Markets
The Making of a Mammoth Merger: Charles Schwab and TD Ameritrade
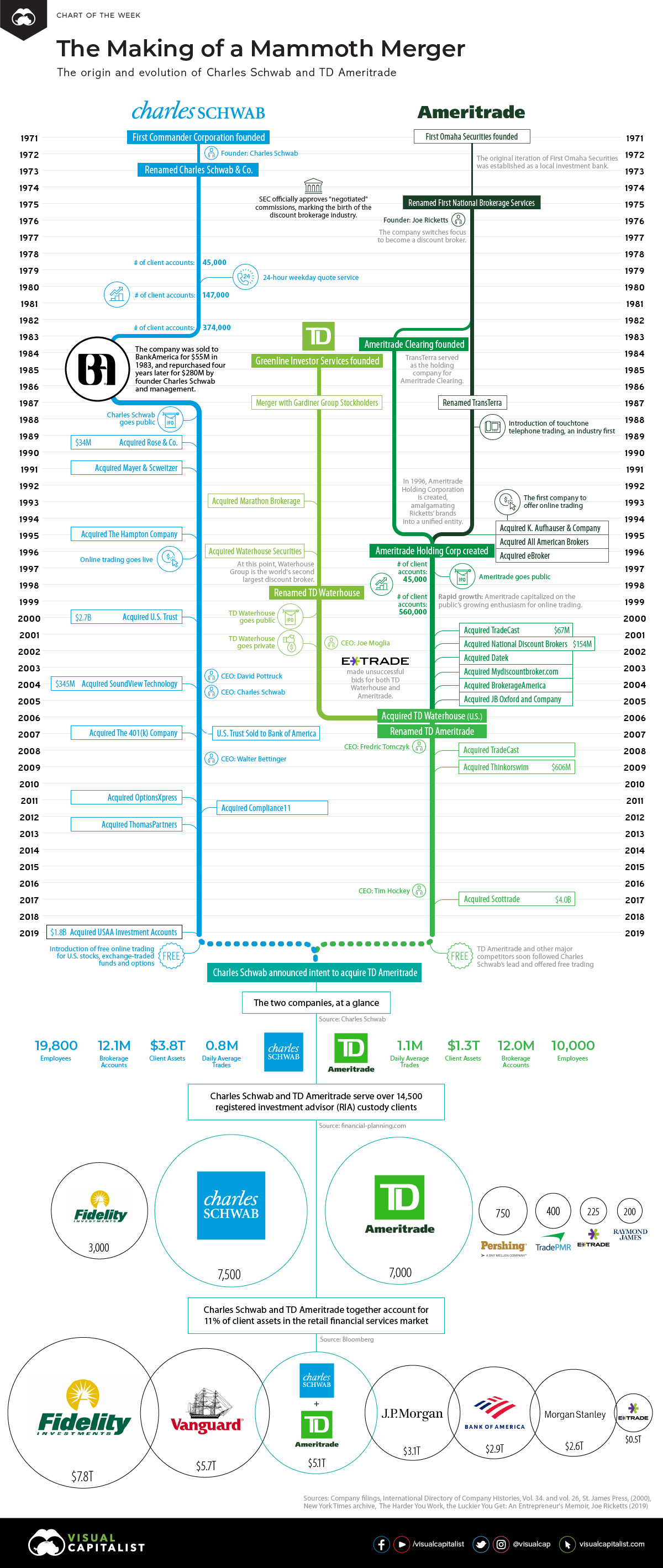
Charles Schwab and TD Ameritrade: A Mammoth Merger
In this era of fierce competition in the discount brokerage space, scale might be the best recipe for success.
Charles Schwab has once again sent shockwaves through the financial services industry, announcing its intent to acquire TD Ameritrade. The all-stock deal — valued at approximately $26 billion — will see the two biggest publicly-traded discount brokers combine into a giant entity with over $5 trillion in client assets.
Today we dive into the history of these two companies, and what effect recent events may have on the financial services industry.
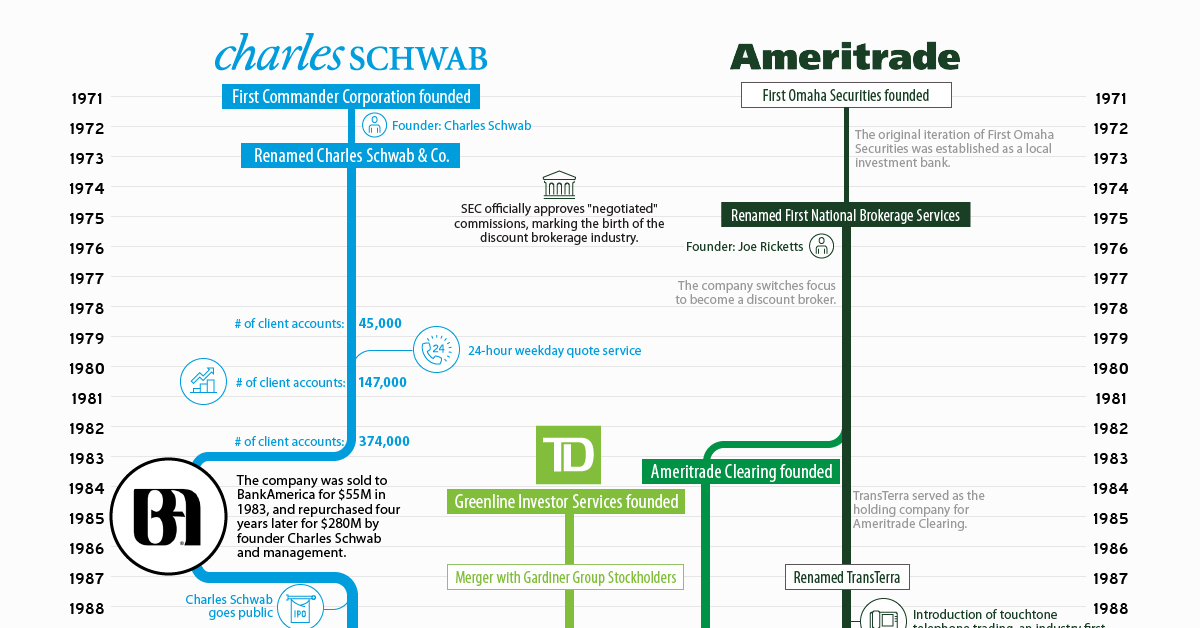
The Evolution of Charles Schwab
1975 – U.S. Congress deregulated the stock brokerage industry by stripping the NYSE of the power to determine the commission rates charged by its members. Discount brokers, which focused primarily on buying and selling securities, seized the opportunity to court more seasoned investors who might not require the advice or research offered by established brokers. It was during this transitional period that Charles Schwab opened a small brokerage in San Francisco and bought a seat on the New York Stock Exchange.
1980s – The company experienced rapid growth thanks to a healthy marketing budget and innovations, such as the industry’s first 24-hour quotation service.
This fast success proved to be a double-edged sword. Charles Schwab became the largest discount broker in the U.S. by 1980, but profits were erratic, and the company was forced to rescind an initial public offering. Eventually, the company sold to BankAmerica Corporation for $55 million in stock. A mere four years later, Charles Schwab would purchase his namesake company back for $280 million.
1987 – By the time the company went public, Charles Schwab had five times as many customers as its nearest competitor, and profit margin twice as high as the industry average.
1990s – In the late ’90s, Charles Schwab moved into the top five among all U.S. brokerages, after a decade of steady growth.
2000s – The company made a number of acquisitions, including U.S. Trust, which was one of the nation’s leading wealth management firms, and most recently, the USAA’s brokerage and wealth management business.
The Race to $0
For Charles Schwab, the elimination of fees is the culmination of its founder’s vision of making investing “accessible to all”.

The company’s fees were slowly declining for decades. In late 2019, it finally took the plunge and introduced free online trading for U.S. stocks, exchange-traded funds, and options. The response was immediate and enthusiastic, with clients opening 142,000 new trading accounts in the first month alone.
Although Charles Schwab sent rivals scrambling to match its no-commission trade offer, fintech upstarts like Robinhood have offered free trading for years now. The “race to zero” reflects a broader generational shift, as millennials are simply more likely than earlier generations to expect services to be free.
The Evolution of TD Ameritrade
1975 – The origin of TD Ameritrade can be traced back to First Omaha Securities, a discount broker founded by Joe Ricketts. The company changed its name to TransTerra in 1987.
1988 – TransTerra’s subsidiary, Accutrade, was the first company to introduce touch-tone telephone trading, a major innovation at the time and one of the first early forays into automation.
Early 1990s – Ricketts’s willingness to integrate emerging technologies into the trading business helped his companies achieve impressive growth. In 1997 the company acquired K. Aufhauser & Co., the first company to run a trading website.
The Internet wasn’t a puzzle. We were crystal clear from the beginning that customers would migrate to this.
– Joe Ricketts (2000)
Late 1990s – The Ameritrade brand was solidified after the company changed its name from TransTerra to Ameritrade Holding Corporation in 1996. The newly named company completed an IPO the following year, and established its new brand Ameritrade, Inc., which amalgamated K. Aufhauser, eBroker, and other businesses into a unified entity.
2000s – Ameritrade entered the new millennium as the fifth largest online investment broker in the United States, fueled in part by marketing deals with AOL and MSN.
The modern incarnation of TD Ameritrade took shape in 2006, when TD Bank sold its TD Waterhouse USA brokerage unit to the Ameritrade Holding Corporation in a stock-and-cash deal valued at about $3.3 billion. At the time of the deal the new company ranked first in the U.S. by the number of daily trades.
2016 – TD Ameritrade acquired the discount brokerage Scottrade for about $4 billion. The deal brought 3 million client accounts and $170 billion in assets under management into the company, and quadrupled the size of its branch network.
What Comes Next?
Naturally, the announcement that these massive discount brokers plan to merge has generated a lot of speculation as to what this means for the two companies, and the broader brokerage industry as a whole.
Here are some of the consensus key predictions we’ve seen on the deal, from both media and industry publications:
- After the deal is approved, the integration process will take 12 to 18 months. The combined company’s headquarters will relocate to a new office park in Westlake, Texas.
- Charles Schwab’s average revenue per trade has dropped nearly 30% since Q1 2017, so the company will likely use scale to its advantage and monetize other products.
- The merged company will continue to adopt features from fintech upstarts, such as the option to trade in fractional shares.
- E*Trade, which was widely considered to be an acquisition target of Schwab or TD Ameritrade, may now face pressure to hunt for a deal elsewhere.
Even though these longtime rivals are now linking up, stiff competition in the financial services market is bound to keep everyone on their toes.
I think Joe Ricketts and I agree that our fierce competitiveness nearly 30 years ago is proof that market competition can be a source of miraculous innovation.
– Charles Schwab
Markets
The European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
On average, the European stock market has valuations that are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations. But how can you access the market?
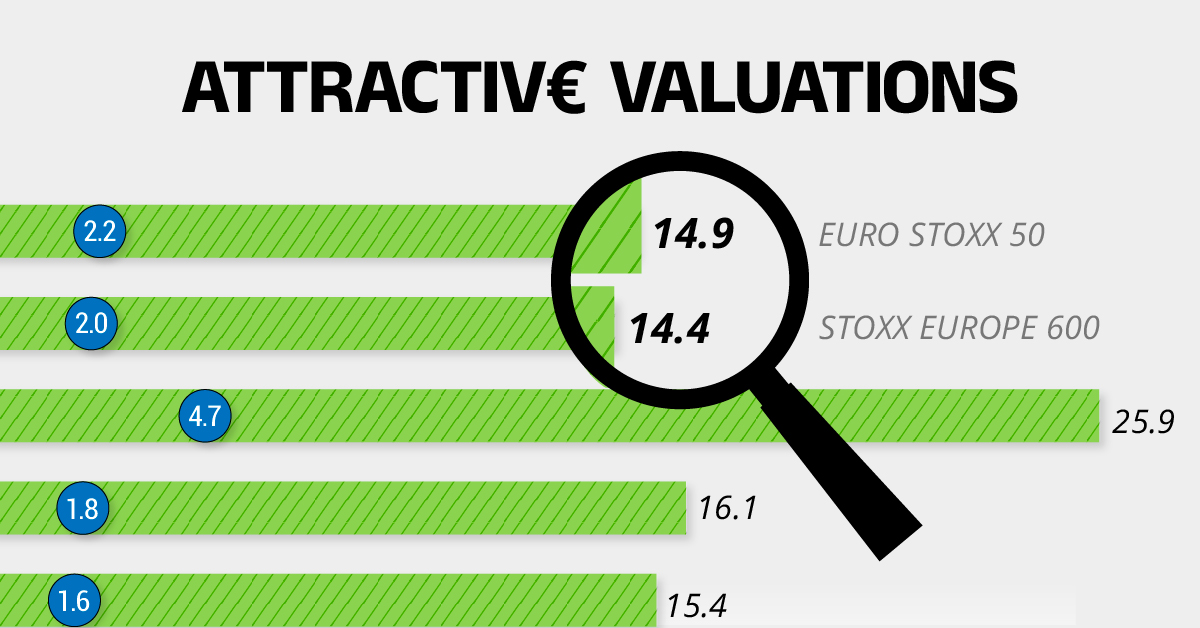
European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
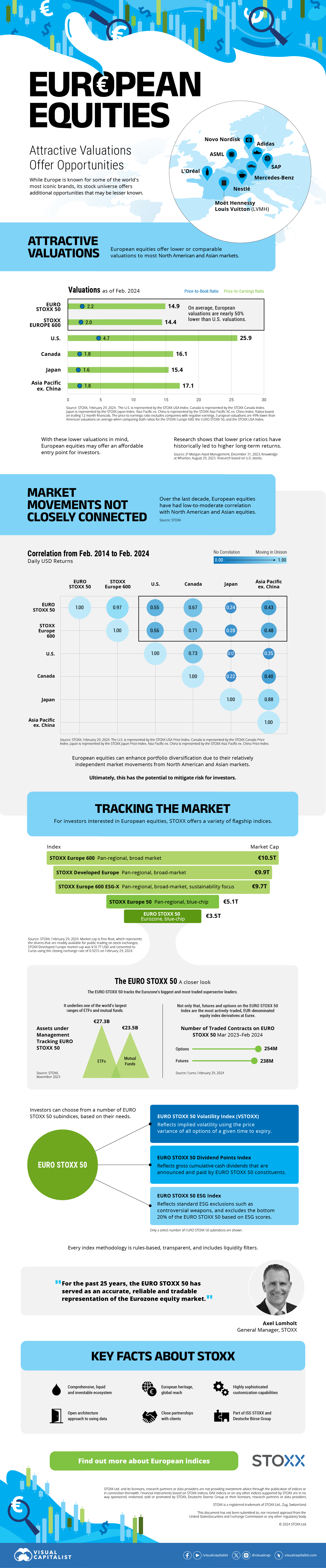
Europe is known for some established brands, from L’Oréal to Louis Vuitton. However, the European stock market offers additional opportunities that may be lesser known.
The above infographic, sponsored by STOXX, outlines why investors may want to consider European stocks.
Attractive Valuations
Compared to most North American and Asian markets, European stocks offer lower or comparable valuations.
| Index | Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Price-to-Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 14.9 | 2.2 |
| STOXX Europe 600 | 14.4 | 2 |
| U.S. | 25.9 | 4.7 |
| Canada | 16.1 | 1.8 |
| Japan | 15.4 | 1.6 |
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 17.1 | 1.8 |
Data as of February 29, 2024. See graphic for full index names. Ratios based on trailing 12 month financials. The price to earnings ratio excludes companies with negative earnings.
On average, European valuations are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations, potentially offering an affordable entry point for investors.
Research also shows that lower price ratios have historically led to higher long-term returns.
Market Movements Not Closely Connected
Over the last decade, the European stock market had low-to-moderate correlation with North American and Asian equities.
The below chart shows correlations from February 2014 to February 2024. A value closer to zero indicates low correlation, while a value of one would indicate that two regions are moving in perfect unison.
| EURO STOXX 50 | STOXX EUROPE 600 | U.S. | Canada | Japan | Asia Pacific ex. China |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| STOXX EUROPE 600 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.48 | |
| U.S. | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| Canada | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.40 | |||
| Japan | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 1.00 |
Data is based on daily USD returns.
European equities had relatively independent market movements from North American and Asian markets. One contributing factor could be the differing sector weights in each market. For instance, technology makes up a quarter of the U.S. market, but health care and industrials dominate the broader European market.
Ultimately, European equities can enhance portfolio diversification and have the potential to mitigate risk for investors.
Tracking the Market
For investors interested in European equities, STOXX offers a variety of flagship indices:
| Index | Description | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| STOXX Europe 600 | Pan-regional, broad market | €10.5T |
| STOXX Developed Europe | Pan-regional, broad-market | €9.9T |
| STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X | Pan-regional, broad market, sustainability focus | €9.7T |
| STOXX Europe 50 | Pan-regional, blue-chip | €5.1T |
| EURO STOXX 50 | Eurozone, blue-chip | €3.5T |
Data is as of February 29, 2024. Market cap is free float, which represents the shares that are readily available for public trading on stock exchanges.
The EURO STOXX 50 tracks the Eurozone’s biggest and most traded companies. It also underlies one of the world’s largest ranges of ETFs and mutual funds. As of November 2023, there were €27.3 billion in ETFs and €23.5B in mutual fund assets under management tracking the index.
“For the past 25 years, the EURO STOXX 50 has served as an accurate, reliable and tradable representation of the Eurozone equity market.”
— Axel Lomholt, General Manager at STOXX
Partnering with STOXX to Track the European Stock Market
Are you interested in European equities? STOXX can be a valuable partner:
- Comprehensive, liquid and investable ecosystem
- European heritage, global reach
- Highly sophisticated customization capabilities
- Open architecture approach to using data
- Close partnerships with clients
- Part of ISS STOXX and Deutsche Börse Group
With a full suite of indices, STOXX can help you benchmark against the European stock market.

Learn how STOXX’s European indices offer liquid and effective market access.

-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001