Technology
The Future of Nanotechnology in Medicine
The Future of Nanotechnology in Medicine
Around the world, researchers are increasingly thinking smaller to solve some of the biggest problems in medicine.
Though most biological processes happen at the nano level, it wasn’t until recently that new technological advancements helped in opening up the possibility of nanomedicine to healthcare researchers and professionals.
Today’s infographic, which comes to us from Best Health Degrees, highlights some of the most promising research in nanomedicine.
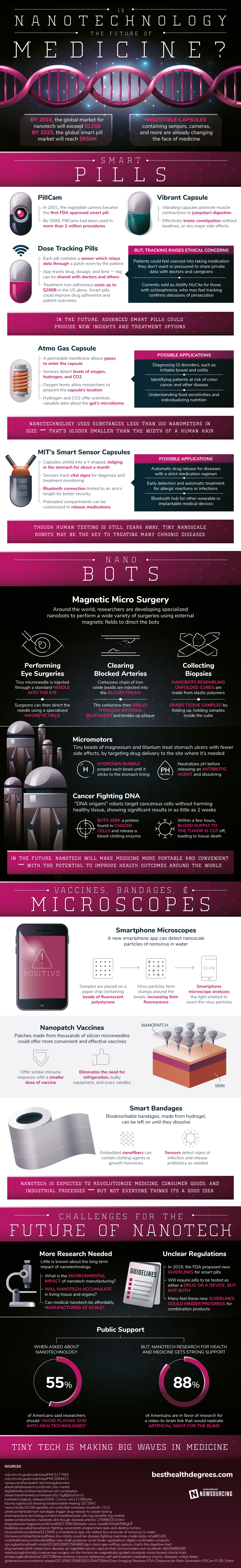
What is Nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology is the engineering of functional systems at the molecular level. The field combines elements of physics and molecular chemistry with engineering to take advantage of unique properties that occur at nanoscale.
One practical example of this technology is the use of tiny carbon nanotubes to transport drugs to specific cells. Not only do these nanotubes have low toxicity and a stable structure, they’re an ideal container for transporting drugs directly to the desired cells.
Small Systems, Big Applications
While many people will be most familiar with nanotech as the technology powering Iron Man’s suit, real world breakthroughs at the nanoscale will soon be saving lives in healthcare.
Here are a few ways nanotechnology is shaping the future of medical treatment:
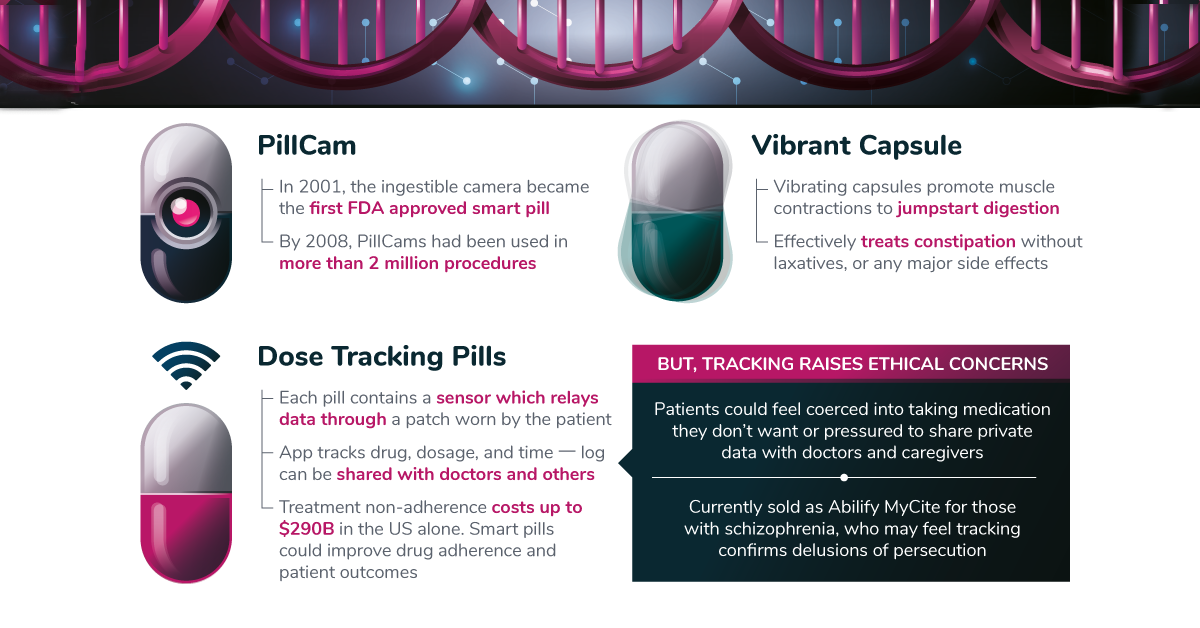
1. Smart Pills
While smart pill technology is not a new idea — a “pill cam” was cleared by the FDA in 2001 — researchers are coming up with innovative new applications for the concept.
For example, MIT researchers designed an ingestible sensor pill that can be wirelessly controlled. The pill would be a “closed-loop monitoring and treatment” solution, adjusting the dosage of a particular drug based on data gathered within the body (e.g. gastrointestinal system).
An example of this technology in action is the recent FDA-approved smart pill that records when medication was taken. The product, which is approved for people living with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, allows patients to track their own medication history through a smartphone, or to authorize physicians and caregivers to access that information online.
2. Beating the Big C
Nearly 40% of humans will be diagnosed with cancer at some point in their lifetime, so any breakthrough in cancer treatment will have a widespread impact on society.
On the key issues with conventional chemotherapy and radiation treatments is that the body’s healthy cells can become collateral damage during the process. For this reason, researchers around the world are working on using nano particles to specifically target cancer cells.
Oncology-related drugs have the highest forecasted worldwide prescription drug sales, and targeting will be a key element in the effectiveness of these powerful new drugs.
3. Diagnostics
Medical implants — such as knee and hip replacements — have improved the lives of millions, but a common problem with these implants is the risk of post-surgery inflammation and infection. In many cases, symptoms from an infection are detected so late that treatment is less effective, or the implant will need to be replaced all together.
Nanoscale sensors embedded directly into the implant or surrounding area could detect infection much sooner. As targeted drug delivery becomes more feasible, it could be possible to administer treatment to an infected area at the first sign of infection.
Examples like this show the true promise of nanotechnology in the field of medicine. Before long, gathering data from within the body and administering treatments in real-time could move from science fiction to the real world.
10,000 years ago, man domesticated plants and animals, now it’s time to domesticate molecules.
– Professor Susan Lindquist
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023