Technology
How Self-Driving Cars “See” the World
How Self-Driving Cars “See” the World
Modern cars bear little resemblance to their early ancestors, but the basic action of steering a vehicle has always remained the same. Whether you’re behind the wheel of a Tesla or a vintage Model T, turning the wheel dictates the direction of movement. This simple premise, which places humans at the center of control, may be ripe for disruption as tech giants and car companies race toward a future that would render human-controlled vehicles obsolete.
How does this next generation of self-driving cars “see” the road? Today’s video from TED-Ed explains one of the mind-bending innovations making autonomous vehicles a reality.
Eye of the Laser
Safely getting a vehicle and its passengers from point A to B is no simple matter.
First, weather and time of day can create a wide variety of challenging situations, affecting things like visibility, braking distances, or speed. Next, other vehicles, bikes, and pedestrians are constantly moving through the transportation network, sometimes in unpredictable ways. To further complicate matters, the road network is rarely in optimum form. Road lines fade and construction can throw ambiguous detours into the mix.
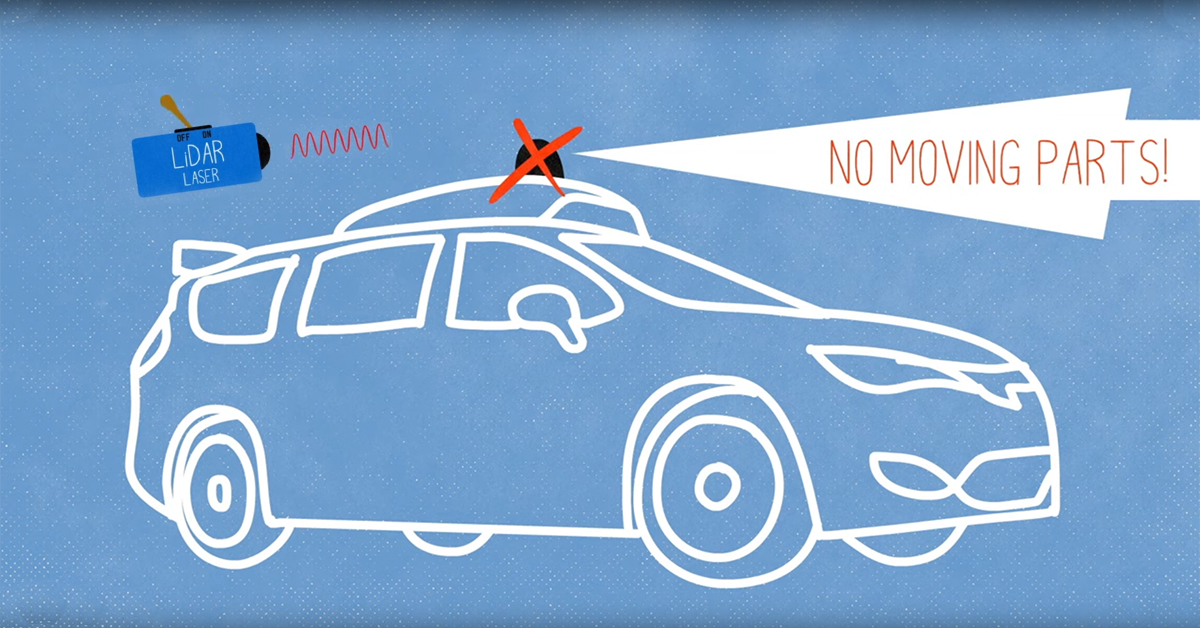
Sensing and analyzing the world at a granular level is crucial in making self-driving cars a viable transportation option. To solve this problem, new generations of autonomous vehicles are using photonic integrated circuits, as well as light detection and ranging (LiDAR) to generate an extremely nuanced picture of the road ahead.
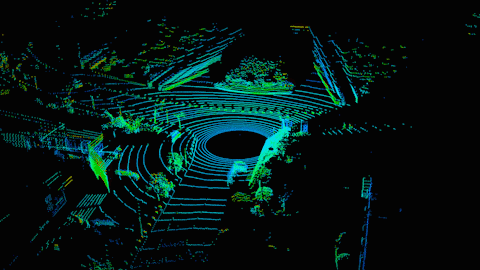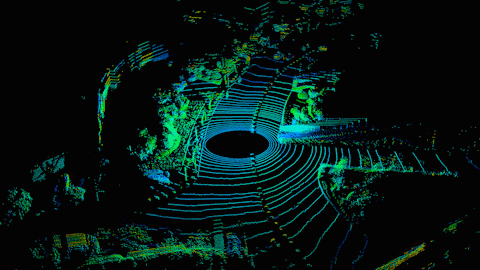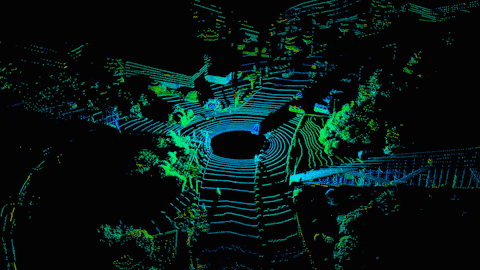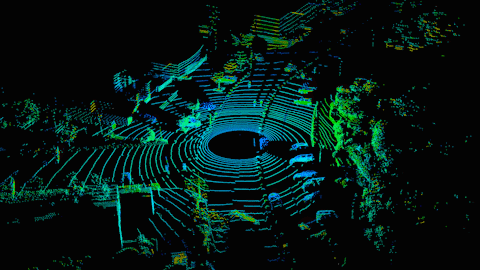
How self-driving cars see the world. (Source: Hesai)
LiDAR – which is related to RADAR – uses short laser pulses to sense the depth and shape of objects. Essentially, scattered bursts reflect off objects around the vehicle, painting a detailed 3D picture of its surroundings. LiDAR’s depth resolution is so accurate that it could eventually see details at the millimeter scale.
A Dissenting Opinion
While most companies in the autonomous vehicle space have fully embraced LiDAR, Tesla has a divergent point of view. The company employs a combination of GPS, cameras, and other sensors to help its cars visualize the world.
LiDAR is a fool’s errand. Anyone relying on LiDAR is doomed.
– Elon Musk
Society and Self-Driving Cars
While companies like Uber and Waymo determine the functional mechanics of self-driving cars, the rest of society is left to ponder how this new technology will affect employment, privacy, and personal autonomy.
In the U.S., more than 70% of goods are moved by truck, and over 80% of commuters take a private vehicle to work on any given day. Even partial automation of the nation’s transportation network will have wide-sweeping impacts on the economy.
As AI-powered cars and trucks hit the streets at scale, how cars see the road will be a detail most of us will overlook. The bigger question will be whether we are ready for a society where we’re no longer in the driver’s seat.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees