Sponsored
The Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
The Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Presented by: Red Cloud Klondike Strike (Equity crowdfunding in mining)
Apple launched the first iPhone in 2007, and since then the iconic smartphone has sold over 700 million units around the world.
This best-selling handset sets the standard for smartphone performance and features. However, the iPhone would not be possible without the extraordinary raw materials that line the insides of the case.
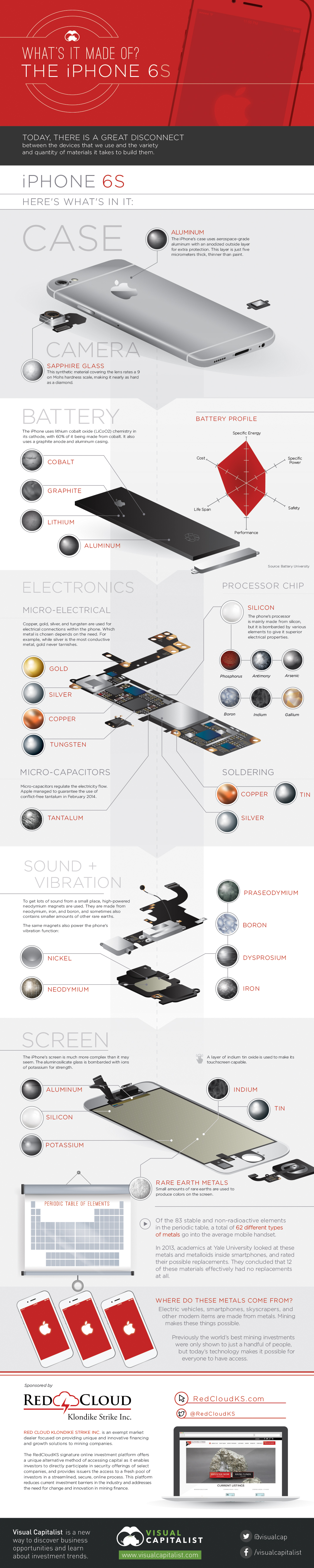
Here’s what’s in an Apple iPhone 6s:
Screen
The iPhone’s screen is much more complex than it may seem. The aluminosilicate glass is bombarded with ions of potassium for strength. Meanwhile, a layer of indium tin oxide makes it touchscreen capable, and small amounts of rare earths enables certain colors on the display.
Battery:
The iPhone uses lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) chemistry in its cathode, with 60% of it being made from cobalt. It also uses a graphite anode and aluminum casing.
Electronics:
Processor Chip: The phone’s processor is mainly made from silicon, but it is bombarded by various elements such as phosphorus, antimony, arsenic, boron, indium, and gallium to give it superior electrical properties.
Micro-Electrical: Copper, gold, silver, and tungsten are used for electrical connections within the phone. Which metal is chosen depends on the need. For example, while silver is the most conductive metal, gold never tarnishes.
Micro-capacitors: regulate electricity flow Apple managed to guarantee it only used conflict-free tantalum in February 2014.
Soldering: Tin, copper, and silver.
Sound and Vibration
Speakers and Headphones: To get lots of sound from a small place, high-powered neodymium magnets are used. They are made from neodymium, iron, and boron, and sometimes also containing smaller amounts of other rare earths.
The same magnets also power the phone’s vibration function.
Case:
Aluminum: The iPhone’s case uses aerospace-grade aluminum with an anodized outside layer for extra protection. This layer is just five micrometers thick, thinner than paint.
Camera:
Sapphire glass: This synthetic material covering the lens rates a 9 on Moh’s hardness scale, making it nearly as hard as a diamond.
Material Substitution?
Of the 83 stable and non-radioactive elements in the periodic table, a total of 62 different types of metals go into the average mobile handset.
In 2013, academics at Yale University looked at these metals and metalloids inside smartphones, and rated their possible replacements. They concluded that 12 of these materials effectively had no replacements at all.
Sponsored
Accelerating a Net-Zero Future with Carbon Credits
To reach net-zero by 2050, trillions in annual investment will be required. Here’s how carbon credits help close this funding gap.
Accelerating a Net-Zero Future with Carbon Credits
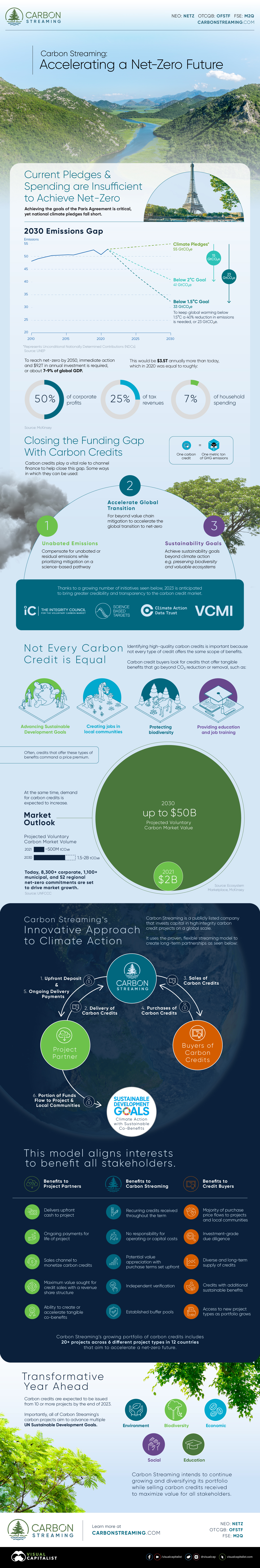
Achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement is critical, yet national climate pledges fall short.
To reach net-zero by 2050, immediate action and $9.2 trillion in annual investment is required, or about 7-9% of global GDP. This would be $3.5 trillion annually more than today, which in 2020 was equal to roughly:
- 50% of corporate profits
- 25% of tax revenues
- 7% of household spending
This infographic sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation shows how carbon credits can help accelerate a net-zero future by funding climate action.
Closing the Funding Gap With Carbon Credits
Carbon credits play a vital role in channelling finance to help close this funding gap. Here are some ways in which carbon credits can be used:
- Unabated Emissions: Compensate for unabated or residual emissions while prioritizing mitigation on a science-based pathway.
- Accelerate Global Transition: For beyond value chain mitigation to accelerate the global transition to net-zero.
- Sustainability Goals: Achieve sustainability goals beyond climate action e.g. preserving biodiversity and valuable ecosystems.
Thanks to a growing number of initiatives listed below, 2023 is anticipated to bring greater credibility and transparency to the carbon credit market.
- The Integrity Council for the Voluntary Carbon Market
- Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi)
- Climate Action Data Trust
- Voluntary Carbon Markets Integrity Initiative
Not Every Carbon Credit is Equal
Identifying high-quality carbon credits is important because not every type of credit offers the same scope of benefits. Carbon credit buyers look for credits that offer tangible benefits that go beyond CO₂ reduction or removal, such as:
- Advancing Sustainable Development Goals
- Creating jobs in local communities
- Protecting biodiversity
- Providing education and job training
Often, credits that offer these types of benefits command a price premium.
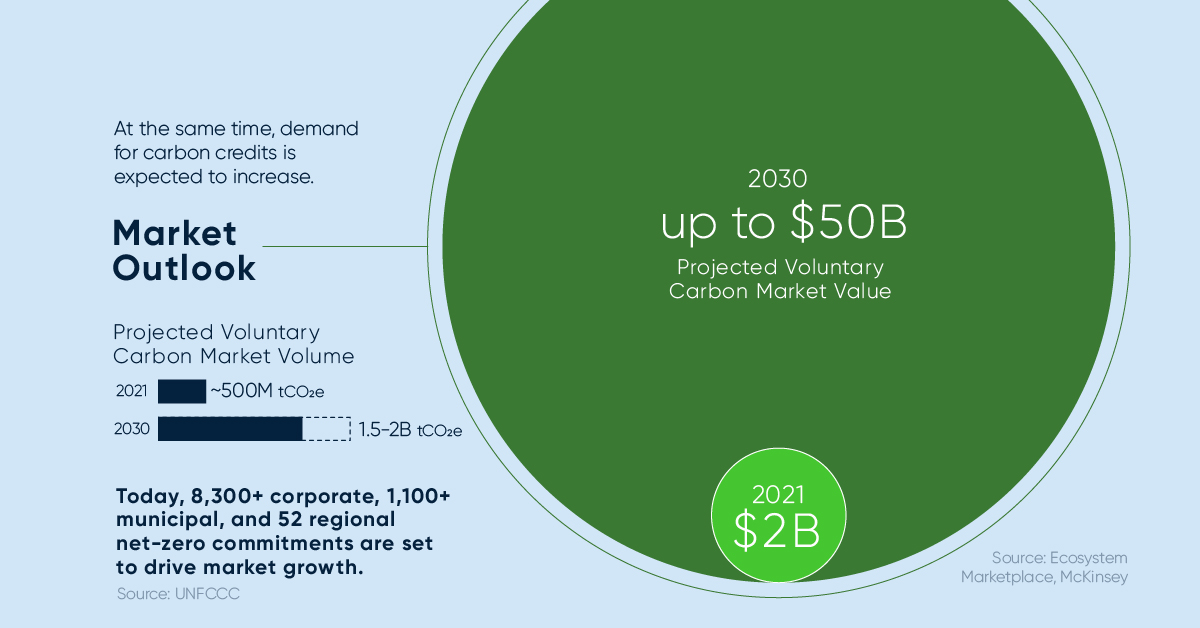
At the same time, demand for carbon credits is expected to increase. Within the decade, the value of the voluntary carbon market could grow from $2 billion up to $50 billion.
Voluntary carbon markets refer to the transactions in which carbon credits are purchased by corporate and other buyers that voluntarily (not required by a regulatory act) want to compensate for their emissions or advance sustainability goals.
| 2021 | 2030 (estimated) | |
|---|---|---|
| Voluntary Carbon Market Value | $2B | Up to $50B |
| Voluntary Carbon Market Volume | ~500M tCO₂e | 1.5-2B tCO₂e |
Source: Ecosystem Marketplace, McKinsey, UNFCCC
Today, over 8,300 corporate, 1,100 municipal, and 52 regional net-zero commitments are set to drive market growth.
Carbon Streaming’s Innovative Approach to Climate Action
Carbon Streaming is a publicly listed company that invests capital in high integrity carbon credit projects on a global scale. It uses the proven, flexible streaming model to create long-term partnerships.
This model aligns interests to benefit all stakeholders.
| Project Partners | Carbon Streaming | Credit Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| Delivers upfront cash to project Ongoing payments for life of project Sales channel to monetize carbon credits Maximum value sought for credit sales with a revenue share structure Ability to create or accelerate tangible co-benefits | Recurring credits received throughout the term No responsibility for operating or capital costs Potential value appreciation with purchase terms set upfront Independent verification Established buffer pools | Majority of purchase price flows to projects and local communities Investment-grade due diligence Diverse and long-term supply of credits Credits with additional sustainable benefits Access to new project types as portfolio grows |
Carbon Streaming’s growing portfolio of carbon credits includes over 20 projects across six different project types in 12 countries that aim to accelerate a net-zero future.
Transformative Year Ahead
By the end of 2023, carbon credits are expected to be issued from 10 or more projects.
Importantly, all of Carbon Streaming’s carbon projects aim to advance multiple UN Sustainable Development Goals. Carbon Streaming intends to continue growing and diversifying its portfolio while selling carbon credits received to maximize value for all stakeholders.
>>>Interested in learning more about Carbon Streaming? Click here to learn more.

-

 Mining3 years ago
Mining3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology…
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.
-

 Debt1 week ago
Debt1 week agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees












