Markets
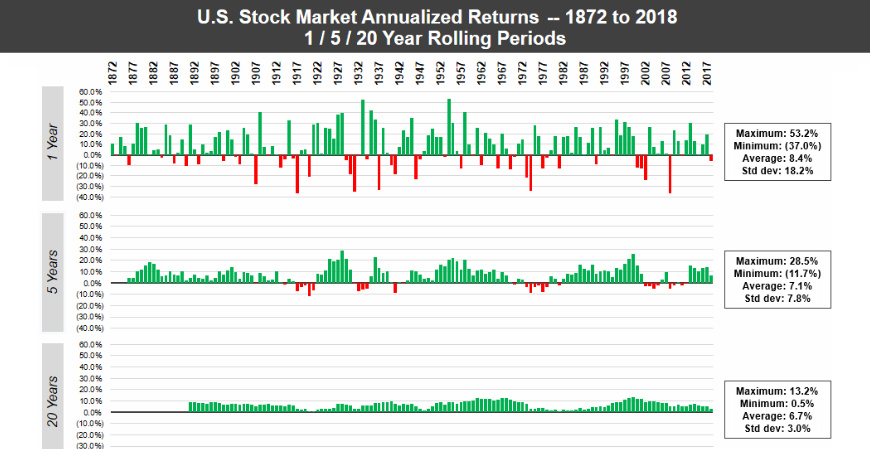
Stock Market Returns Over Different Time Periods (1872-2018)
Putting hard-earned money in the stock market can make some people nervous.
It’s well known that a correction can occur at any time, and the fear of market crashes can make even the most seasoned investors to make questionable decisions.
While it’s true that putting your money on the line is never easy, the historical record of the stock market is virtually irrefutable: U.S. markets have consistently performed over long holding periods, even going back to the 19th century.
Market Performance (1872-2018)
Today’s animation comes to us from The Measure of a Plan, and it shows the performance of the U.S. market over different rolling time horizons using annualized returns.
Note: The animation uses real total returns from the S&P Composite Index from 1872 to 1957, and then the S&P 500 Index from 1957 onwards. Data has been adjusted for reinvestment of dividends as well as inflation.
Using just one-year intervals of time, the market can be a crapshoot. Unfortunately, if you were to just choose a one-year period at random, there would be a significant chance of losing money.
However, as the timeframes get longer – the animation goes to 5-year, 10-year, and then 20-year rolling periods – the frequency of losses rapidly decreases. By the time you get to the 20-year windows, there isn’t a single instance in which the market had a negative return.
Why Time Matters
Over 146 years of data, the chance of seeing negative returns for any given year is about 31%.
That fact in itself is quite alarming, but even more important to note is the distribution of returns in those down years. As you can see in the following chart also from The Measure of a Plan, it’s not uncommon for a down year to skew in the high negatives, just as it did during the crisis of 2008:
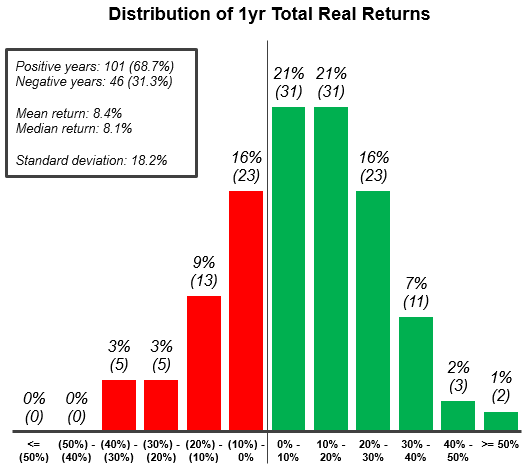
According to the data, there have been 10 individual years where the market has lost upwards of 20% – and while those off years are greatly outnumbered by the years with positive returns, it makes it clear that timeframe matters.
Past performance obviously doesn’t guarantee future results, but the historical track record in this case is quite robust.
Long-term investors can see that as long as their time horizon is measured in the decades, you can take the odds of making money in the stock market to the bank.
Markets
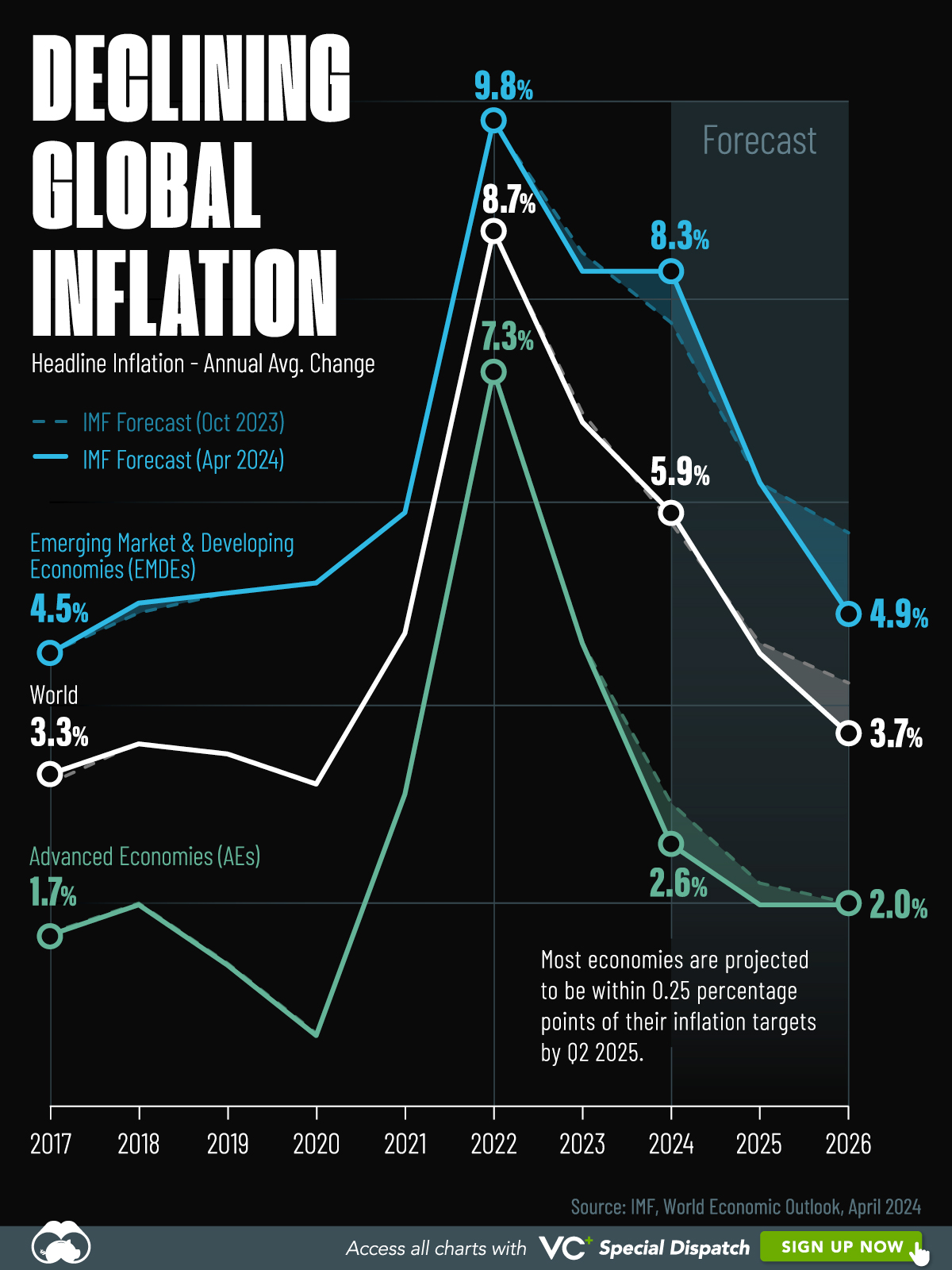
Visualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
Here are IMF forecasts for global inflation rates up to 2026, highlighting a slow descent of price pressures amid resilient global growth.
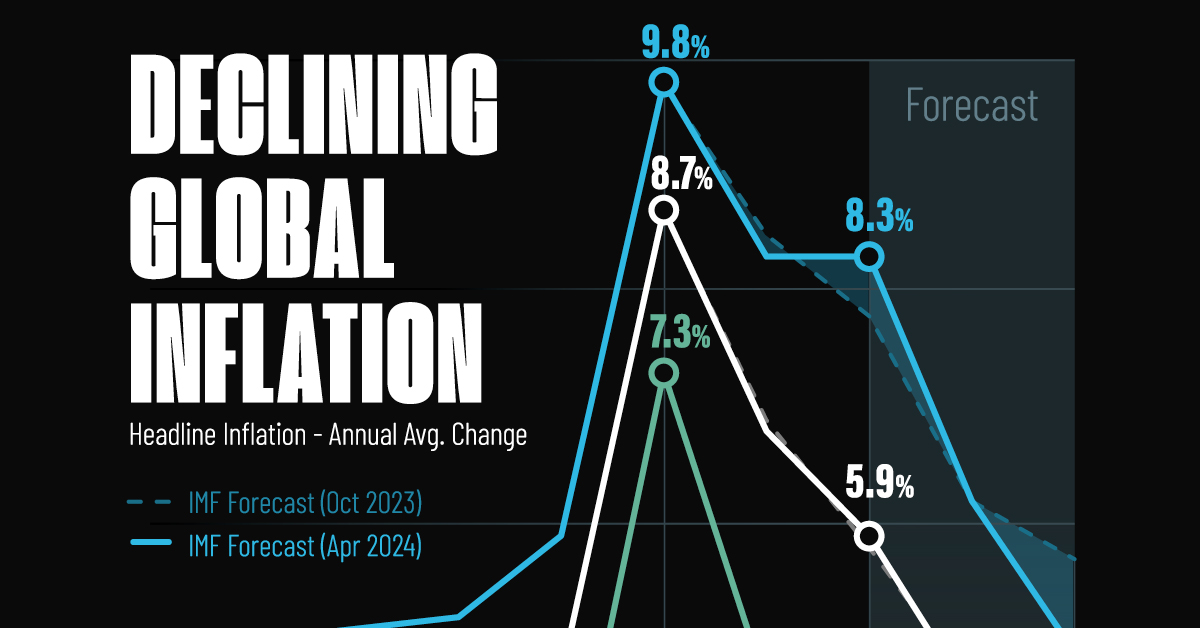
Visualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
Global inflation rates are gradually descending, but progress has been slow.
Today, the big question is if inflation will decline far enough to trigger easing monetary policy. So far, the Federal Reserve has held rates for nine months amid stronger than expected core inflation, which excludes volatile energy and food prices.
Yet looking further ahead, inflation forecasts from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) suggest that inflation will decline as price pressures ease, but the path of disinflation is not without its unknown risks.
This graphic shows global inflation forecasts, based on data from the April 2024 IMF World Economic Outlook.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
The IMF’s Inflation Outlook
Below, we show the IMF’s latest projections for global inflation rates through to 2026:
| Year | Global Inflation Rate (%) | Advanced Economies Inflation Rate (%) | Emerging Market and Developing Economies Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 5.1 |
| 2020 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 5.2 |
| 2021 | 4.7 | 3.1 | 5.9 |
| 2022 | 8.7 | 7.3 | 9.8 |
| 2023 | 6.8 | 4.6 | 8.3 |
| 2024 | 5.9 | 2.6 | 8.3 |
| 2025 | 4.5 | 2.0 | 6.2 |
| 2026 | 3.7 | 2.0 | 4.9 |
After hitting a peak of 8.7% in 2022, global inflation is projected to fall to 5.9% in 2024, reflecting promising inflation trends amid resilient global growth.
While inflation has largely declined due to falling energy and goods prices, persistently high services inflation poses challenges to mitigating price pressures. In addition, the IMF highlights the potential risk of an escalating conflict in the Middle East, which could lead to energy price shocks and higher shipping costs.
These developments could negatively affect inflation scenarios and prompt central banks to adopt tighter monetary policies. Overall, by 2026, global inflation is anticipated to decline to 3.7%—still notably above the 2% target set by several major economies.
Adding to this, we can see divergences in the path of inflation between advanced and emerging economies. While affluent nations are forecast to see inflation edge closer to the 2% target by 2026, emerging economies are projected to have inflation rates reach 4.9%—falling closer to their pre-pandemic averages.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands2 weeks ago
Brands2 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?