Markets
From Coast to Coast: How U.S. Muni Bonds Help Build the Nation

Over 200 Years of U.S. Municipal Bond History
Our modern society shares few characteristics with the 1800s. In the last two centuries, styles have changed, laws have evolved, and cities look entirely different. However, one thing that has prevailed is the way state and local governments finance public projects.
Far from a new invention, municipal bonds have been shaping U.S. communities for more than 200 years. In today’s infographic from New York Life Investments, we take a look back at their long history.
Early Beginnings – 1800s
1812: First Official Issue
New York City issues a general obligation bond for a canal.
1817-1825: Facilitating Economic Growth
A few years later, 42 separate bond issues help fund the successful Erie Canal project.
1843: Growing Popularity
Municipal debt sits at about $25 million. Over the next two decades, this total increases exponentially to fund urban improvement and free public education.
Circa 1865: Railroad Expansion
For a few years after the American Civil War, a great deal of debt is issued to build railroads.
1873: The Panic of 1873
Excessive investment in railroads, real estate, and nonessential services leads to the downfall of the large bank Jay Cooke and Co., smaller firms, and the stock market. Many state and local governments default, temporarily halting municipal financing.
The 20th Century
1913: Exception Granted
U.S. Congress introduces a permanent federal income tax, and specifically excludes municipal bond income from taxation.
Note: today, a portion of municipal bonds are taxable.
1930: Expansion in the West
In the midst of the Great Depression, voters approve $35 million in funding to build the Golden Gate Bridge.
1939-1945: Diverted Resources
With financial resources directed to the military in WWII, municipal debt falls. By 1945, total debt sits at less than $20 billion.
1960: Exponential Growth
Only 25 years later, outstanding public debt—the total amount owed to creditors—more than triples to $66 billion.
1971: Investor Protection
Municipal bond insurance is introduced. That same year, insured municipal bonds finance the construction of hospital facilities in Alaska—bringing essential services and investment opportunities to a remote area.
1975: Marketplace Stewardship
Bringing further reassurance to the municipal bond market, the Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board (MSRB) is introduced to establish regulations for dealers, and for advisors at a later date.
1981: Continued Growth
Outstanding public debt reaches $361 billion.
Modern Day
2009-2010: Economic Recovery
More than $181 billion of federally-subsidized Build America Bonds are issued by state and local governments to help stimulate the economy after the financial crisis.
2016-2018: Investor Dollars at Work
In recent years, state and local debt has financed many important projects across the country.
- 2016: The New York State Thruway Authority issues $850 million in bonds to finance a portion of the new NY Bridge Project.
- 2017: California’s Department of Water Resources issues $428 million in bonds for the maintenance and construction of its water management infrastructure.
- 2018: The Denver International Airport issues $2.5B in bonds to finance capital improvements, the largest airport revenue bond in municipal bond history.
2018: Helping People and the Planet
Sustainable applications for municipal bonds continue to grow, with Californian voters approving $2 billion in financing for supportive housing. In addition, state and local governments issue $4.9 billion in U.S. municipal green bonds.
Today: A Sizable Investment Opportunity
As financing spans the nation, the U.S. municipal bond market is both large and active:
- $3.8 trillion capital market
- One million outstanding securities
- $11.6 billion in par traded per/day
- 40,000 daily trades
Not only that, municipals have offered a compelling after-tax yield. For example, high yield municipals offered 121% of the after-tax yield of high yield corporates as of September 30, 2019.
The Foundation of Infrastructure
For over 200 years, municipal bonds have provided critical financing to build hospitals, schools, highways, airports, and more. Today, two out of three infrastructure projects in the U.S. are financed by municipal bonds.
Additionally, municipals have weathered almost every economic storm, providing much-needed capital stimulus during some of the deepest U.S. recessions. As history continues to unfold, municipals hold great potential for issuers, communities, and investors.
Markets
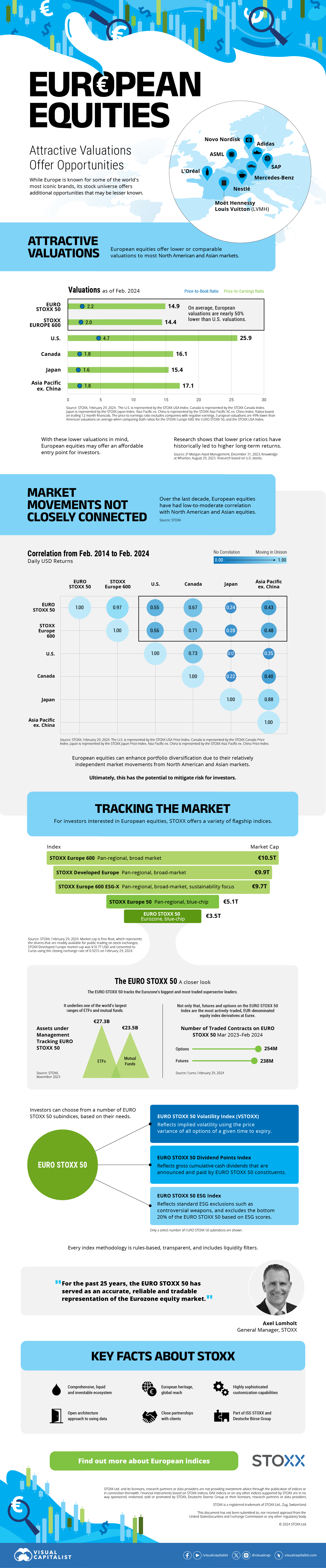
The European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
On average, the European stock market has valuations that are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations. But how can you access the market?
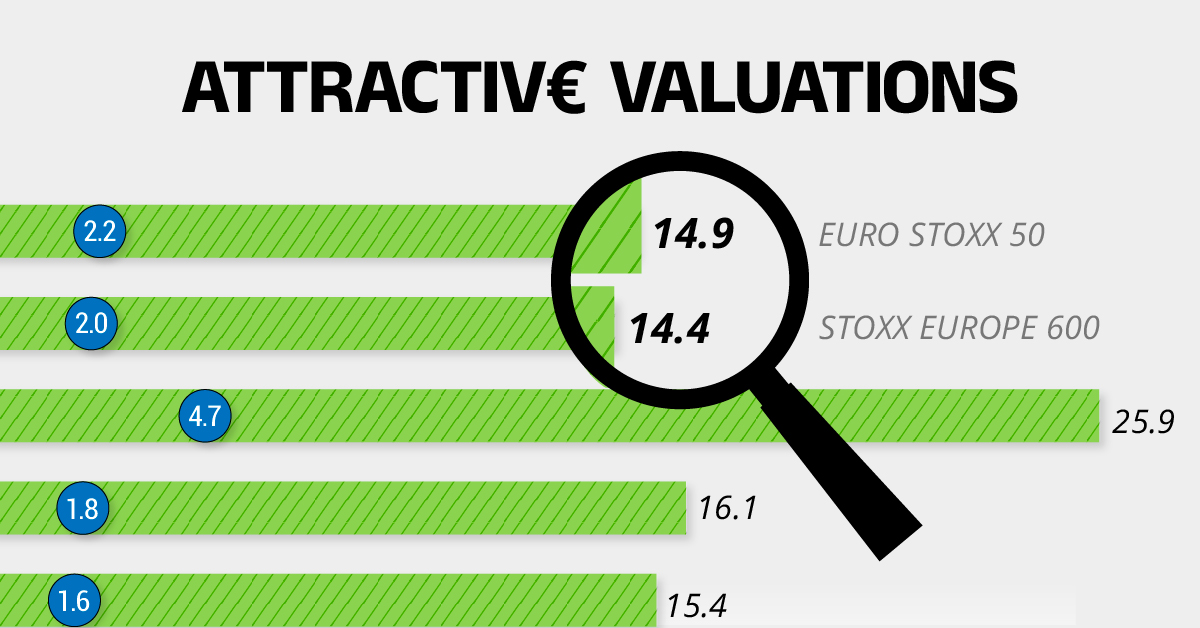
European Stock Market: Attractive Valuations Offer Opportunities
Europe is known for some established brands, from L’Oréal to Louis Vuitton. However, the European stock market offers additional opportunities that may be lesser known.
The above infographic, sponsored by STOXX, outlines why investors may want to consider European stocks.
Attractive Valuations
Compared to most North American and Asian markets, European stocks offer lower or comparable valuations.
| Index | Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Price-to-Book Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 14.9 | 2.2 |
| STOXX Europe 600 | 14.4 | 2 |
| U.S. | 25.9 | 4.7 |
| Canada | 16.1 | 1.8 |
| Japan | 15.4 | 1.6 |
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 17.1 | 1.8 |
Data as of February 29, 2024. See graphic for full index names. Ratios based on trailing 12 month financials. The price to earnings ratio excludes companies with negative earnings.
On average, European valuations are nearly 50% lower than U.S. valuations, potentially offering an affordable entry point for investors.
Research also shows that lower price ratios have historically led to higher long-term returns.
Market Movements Not Closely Connected
Over the last decade, the European stock market had low-to-moderate correlation with North American and Asian equities.
The below chart shows correlations from February 2014 to February 2024. A value closer to zero indicates low correlation, while a value of one would indicate that two regions are moving in perfect unison.
| EURO STOXX 50 | STOXX EUROPE 600 | U.S. | Canada | Japan | Asia Pacific ex. China |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURO STOXX 50 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| STOXX EUROPE 600 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.48 | |
| U.S. | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.25 | ||
| Canada | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.40 | |||
| Japan | 1.00 | 0.88 | ||||
| Asia Pacific ex. China | 1.00 |
Data is based on daily USD returns.
European equities had relatively independent market movements from North American and Asian markets. One contributing factor could be the differing sector weights in each market. For instance, technology makes up a quarter of the U.S. market, but health care and industrials dominate the broader European market.
Ultimately, European equities can enhance portfolio diversification and have the potential to mitigate risk for investors.
Tracking the Market
For investors interested in European equities, STOXX offers a variety of flagship indices:
| Index | Description | Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| STOXX Europe 600 | Pan-regional, broad market | €10.5T |
| STOXX Developed Europe | Pan-regional, broad-market | €9.9T |
| STOXX Europe 600 ESG-X | Pan-regional, broad market, sustainability focus | €9.7T |
| STOXX Europe 50 | Pan-regional, blue-chip | €5.1T |
| EURO STOXX 50 | Eurozone, blue-chip | €3.5T |
Data is as of February 29, 2024. Market cap is free float, which represents the shares that are readily available for public trading on stock exchanges.
The EURO STOXX 50 tracks the Eurozone’s biggest and most traded companies. It also underlies one of the world’s largest ranges of ETFs and mutual funds. As of November 2023, there were €27.3 billion in ETFs and €23.5B in mutual fund assets under management tracking the index.
“For the past 25 years, the EURO STOXX 50 has served as an accurate, reliable and tradable representation of the Eurozone equity market.”
— Axel Lomholt, General Manager at STOXX
Partnering with STOXX to Track the European Stock Market
Are you interested in European equities? STOXX can be a valuable partner:
- Comprehensive, liquid and investable ecosystem
- European heritage, global reach
- Highly sophisticated customization capabilities
- Open architecture approach to using data
- Close partnerships with clients
- Part of ISS STOXX and Deutsche Börse Group
With a full suite of indices, STOXX can help you benchmark against the European stock market.

Learn how STOXX’s European indices offer liquid and effective market access.

-

 Economy2 days ago
Economy2 days agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
This graphic shows the states with the highest real GDP growth rate in 2023, largely propelled by the oil and gas boom.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
In this graphic, we show the highest earning flight routes globally as air travel continued to rebound in 2023.
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
The U.S. residential real estate market is worth a staggering $47.5 trillion. Here are the most valuable housing markets in the country.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees