Evaluating a Company’s Net-Zero Carbon Target
The following content is sponsored by MSCI.

Evaluating a Company’s Net-Zero Carbon Target
A net-zero carbon target is a climate essential.
Companies from Apple to Microsoft are making commitments to halve their emissions by roughly 2030—and eliminate them altogether by 2050. These targets follow the recommendations set forward by the Paris Agreement in order to avoid devastating climate conditions for future generations.
However, not all targets are rigorous, let alone feasible. To shine a light on this problem, MSCI developed a Net-Zero tracker that helps investors analyze the strength of company targets.
What is Net-Zero?
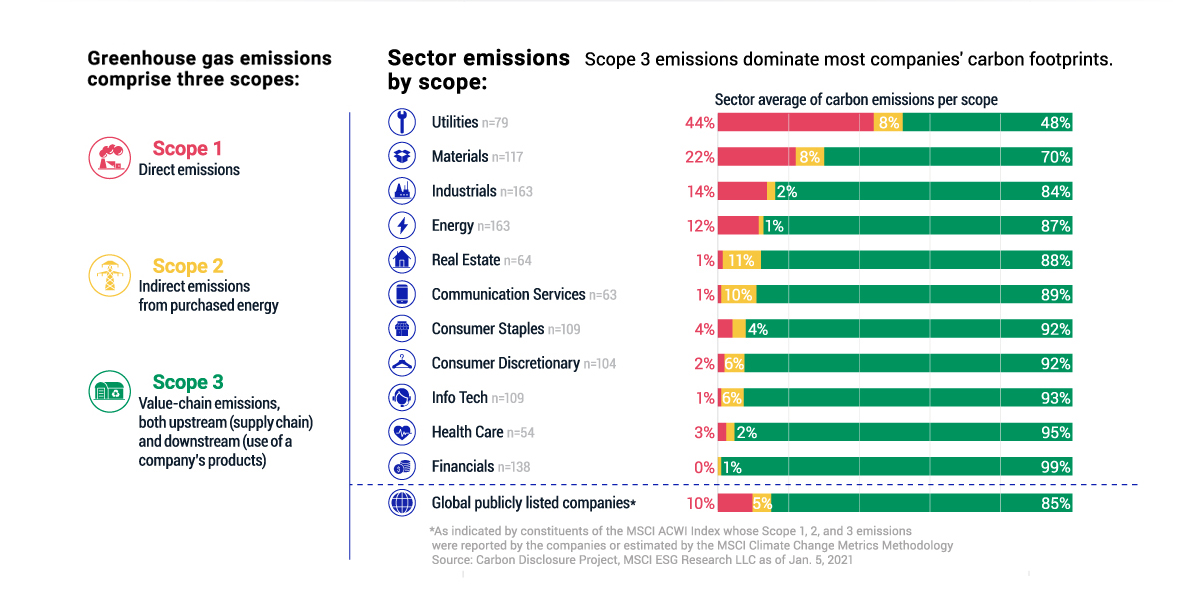
Net-zero refers to driving down greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) to zero by mid-century.
To achieve this, processes such as carbon removal, carbon reduction, renewable alternatives, and energy efficiency will aid in the transition to carbon neutrality. To date, at least 50 countries and 21% of the largest corporations worldwide have set net-zero targets.
Net-Zero Carbon Analysis
MSCI developed a framework centered on two primary criteria:
| Comprehensiveness | Ambition | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Does the target focus on the majority of a company’s emissions? | How much and how quickly does a target aim to reduce emissions? |
| Key Components | % of company footprint covered by targets Unit Target scopes | Projected target emissions against net-zero trajectory in 2030 & 2050 Intention to use carbon offsets Target year |
Thanks to its standardized framework, the analysis helps investors evaluate all companies’ net-zero targets on the same components.
The Net-Zero Dataset
Where is data drawn from, and what determines the net-zero score?
Using MSCI’s Climate Target and Commitments dataset, the drivers of carbon emissions fall into scope 1,2, and 3 emissions. Here is a hypothetical example of how these emission are analyzed:
| Drivers of Emissions | Description | Reported/ Estimated | Emissions (Mega tCO₂e) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 | Direct emissions | Reported | 0.04 |
| Scope 2 | Indirect emissions from purchased energy | Estimated | 0.18 |
| Scope 3 | Value-chain emissions* | Estimated Reported | 12.47 11.17 |
* Both upstream (supply chain) and downstream (use of a company’s products)
For investors looking to sincerely address climate change and reduce their portfolio emissions, the Net-Zero Tracker lets investors compare commitments with other companies, informs their climate risk profile, and report portfolio emissions according to frameworks such as the Task Force on Climate-Related Disclosures.
The Net-Zero Scorecard
The Climate Target and Commitments dataset tackles two key issues:
- Identifies disparities in a company’s net-zero carbon target
- Identifies the main sources of carbon emissions for a company
Sometimes, companies will set lofty net-zero pledges without having systems of short-term accountability. In other cases companies will set targets that exclude segments of their business.
Let’s consider the following hypothetical leading company, whose net-zero carbon target covers 100% of their business and has 3.8% projected emission reductions annually.
| Net-Zero Scorecard | Key Components | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensiveness | % of company footprint covered by target Unit Target scopes | 100% tCO₂ 1,2,3 |
| Ambition | Projected reduction per year to meet stated target Intention to use carbon offsets Target year | 3.77% p.a. No 2030 |
With a target year of 2030, the company’s net-zero commitment covers all scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. For these reasons, the company’s net-zero target is credible and has short-term accountability.
Green Credentials
As the year 2030 closes in, there is hope that business as usual will become even less viable.
Companies who refuse to acknowledge the climate crisis will likely face greater pressure from shareholders. Financial markets may reward those with achievable climate strategies. The net-zero carbon target tracker allows investors to think critically as they play a part in this transition.
-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology...
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.