Mining
All the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
View the full-size infographic
All the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on natural resource megatrends in your email every week.
Metals are all around us, from our phones and cars to our homes and office buildings.
While we often overlook the presence of these raw materials, they are an essential part of the modern economy. But obtaining these materials can be a complex process that involves mining, refining, and then converting them into usable forms.
So, how much metal gets mined in a year?
Metals vs Ores
Before digging into the numbers, it’s important that we distinguish between ores and metals.
Ores are naturally occurring rocks that contain metals and metal compounds. Metals are the valuable parts of ores that can be extracted by separating and removing the waste rock. As a result, ore production is typically much higher than the actual metal content of the ore. For example, miners produced 347 million tonnes of bauxite ore in 2019, but the actual aluminum metal content extracted from that was only 62.9 million tonnes.
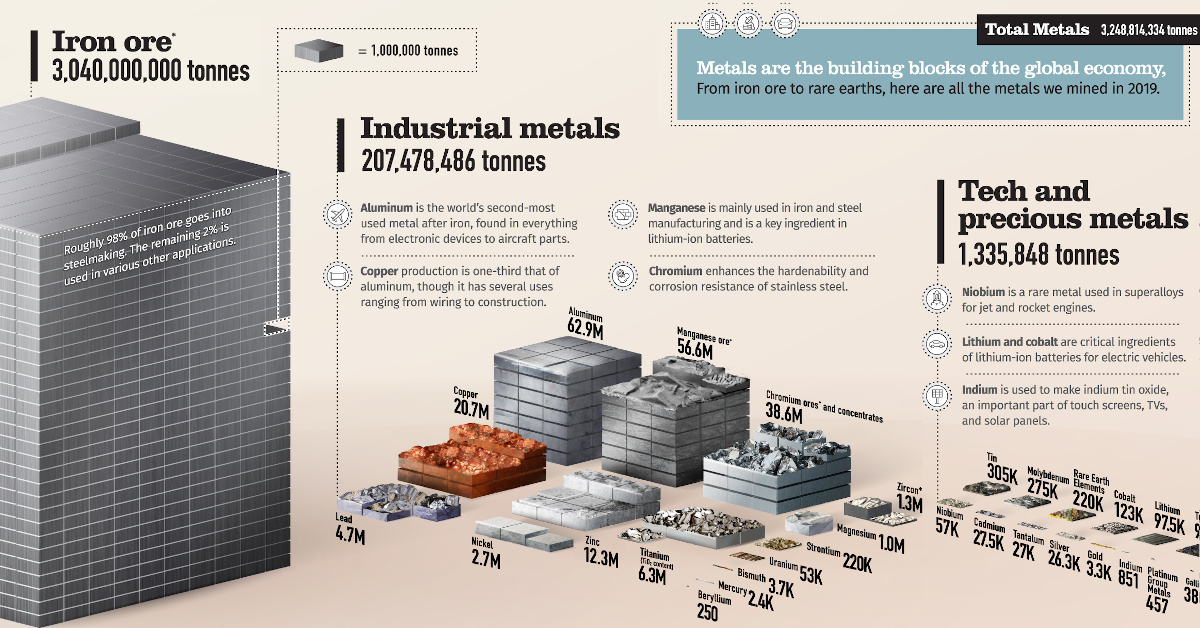
Here are all the metals and metal ores mined in 2019, according to the British Geological Survey:
| Metal/Ore | Quantity Mined (tonnes) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Ore | 3,040,000,000 | 93.57% |
| Industrial Metals | 207,478,486 | 6.39% |
| Technology and Precious Metals | 1,335,848 | 0.04% |
| Total | 3,248,814,334 | 100% |
Miners produced roughly three billion tonnes of iron ore in 2019, representing close to 94% of all mined metals. The primary use of all this iron is to make steel. In fact, 98% of iron ore goes into steelmaking, with the rest fulfilling various other applications.
Industrial and technology metals made up the other 6% of all mined metals in 2019. How do they break down?
Industrial Metals
From construction and agriculture to manufacturing and transportation, virtually every industry harnesses the properties of metals in different ways.
Here are the industrial metals we mined in 2019.
| Metal | Quantity Mined (tonnes) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 62,900,000 | 30% |
| Manganese Ore | 56,600,000 | 27% |
| Chromium Ores and Concentrates | 38,600,000 | 19% |
| Copper | 20,700,000 | 10% |
| Zinc | 12,300,000 | 6% |
| Titanium (Titanium Dioxide Content) | 6,300,000 | 3% |
| Lead | 4,700,000 | 2% |
| Nickel | 2,702,000 | 1% |
| Zirconium Minerals (Zircon) | 1,337,000 | 1% |
| Magnesium | 1,059,736 | 1% |
| Strontium | 220,000 | 0.11% |
| Uranium | 53,400 | 0.03% |
| Bismuth | 3,700 | 0.002% |
| Mercury | 2,400 | 0.001% |
| Beryllium | 250 | 0.0001% |
| Total | 207,478,486 | 100% |
Percentages may not add up to 100 due to rounding.
It’s no surprise that aluminum is the most-produced industrial metal. The lightweight metal is one of the most commonly used materials in the world, with uses ranging from making foils and beer kegs to buildings and aircraft parts.
Manganese and chromium rank second and third respectively in terms of metal mined, and are important ingredients in steelmaking. Manganese helps convert iron ore into steel, and chromium hardens and toughens steel. Furthermore, manganese is a critical ingredient of lithium-manganese-cobalt-oxide (NMC) batteries for electric vehicles.
Although copper production is around one-third that of aluminum, copper has a key role in making modern life possible. The red metal is found in virtually every wire, motor, and electrical appliance in our homes and offices. It’s also critical for various renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles.
Technology and Precious Metals
Technology is only as good as the materials that make it.
Technology metals can be classified as relatively rare metals commonly used in technology and devices. While miners produce some tech and precious metals in large quantities, others are relatively scarce.
| Metal | Quantity Mined in 2019 (tonnes) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Tin | 305,000 | 23% |
| Molybdenum | 275,000 | 21% |
| Rare Earth Elements | 220,000 | 16% |
| Cobalt | 123,000 | 9% |
| Lithium | 97,500 | 7% |
| Tungsten | 91,500 | 7% |
| Vanadium | 81,000 | 6% |
| Niobium | 57,000 | 4% |
| Cadmium | 27,500 | 2% |
| Tantalum | 27,000 | 2% |
| Silver | 26,261 | 2% |
| Gold | 3,350 | 0.3% |
| Indium | 851 | 0.06% |
| Platinum Group Metals | 457 | 0.03% |
| Gallium | 380 | 0.03% |
| Rhenium | 49 | 0.004% |
| Total | 1,335,848 | 100.00% |
Percentages may not add up to 100 due to rounding.
Tin was the most-mined tech metal in 2019, and according to the International Tin Association, nearly half of it went into soldering.
It’s also interesting to see the prevalence of battery and energy metals. Lithium, cobalt, vanadium, and molybdenum are all critical for various energy technologies, including lithium-ion batteries, wind farms, and energy storage technologies. Additionally, miners also extracted 220,000 tonnes of rare earth elements, of which 60% came from China.
Given their rarity, it’s not surprising that gold, silver, and platinum group metals (PGMs) were the least-mined materials in this category. Collectively, these metals represent just 2.3% of the tech and precious metals mined in 2019.
A Material World
Although humans mine and use massive quantities of metals every year, it’s important to put these figures into perspective.
According to Circle Economy, the world consumes 100.6 billion tonnes of materials annually. Of this total, 3.2 billion tonnes of metals produced in 2019 would account for just 3% of our overall material consumption. In fact, the world’s annual production of cement alone is around 4.1 billion tonnes, dwarfing total metal production.
The world’s appetite for materials is growing with its population. As resource-intensive megatrends such as urbanization and electrification pick up the pace, our material pie will only get larger.
Lithium
Ranked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
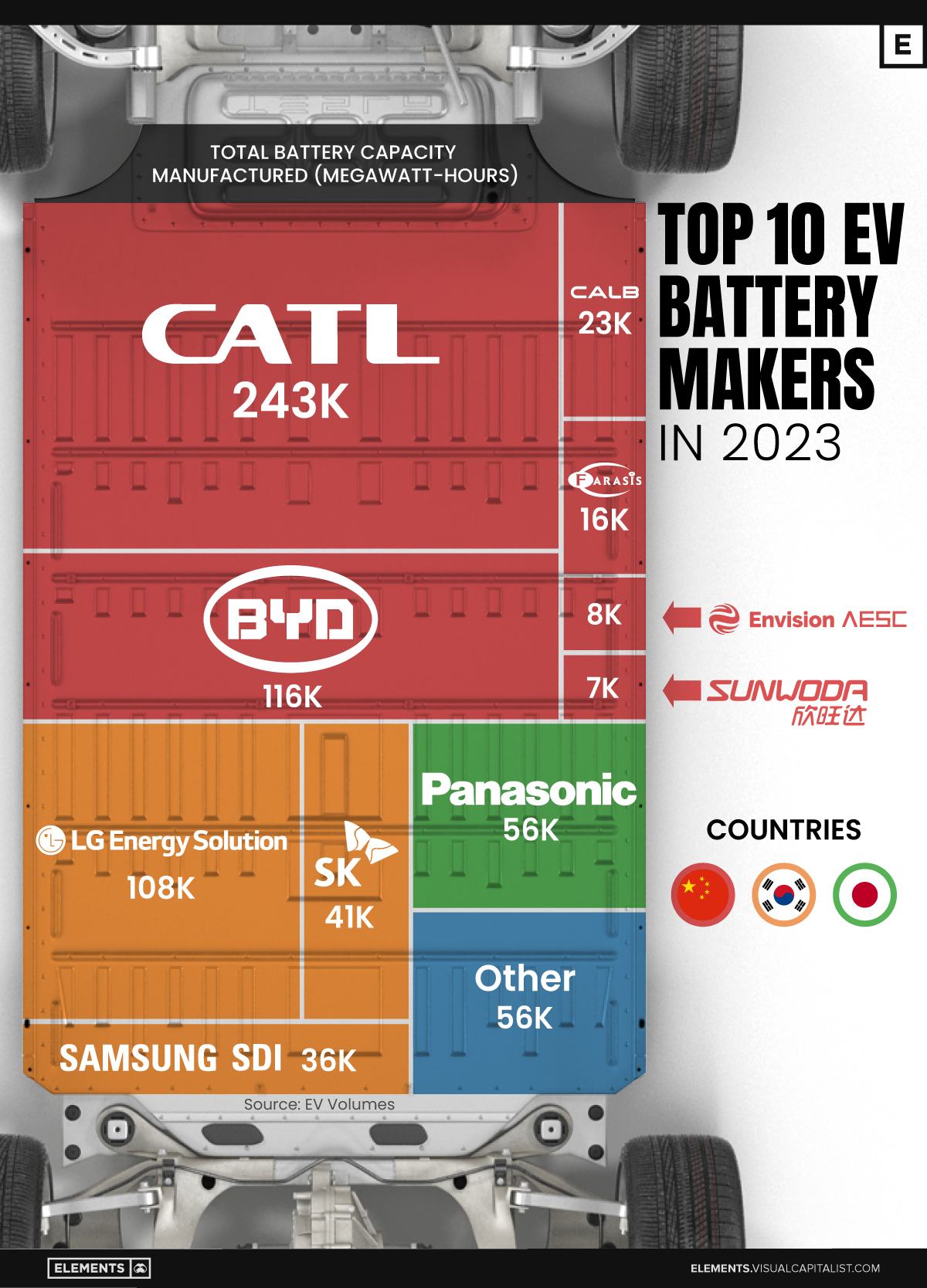
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts from the U.S. and EU to secure local domestic supply, all major EV battery manufacturers remain based in Asia.
In this graphic we rank the top 10 EV battery manufacturers by total battery deployment (measured in megawatt-hours) in 2023. The data is from EV Volumes.
Chinese Dominance
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has swiftly risen in less than a decade to claim the title of the largest global battery group.
The Chinese company now has a 34% share of the market and supplies batteries to a range of made-in-China vehicles, including the Tesla Model Y, SAIC’s MG4/Mulan, and various Li Auto models.
| Company | Country | 2023 Production (megawatt-hour) | Share of Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL | 🇨🇳 China | 242,700 | 34% |
| BYD | 🇨🇳 China | 115,917 | 16% |
| LG Energy Solution | 🇰🇷 Korea | 108,487 | 15% |
| Panasonic | 🇯🇵 Japan | 56,560 | 8% |
| SK On | 🇰🇷 Korea | 40,711 | 6% |
| Samsung SDI | 🇰🇷 Korea | 35,703 | 5% |
| CALB | 🇨🇳 China | 23,493 | 3% |
| Farasis Energy | 🇨🇳 China | 16,527 | 2% |
| Envision AESC | 🇨🇳 China | 8,342 | 1% |
| Sunwoda | 🇨🇳 China | 6,979 | 1% |
| Other | - | 56,040 | 8% |
In 2023, BYD surpassed LG Energy Solution to claim second place. This was driven by demand from its own models and growth in third-party deals, including providing batteries for the made-in-Germany Tesla Model Y, Toyota bZ3, Changan UNI-V, Venucia V-Online, as well as several Haval and FAW models.
The top three battery makers (CATL, BYD, LG) collectively account for two-thirds (66%) of total battery deployment.
Once a leader in the EV battery business, Panasonic now holds the fourth position with an 8% market share, down from 9% last year. With its main client, Tesla, now sourcing batteries from multiple suppliers, the Japanese battery maker seems to be losing its competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, the global EV battery market size is projected to grow from $49 billion in 2022 to $98 billion by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights.
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023