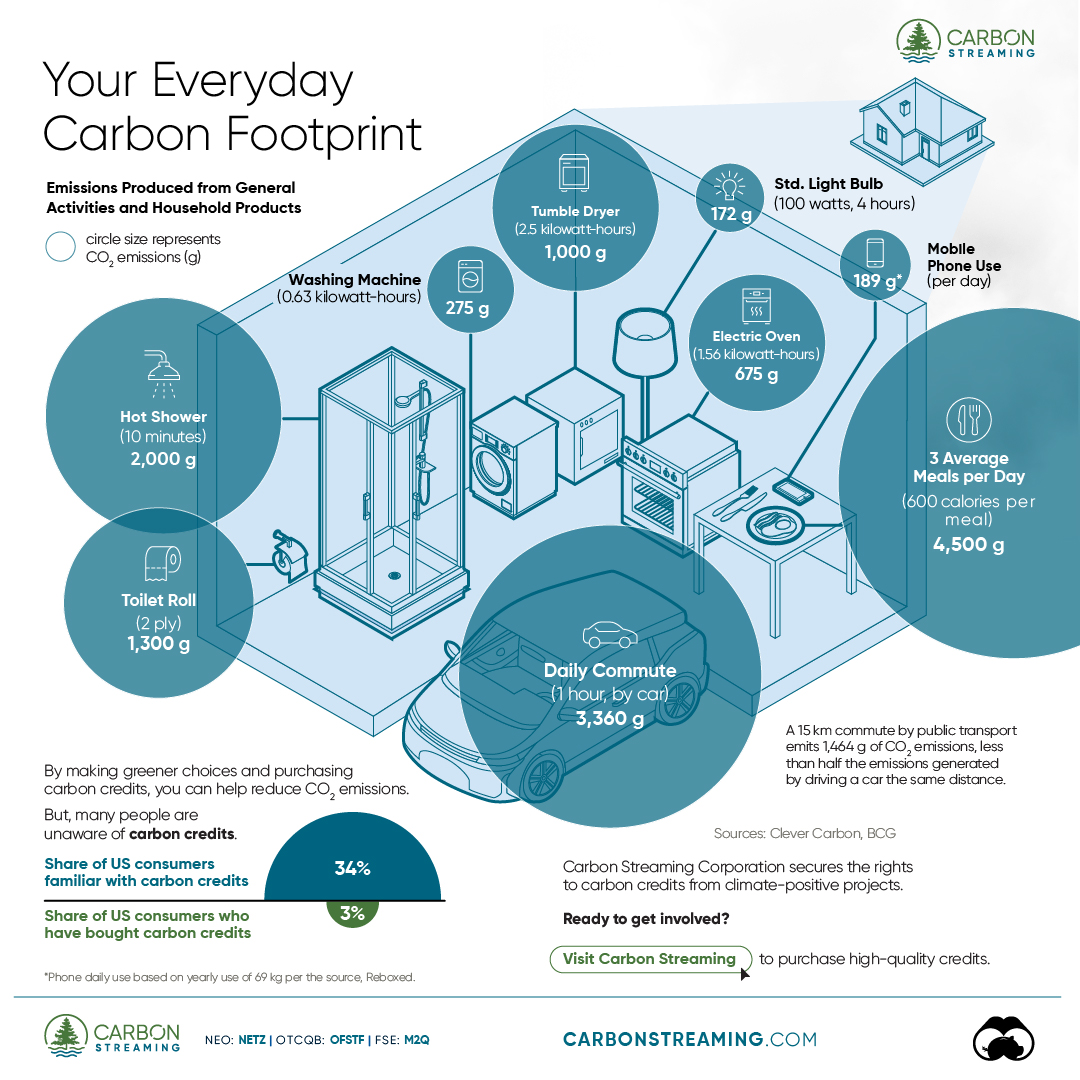
- A person’s carbon footprint is substantial, with activities such as food consumption creating as much as 4,500 g of CO₂ emissions daily.
- By purchasing carbon credits from Carbon Streaming Corporation, you can offset your own emissions and fund positive climate action.
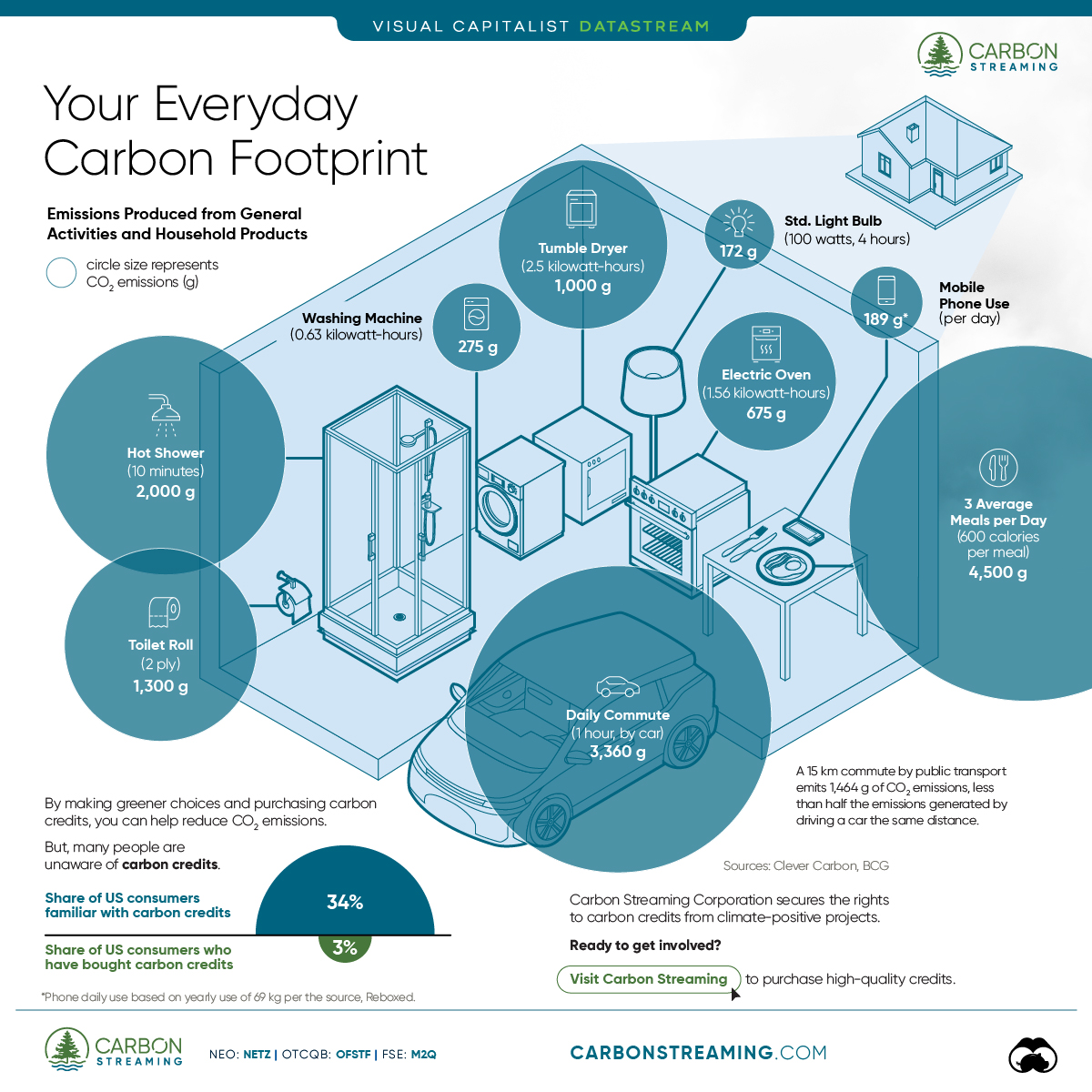
Your Everyday Carbon Footprint
While many large businesses and countries have committed to net-zero goals, it is essential to acknowledge that your everyday activities also contribute to global emissions.
In this graphic, sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation, we will explore how the choices we make and the products we use have a profound impact on our carbon footprint.
Carbon Emissions by Activity
Here are some of the daily activities and products of the average person and their carbon footprint, according to Clever Carbon.
| Household Activities & Products | CO2 Emissions (g) |
|---|---|
| 💡 Standard Light Bulb (100 watts, four hours) | 172 g |
| 📱 Mobile Phone Use (195 minutes per day)* | 189 g |
| 👕 Washing Machine (0.63 kWh) | 275 g |
| 🔥 Electric Oven (1.56 kWh) | 675 g |
| ♨️ Tumble Dryer (2.5 kWh) | 1,000 g |
| 🧻 Toilet Roll (2 ply) | 1,300 g |
| 🚿 Hot Shower (10 mins) | 2,000 g |
| 🚙 Daily Commute (one hour, by car) | 3,360 g |
| 🍽️ Average Daily Food Consumption (three meals of 600 calories) | 4,500 g |
| *Phone use based on yearly use of 69kg per the source, Reboxed | |
Your choice of transportation plays a crucial role in determining your carbon footprint. For instance, a 15 km daily commute to work on public transport generates an average of 1,464 g of CO₂ emissions. Compared to 3,360 g—twice the volume for a journey the same length by car.
By opting for more sustainable modes of transport, such as cycling, walking, or public transportation, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
Addressing Your Carbon Footprint
One way to compensate for your emissions is by purchasing high-quality carbon credits.
Carbon credits are used to help fund projects that avoid, reduce or remove CO₂ emissions. This includes nature-based solutions such as reforestation and improved forest management, or technology-based solutions such as the production of biochar and carbon capture and storage (CCS).
While carbon credits offer a potential solution for individuals to help reduce global emissions, public awareness remains a significant challenge. A BCG-Patch survey revealed that only 34% of U.S. consumers are familiar with carbon credits, and only 3% have purchased them in the past.
About Carbon Streaming
By financing the creation or expansion of carbon projects, Carbon Streaming Corporation secures the rights to future carbon credits generated by these sustainable projects. You can then purchase these carbon credits to help fund climate solutions around the world and compensate for your own emissions.
Ready to get involved?
>> Learn more about purchasing carbon credits at Carbon Streaming
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001