Technology
This Chart Reveals Google’s True Dominance Over the Web
This Chart Reveals Google’s True Dominance Over the Web
The Chart of the Week is a weekly Visual Capitalist feature on Fridays.
Yes, we all know that Google is dominant in the realm of search.
But at the same time, the internet is also a huge place – and building a decent searching algorithm can’t be that hard, right?
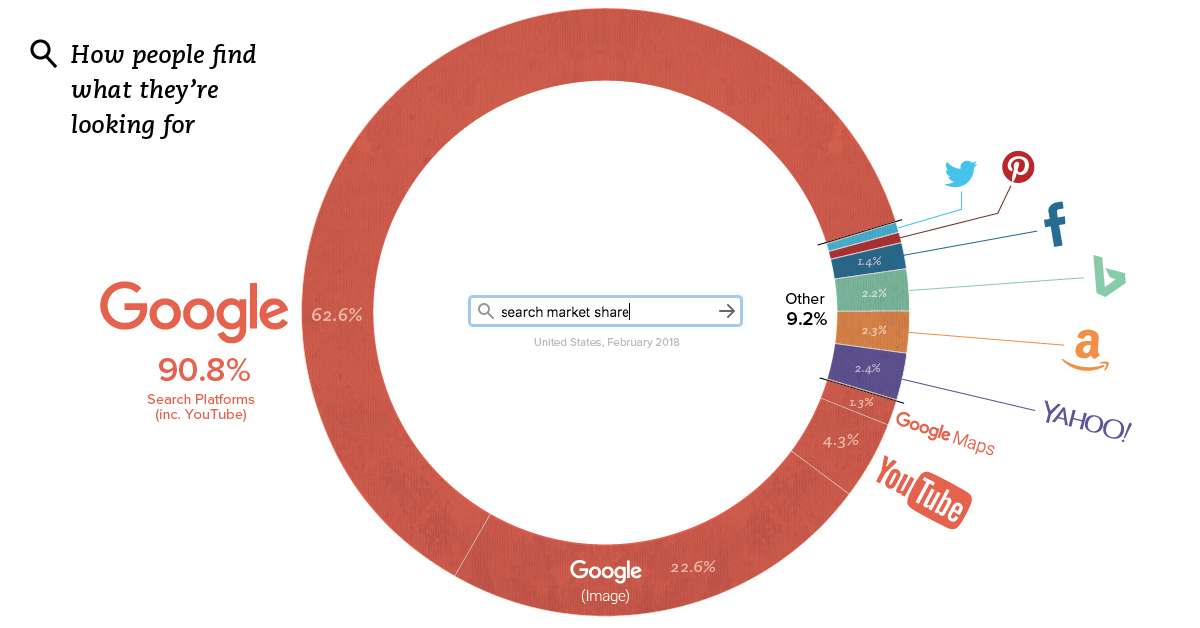
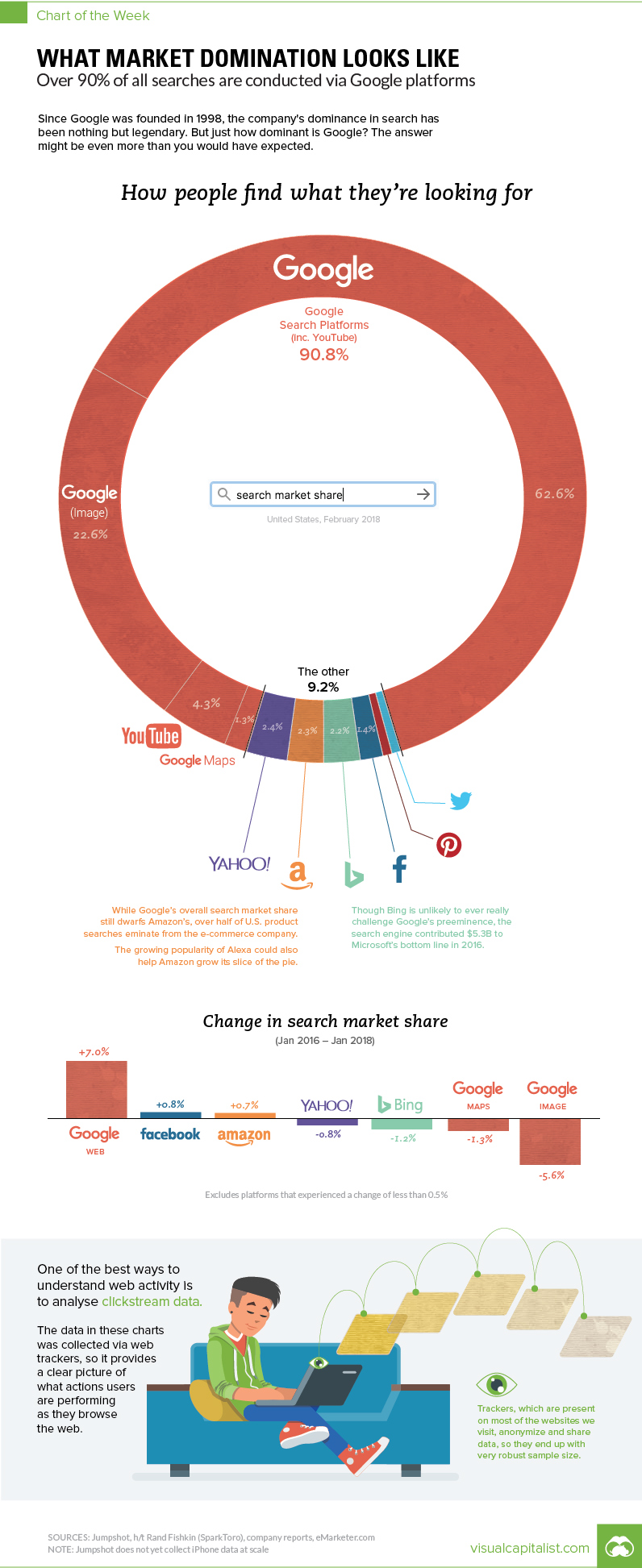
This week’s chart is a bit mind-boggling, because it makes the case that Google is even more dominant than you may have guessed. Between all Google features and the search giant’s YouTube subsidiary, more than 90% of all internet searches are taking place through the company.
The Hard Data
According to Jumpshot (via SparkToro), a marketing analytics firm that licenses anonymous ClickStream data from hundreds of millions of users, about 62.6% of all searches online are through Google’s core function.
But that’s just the beginning, as that number doesn’t include other Google functions like image search or Google Maps, or properties such as YouTube:
| Search Platform | % of Searches |
|---|---|
| 62.6% | |
| Google (image) | 22.6% |
| YouTube | 4.3% |
| Google Maps | 1.3% |
| Google Total | 90.8% |
Together, Google holds onto an impressive 90.8% market share of web, mobile, and in-app searches – though it should be noted that the above source does not include iPhone data at scale yet.
The Google-opoly
How does Google keep up such a massive market share, and why can’t a real competitor in search emerge?
The answer has to do with platforms and apps. Google’s strategy is to go where the users are, and to ensure that wherever they go, a Google search is not hard to do.
Over a decade ago, this meant being the home page on every internet browser – but more recently, it’s taken the form of internet browser market share (Chrome), mobile OS market share (Android), owning the dominant video platform (YouTube), and even venturing into your dwelling with Google Home.
As a result of these efforts, whenever users are searching, Google has never been far away.
Low Bids from Competition
There are competitors that dare to pluck away at Google’s market share in search and ad revenue.
Microsoft’s Bing is the most known one, and it has the advantage of being integrated into Microsoft products all over the globe. Meanwhile, DuckDuckGo is another name worth mentioning – the privacy-focused search engine doesn’t have anywhere near the same kind of financial backing as Microsoft, but it does differentiate its product considerably.
Yet, here’s a picture of U.S. search ad revenues. Bing is small, but others are smaller. DuckDuckGo doesn’t even register.

Why can no one match Google?
Part of the reason lies in the math. Google operates at an insane level, processing 3.5 billion searches per day. To get millions of people to try a different search algorithm is expensive – and to get them to keep that behavior permanently is even more expensive.
The only way such change becomes feasible is if a product comes out that is 10x better than Google, and at this point, such an event seems unlikely – at least in the current ecosystem.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees