Technology
Ranked: The Most Popular Websites Since 1993
The Most Popular Websites Since 1993
The internet has become an increasingly important part of our everyday lives.
While it’s hard to imagine modern life without Google or YouTube, it’s interesting to reflect on how much the web has changed over the last few decades.
This animation by Captain Gizmo provides a historical rundown of the most popular websites since 1993, showing how much the internet has evolved since the early ’90s.
The Top Websites
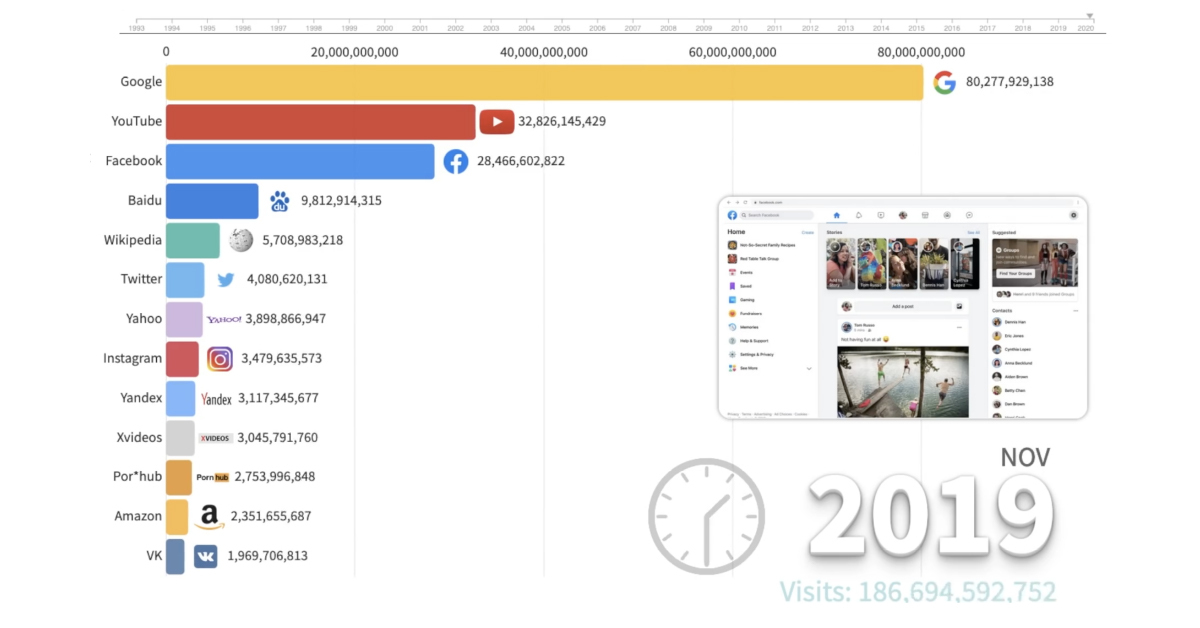
While the web has changed drastically over the years, the top-ranking websites have remained relatively consistent. Here’s a look at the websites with the most traffic since 1993, and when each site held the number one spot:
| Date Range | Top Ranking Website | Highest Number of Monthly Visits |
|---|---|---|
| Jan 1993 - Jun 2000 | AOL | 405,000,000 |
| Jul 2000 - May 2006 | Yahoo | 5,500,000,000 |
| Jun 2006 - Jul 2008 | 8,300,000,000 |
|
| Aug 2008 - Jun 2010 | Yahoo | 11,600,000,000 |
| Jul 2010 - current | 81,000,000,000 |
*Note: Numbers rounded for clarity.
AOL
AOL was one of the first major web portals, back in the era of CD-ROMs and dial-up modems. In its heyday, the company dominated the market, largely due to an aggressive free trial campaign that cost millions (possibly even billions) of dollars to execute.
Despite the large investment, the campaign worked—at its peak, AOL had over 30 million users, and a market cap of over $200 billion. It was the most popular website online until the early 2000s, when broadband started to replace dial-up. As the sands shifted, AOL struggled to stay relevant and was eventually sold to Verizon for just $4.4 billion.
Yahoo
Following AOL’s downfall, Yahoo became the next internet giant.
Starting off as a web directory, Yahoo was the first website to offer localized indexes for major cities. At Yahoo’s zenith, it was worth $125 billion, but a series of missed opportunities and failed acquisitions meant that it could not keep up. Like AOL, Yahoo is now also owned by Verizon, but remains a top 10 website globally.
It’s no surprise that Google currently comes in at number one. It started out in the early ’90s as a university research project. Today, it’s become virtually synonymous with the internet, which makes sense, considering 90% of all internet searches are made on Google-owned properties.
Old School Search Engines
Prior to Google’s success, there were several other go-to search engines that paved the way for Google in many ways:
- WebCrawler: One of the earlier search engines, WebCrawler was the first search engine to enable full-text search. At one point, the website was so popular, it’s server would constantly crash, making it virtually unusable during peak hours.
- Lycos: This was another pivotal search engine, created in 1994 (a year before Yahoo). Lycos was the first of its kind to incorporate relevance retrieval, prefix matching, and word proximity.
- Infoseek: As Netscape’s default search engine, Infoseek was popular during the web browser’s heyday. Eventually, Infoseek was purchased by Disney and rebranded to go.com.
Unlike Infoseek, Lycos and WebCrawler have somehow managed to stick around—both companies still exist today. Of course, they’re nowhere near comparable to Google in terms of revenue or daily search volume.
The Evolution of Social Media
Unless you are a Gen Zer, you probably remember MySpace. Like Lycos and WebCrawler, MySpace technically still exists, although it’s certainly not the high traffic site it used to be.
Created in 2004, MySpace became a hub for musicians and music fans on the web. In just a year, the website saw massive growth, and by 2005, it was acquired by News Corp. MySpace continued to dominate the social media landscape until 2008, when Facebook took over as the internet’s most popular social media platform.
Facebook’s story is well-known at this point. The Zuckerberg-led creation was a social networking site that was exclusive to Harvard students, but it soon opened up to dozens of other universities and then finally the general public in 2006. Just two years later, and the site had 100 million active users, rising to the top of the social media spectrum.
Although Facebook often finds itself mired in controversy today, the site remains the world’s most popular social media platform on the internet with close to 3 billion users.
What’s Next?
It’s hard to predict what the future holds for Facebook, or for any of the other websites currently dominating the web.
If anything is clear from the above animation, it’s that the list of the world’s most popular websites is constantly shifting—and only time will tell what the next few decades will bring.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001